Crushed Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (CAAC), a Potential Reactive Filter Medium for Enhancing Phosphorus Removal in Nature-Based Solutions—Preliminary Batch Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Adsorbent Preparation
2.2. Chemical and Physical Characterization of the Adsorbent
2.3. Kinetic Bath Studies
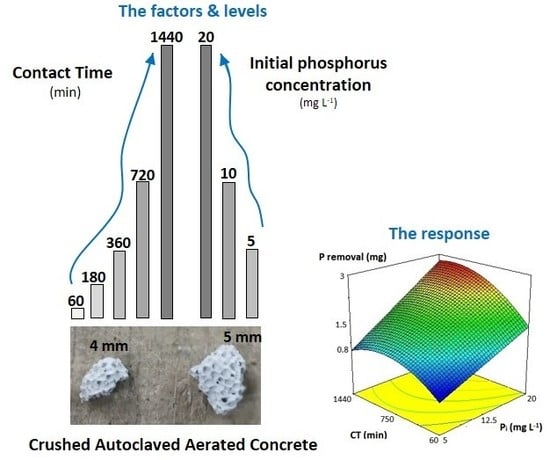
2.3.1. General Information
2.3.2. Phosphorus Removal Indicators
2.3.3. Statistics
2.3.4. Kinetic Models
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical and Chemical Properties of the Adsorbent (CAAC)
3.2. Kinetics Batch Experiments
3.2.1. Interactions and Main Effects of Pi, PS and CT
3.2.2. Potential Removal Process
3.2.3. Removal Rates
3.2.4. Kinetic Models
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rockström, J.; Steffen, W.; Noone, K.; Lambin, E.; Lenton, T.M.; Scheffer, M.; Folke, C.; Schellnhuber, H.J.; Wit, C.D.; Hughes, T.; et al. Planetary Boundaries: Exploring the Safe Operating Space for Humanity. Ecol. Soc. 2009, 14, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-G.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Kim, H.-G.; Jeong, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.B.; Lee, S.-H.; Choi, J.-W. Phosphorous recovery from sewage sludge using calcium silicate hydrates. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melia, P.M.; Cundy, A.B.; Sohi, S.P.; Hooda, P.S.; Busquets, R. Trends in the recovery of phosphorus in bioavailable forms from wastewater. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berg, U.; Donnert, D.; Ehbrecht, A.; Bumiller, W.; Kusche, I.; Weidler, P.G.; Nüesch, R. “Active filtration” for the elimination and recovery of phosphorus from waste water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 265, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renman, G.; Renman, A. Sustainable use of crushed autoclaved aerated concrete (CAAC) as a filter medium in wastewater purification. In Proceedings of the WASCON 8th International Conference on Sustainable Management of Waste and Recycled Materials in Construction: Towards Effective, Durable and Sustainable Production and Use of Alternative Materials in Construction, Gothenburg, Sweden, 30 May–1 June 2012; Arm, M., Vandecasteele, C., Heynen, J., Suer, P., Lind, B., Eds.; ISCOWA and SGI: Gothenburg, Sweden, 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Karczmarczyk, A.; Baryła, A.; Agnieszka, B. Effect of P-Reactive Drainage Aggregates on Green Roof Runoff Quality. Water 2014, 6, 2575–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Commission. Towards an EU Research and Innovation Policy Agenda for Nature-Based Solutions & Re-Naturing Cities; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2015; ISBN 978-92-79-46051-7. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Holguera, M.; Clark, O.G.; Sprecher, A.; Gaskin, S.J. Ecosystem biomimetics for resource use optimization in buildings. Build. Res. Inf. 2015, 44, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blok, V.; Gremmen, B. Ecological Innovation: Biomimicry as a New Way of Thinking and Acting Ecologically. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2016, 29, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, T.; Chen, T.; Wille, M.L.; Chen, D.; Bian, J.; Qing, C.; Wu, W.; Frost, R.L. Advanced wastewater treatment with autoclaved aerated concrete particles in biological aerated filters. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 9, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Ferro, N.; Ibrahim, H.M.S.; Borin, M. Newly-established free water-surface constructed wetland to treat agricultural waters in the low-lying Venetian plain: Performance on nitrogen and phosphorus removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, L.R.D.; Tonderski, K.; Iversen, B.V.; Kjaergaard, C. Phosphorus retention in surface-flow constructed wetlands targeting agricultural drainage water. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 380, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, C.; Lakshmanan, R.; Renman, G.; Rajarao, G.K. Efficacy of reactive mineral-based sorbents forphosphate, bacteria, nitrogen and TOC removal-Column experiment in recirculation batch mode. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5165–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Wheatley, A. Mechanisms of phosphorus removal by recycled crushed concrete. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okano, K.; Miyamaru, S.; Kitao, A.; Takano, H.; Aketo, T.; Toda, M.; Honda, K.; Ohtake, H. Amorphous calcium silicate hydrates and their possible mechanism for recovering phosphate from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 144, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakkas, P. Domestic Greywater Treatment through the Integration of Constucted Wetlands in Living Wall Systems (LWS). Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Architecture & Building Sciences, Technical University of Delft, Delft, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Damrongsiri, S. Feasibility of using demolition waste as an alternative heavy metal immobilising agent. