Ammonium-Nitrogen (NH4+-N) Removal from Groundwater by a Dropping Nitrification Reactor: Characterization of NH4+-N Transformation and Bacterial Community in the Reactor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthetic NH4+-N-Contaminated Groundwater
2.2. Setup of the Laboratory-Scale Dropping Nitrification Reactor
2.3. Operating Conditions of the Laboratory-Scale Dropping Nitrification Reactor
2.4. Physicochemical Parameters and Nitrogen Concentration in Water Samples
2.5. Kinetics of NH4+-N Removal Along the Single Axis of the Dropping Nitrification Reactor
2.6. DNA Extraction from Sponge Samples and Quantification of Functional Microbial Genes
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Bacterial Community
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Physicochemical Parameters
3.2. Removal Efficiency of NH4+-N and Nitrogen Transformations in the Dropping Nitrification Reactor
3.3. Variations in the Abundances of the Functional Microbial Genes Involved in the Nitrogen Transformations
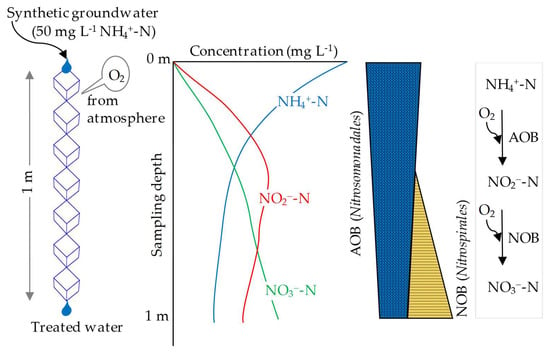
3.4. NH4+-N, NO2−-N, and NO3−-N Concentration and Functional N-Transformation Gene Profiles along the Single Axis of the Dropping Nitrification Reactor
3.5. Bacterial Community Structure Profiles along the Single Axis of the Dropping Nitrification Reactor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, S.; Ma, T.; Du, Y.; Luo, K.; Deng, Y.; Lu, Z. Temporal variations in groundwater nitrogen under intensive groundwater/surface-water interaction. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 1753–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieczka, A.; Koda, E. Kinetic and equilibrium studies of sorption of ammonium in the soil-water environment in agricultural areas of Central Poland. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vocciante, M.; De Folly D’Auris, A.; Finocchi, A.; Tagliabue, M.; Bellettato, M.; Ferrucci, A.; Reverberi, A.P.; Ferro, S. Adsorption of ammonium on clinoptilolite in presence of competing cations: Investigation on groundwater remediation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieczka, A.; Bujakowski, F.; Falkowski, T.; Koda, E. Morphogenesis of a floodplain as a criterion for assessing the susceptibility to water pollution in an agriculturally rich valley of a lowland river. Water 2018, 10, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malla, R.; Shrestha, S.; Chapagain, S.K.; Shakya, M.; Nakamura, T. Physico-chemical and oxygen-hydrogen isotopic assessment of Bagmati and Bishnumati rivers and the shallow groundwater along the river corridors in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2015, 7, 1435–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patterson, B.M.; Grassi, M.E.; Davis, G.B.; Robertson, B.S.; McKinley, A.J. Use of polymer mats in series for sequential reactive barrier remediation of ammonium-contaminated groundwater: Laboratory column evaluation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3439–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenbaum, J. Identification of Sources of Ammonium in Groundwater Using Stable Nitrogen and Boron Isotopes in Nam Du, Hanoi. Master’s Thesis, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, F.; Yang, Y.; Kong, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, D. Ammonium-nitrogen-contaminated groundwater remediation by a sequential three-zone permeable reactive barrier (multibarrier) with oxygen-releasing compound (ORC)/clinoptilolite/spongy iron: Column studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3705–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapagain, S.K.; Kazama, F. Overview of chemical quality of groundwater in the Kathmandu Valley. In Kathmandu Valley Groundwater Outlook; Shrestha, S., Pradhananga, D., Pandey, V.P., Eds.; Asian Institute of Technology (AIT), The Small Earth Nepal (SEN), Center of Research for Environment Energy and Water (CREEW), International Research Center for River Basin Environment-University of Yamanashi (ICRE-UY): Kathmandu, Nepal, 2012; pp. 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, F.; Yang, Y.; Deng, W.; Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Kong, X. Removal of ammonium-nitrogen from groundwater using a fully passive permeable reactive barrier with oxygen-releasing compound and clinoptilolite. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 154, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, G.; Kong, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, F.; Hou, G.; Chen, H. Ammonium removal from groundwater using a zeolite permeable reactive barrier: A pilot-scale demonstration. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 1540–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, B.M.; Grassi, M.E.; Robertson, B.S.; Davis, G.B.; Smith, A.J.; Mckinley, A.J. Use of polymer mats in series for sequential reactive barrier remediation of ammonium-contaminated groundwater: Field evaluation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6846–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiri-Nyarko, F.; Grajales-Mesa, S.J.; Malina, G. An overview of permeable reactive barriers for in situ sustainable groundwater remediation. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, S.; Harada, H. Application of UASB technology for sewage treatment with a novel post-treatment process. In Environmental Anaerobic Technology, Applications and New Developments; Fang, H.H.P., Ed.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2010; pp. 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machdar, I.; Harada, H.; Ohashi, A.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Okui, H.; Ueki, K. A novel and cost-effective sewage treatment system consisting of UASB pre-treatment and aerobic post-treatment units for developing countries. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, A.; Ohashi, A.; Harada, H. Sewage treatment in a combined up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB)-down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) system. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 29, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, T.; Onodera, T.; Uemura, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ohashi, A.; Harada, H. On-site evaluation of the performance of a full-scale down-flow hanging sponge reactor as a post-treatment process of an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor for treating sewage in India. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 194, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onodera, T.; Okubo, T.; Uemura, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ohashi, A.; Harada, H. Long-term performance evaluation of down-flow hanging sponge reactor regarding nitrification in a full-scale experiment in India. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 204, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onodera, T.; Tandukar, M.; Sugiyana, D.; Uemura, S.; Ohashi, A.; Harada, H. Development of a sixth-generation down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) reactor using rigid sponge media for post-treatment of UASB treating municipal sewage. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamoto, M.; Okubo, T.; Kubota, K.; Yamaguchi, T. Characterization of downflow hanging sponge reactors with regard to structure, process function, and microbial community compositions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 10345–10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, N.; Ohashi, A.; Machdar, I.; Harada, H. Behaviors of nitrifiers in a novel biofilm reactor employing hanging sponge-cubes as attachment site. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandukar, M.; Machdar, I.; Uemura, S.; Ohashi, A.; Harada, H. Potential of a combination of UASB and DHS reactor as a novel sewage treatment system for developing countries: Long-term evaluation. J. Environ. Eng. 2006, 132, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanitchaidecha, W.; Shakya, M.; Nakano, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Kazama, F. Development of an attached growth reactor for NH4-N removal at a drinking water supply system in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. J. Environ. Sci. Heal.-Part A Toxic/Hazardous Subst. Environ. Eng. 2012, 47, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; Clesceri, L.S., Greenberg, A.E., Eaton, A.D., Eds.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, D.J.; Watmough, N.J. Inorganic nitrogen metabolism in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1999, 3, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, I.; Sliekers, O.; Schmid, M.; Bock, E.; Fuerst, J.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Strous, M. New concepts of microbial treatment processes for the nitrogen removal in wastewater. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machdar, I.; Muhammad, S.; Onodera, T.; Syutsubo, K. A pilot-scale study on a down-flow hanging sponge reactor for septic tank sludge treatment. Environ. Eng. Res. 2018, 23, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, T.; Kubota, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Uemura, S.; Harada, H. Development of a new non-aeration-based sewage treatment technology: Performance evaluation of a full-scale down-flow hanging sponge reactor employing third-generation sponge carriers. Water Res. 2016, 102, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 380, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.B.; Vannelli, T.; Bergmann, D.J.; Arciero, D.M. Enzymology of the oxidation of ammonia to nitrite by bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1997, 71, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagopian, D.S.; Riley, J.G. A closer look at the bacteriology of nitrification. Aquac. Eng. 1998, 18, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Irvin, S.; Baker, K. The variation of nitrifying bacterial population sizes in a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) treating low, mid, high concentrated synthetic wastewater. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2007, 6, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.J.; Hsu, C.L.; Chuang, S.H.; Ouyang, C.F. Nitrification efficiency and nitrifying bacteria abundance in combined AS-RBC and A2O systems. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2281–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, B. Nitrification. Encycl. Ecol. 2013, 2, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Peng, D.C. Nitrite oxidizing bacteria (NOB) dominating in nitrifying community in full-scale biological nutrient removal wastewater treatment plants. AMB Express 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kubota, K.; Hayashi, M.; Matsunaga, K.; Iguchi, A.; Ohashi, A.; Li, Y.Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Harada, H. Microbial community composition of a down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) reactor combined with an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor for the treatment of municipal sewage. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 151, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cébron, A.; Garnier, J. Nitrobacter and Nitrospira genera as representatives of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria: Detection, quantification and growth along the lower Seine River (France). Water Res. 2005, 39, 4979–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okabe, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Satoh, H. Community structure and in situ activity of nitrifying bacteria in Phragmites root-associated biofilms. Microbes Environ. 2012, 27, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gieseke, A.; Nielsen, J.L.; Amann, R.; Nielsen, P.H.; De Beer, D. In situ substrate conversion and assimilation by nitrifying bacteria in a model biofilm. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, P.; Nielsen, J.L.; Svendsen, T.C.; Nielsen, P.H. Adhesion characteristics of nitrifying bacteria in activated sludge. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2814–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripong, S.; Rittmann, B.E. Diversity study of nitrifying bacteria in full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Nelson, W.C.; Shi, L.; Xu, F.; Liu, Y.; Yan, A.; Zhong, L.; Thompson, C.; Fredrickson, J.K.; et al. Effect of water chemistry and hydrodynamics on nitrogen transformation activity and microbial community functional potential in hyporheic zone sediment columns. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4877–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Ng, S.-K.; Lim, C.K.; Lu, H.; Jia, Y.; Lee, P.K.H. Physiological and metagenomic characterizations of the synergistic relationships between ammonia- and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in freshwater nitrification. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, S.; Satoh, H.; Watanabe, Y. In situ analysis of nitrifying biofilms as determined by in situ hybridization and the use of microelectrodes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 3182–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maharjan, A.K.; Kamei, T.; Amatya, I.M.; Mori, K.; Kazama, F.; Toyama, T