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, U.; Donnert, D.; Weidler, P.G.; Kaschka, E.; Knoll, G.; Nuesch, R. Phosphorus removal and recovery from wastewater by tobermorite-seeded crystallisation of calcium phosphate. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucarella, V.; Renman, G. Phosphorus Sorption Capacity of Filter Materials Used for On-site Wastewater Treatment Determined in Batch Experiments—A Comparative Study. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association. APHA Method 4500-P: Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. In Ascorbic Acid Method; American Public Health Association: Washignton, DC, USA, 1998; pp. 115–116. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Yang, L.; Zhong, W.; Cui, J.; Wei, Z. Poorly crystalline hydroxyapatite: A novel adsorbent for enhanced fulvic acid removal from aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 332, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 8th ed.; Montgomery, D.C., Peck, E.A., Vining, G.G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 9781118146927. [Google Scholar]
- Formosa, J.; Chimenos, J.M.; Lacasta, A.M.; Niubo, M. Interaction between low-grade magnesium oxide and boric acid in chemically bonded phosphate ceramics formulation. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 2483–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Mckay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, J. On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moussout, H.; Ahlafi, H.; Aazza, M.; Maghat, H. Critical of linear and nonlinear equations of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order kinetic models. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Sci. 2018, 4, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, J.P.; Srivastava, V.C.; Mall, I.D. Bioresource Technology Treatment of dairy wastewater by commercial activated carbon and bagasse fly ash: Parametric, kinetic and equilibrium modelling, disposal studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3474–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, D.W. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 1963, 11, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Huang, L.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Ji, F. Evaluation of porous calcium silicate hydrate derived from carbide slag for removing phosphate from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Buhl, J.; Lutz, W. Synthesis and Properties of Zeolites from Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (AAC) Waste. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2012, 638, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, J.; Stark, A.; Kiefer, A.L.; Glade, H. Infrared Spectroscopic Analysis of the Inorganic Deposits from Water in Domestic and Technical Heat Exchangers. Energies 2018, 11, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, D.; Yu, C.; Bao, T.; Zhu, C.; Qing, C. Simultaneous removal of nitrogen and phosphorus using autoclaved aerated concrete particles in biological aerated filters. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 19402–19410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, H.; Arias, C.A.; Del Bubba, M. Media selection for sustainable phosphorus removal in subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadhraoui, M.; Watanabe, T.; Kuroda, M. The effect of the physical structure of a porous Ca-based sorbent on its phosphorus removal capacity. Water Res. 2002, 36, 3711–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, C.A.; Brix, H.; Johansen, N.H. Phosphorus removal from municipal wastewater in an experimental two-stage vertical flow constructed wetland system equipped with a calcite filter. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, C.A.; Brix, H. Phosphorus removal in constructed wetlands: Can suitable alternative media be identified? Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Kong, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Lin, Y. Phosphate removal and recovery through crystallization of hydroxyapatite using xonotlite as seed crystal. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, K.; Uemoto, M.; Kagami, J.; Miura, K.; Aketo, T.; Toda, M.; Honda, K.; Ohtake, H. Novel technique for phosphorus recovery from aqueous solutions using amorphous calcium silicate hydrates (A-CSHs). Water Res. 2013, 47, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, S.; Chhoden, K.; Khaiwal, R. Application of Agro-waste Rice Husk Ash for the Removal of Phosphate from the Wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 129, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molle, P.; Liénard, A.; Grasmick, A.; Iwena, A. Phosphorus sorption in subsurface constructed wetlands: Investigations focused on calcareous materials and their chemical reactions. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Kong, Y.; Shi, X. Sequestration of phosphorus from wastewater by cement-based or alternative cementitious materials. Water Res. 2014, 62, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, J.P.; Renman, A.; Renman, G.; Poll, K. Phosphate removal by mineral-based sorbents used in filters for small-scale wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2008, 42, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cucarella, V.; Zaleski, T.; Mazurek, R.; Renman, G. Effect of reactive substrates used for the removal of phosphorus from wastewater on the fertility of acid soils. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4308–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westholm, L.J. Substrates for phosphorus removal—Potential benefits for on-site wastewater treatment? Water Res. 2006, 40, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, I.; Jourak, A.; Gustafsson, J.P.; Hedström, A.; Lundström, T.S.; Viklander, M. Modeling phosphate transport and removal in a compact bed filled with a mineral-based sorbent for domestic wastewater treatment. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2013, 154, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, A.S.; Rozenwald, M.N.; Geohring, L.D.; Lion, L.W.; Steenhuis, T.S. Phosphorus removal by wollastonite: A constructed wetland substrate. Ecol. Eng. 2000, 15, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Yang, K. Synthesis and characterization of different crystalline calcium silicate hydrate: Application for the removal of aflatoxin b1 from aqueous solution. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 431925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Chemical | Current Study | Literature | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | PS 4 mm | PS 5 mm | |
| SiO2 (%) | 47.46 | 46.88 | 1,2,3,4 44.8–57.0 |
| CaO (%) | 26.53 | 26.95 | 1,2,3,4 24.9–27.6 |
| Al2O3 (%) | 3.28 | 3.28 | 1,2,3,4 1.95–16.06 |
| Fe2O3 (%) | 1.18 | 1.18 | 1,2,3 1.0–4.2 |
| K2O (%) | 0.74 | 0.74 | 4 0.7 |
| MgO (%) | 0.65 | 0.64 | 2,4 0.5–0.6 |
| Pi (mg L−1) | Factors | df | F | α | ηp2 | PS (mm) | Factors | df | F | α | ηp2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | CT | 4 | 263.855 | <0.01 | 0.981 | 4 | CT | 4 | 395.825 | <0.01 | 0.981 |
| PS | 1 | 25.903 | <0.01 | 0.564 | Pi | 2 | 2332.852 | <0.01 | 0.994 | ||
| CT × PS | 4 | 4.895 | <0.01 | 0.495 | CT × Pi | 8 | 56.205 | <0.01 | 0.937 | ||
| 10 | CT | 4 | 442.058 | <0.01 | 0.989 | 5 | CT | 4 | 1192.745 | <0.01 | 0.994 |
| PS | 1 | 124.721 | <0.01 | 0.862 | Pi | 2 | 7985.244 | <0.01 | 0.998 | ||
| CT × PS | 4 | 1.071 | 0.40 | 0.176 | CT × Pi | 8 | 143.770 | <0.01 | 0.975 | ||
| 20 | CT | 4 | 595.938 | <0.01 | 0.992 | ||||||
| PS | 1 | 149.948 | <0.01 | 0.882 | |||||||
| CT × PS | 4 | 0.978 | 0.44 | 0.164 |
| Factors | Experimental | PFO | PSO | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS | Pi | q(e)exp | 1CTANOVA | q(e)calc | 2q(CTANOVA)calc | K1 | R2 | MPSD | q(e)calc | q(CTANOVA)calc | K2 | R2 | MPSD |
| 4 | 5 | 0.056 | 1440 | 0.053 | 0.053 | 0.954 | 0.173 | 0.063 | 0.055 | 0.991 | 0.078 | ||
| 4 | 10 | 0.119 | 720 | 0.124 | 0.120 | 0.999 | 0.038 | 0.146 | 0.116 | 0.986 | 0.077 | ||
| 4 | 20 | 0.246 | 720 | 0.246 | 0.242 | 0.969 | 0.137 | 0.280 | 0.236 | 0.976 | 0.074 | ||
| 5 | 5 | 0.067 | 1440 | 0.065 | 0.064 | 0.970 | 0.175 | 0.079 | 0.066 | 0.988 | 0.107 | ||
| 5 | 10 | 0.143 | 720 | 0.145 | 0.142 | 0.980 | 0.126 | 0.167 | 0.137 | 0.984 | 0.061 | ||
| 5 | 20 | 0.281 | 720 | 0.278 | 0.275 | 0.965 | 0.123 | 0.313 | 0.270 | 0.982 | 0.053 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castellar, J.A.d.C.; Formosa, J.; Chimenos, J.M.; Canals, J.; Bosch, M.; Rosell, J.R.; Silva, H.P.d.; Morató, J.; Brix, H.; Arias, C.A. Crushed Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (CAAC), a Potential Reactive Filter Medium for Enhancing Phosphorus Removal in Nature-Based Solutions—Preliminary Batch Studies. Water 2019, 11, 1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071442
Castellar JAdC, Formosa J, Chimenos JM, Canals J, Bosch M, Rosell JR, Silva HPd, Morató J, Brix H, Arias CA. Crushed Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (CAAC), a Potential Reactive Filter Medium for Enhancing Phosphorus Removal in Nature-Based Solutions—Preliminary Batch Studies. Water. 2019; 11(7):1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071442
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastellar, Joana América da Cunha, Joan Formosa, Josep Maria Chimenos, Joan Canals, Montserrat Bosch, Joan Ramon Rosell, Heraldo Peixoto da Silva, Jordi Morató, Hans Brix, and Carlos Alberto Arias. 2019. "Crushed Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (CAAC), a Potential Reactive Filter Medium for Enhancing Phosphorus Removal in Nature-Based Solutions—Preliminary Batch Studies" Water 11, no. 7: 1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071442
APA StyleCastellar, J. A. d. C., Formosa, J., Chimenos, J. M., Canals, J., Bosch, M., Rosell, J. R., Silva, H. P. d., Morató, J., Brix, H., & Arias, C. A. (2019). Crushed Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (CAAC), a Potential Reactive Filter Medium for Enhancing Phosphorus Removal in Nature-Based Solutions—Preliminary Batch Studies. Water, 11(7), 1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071442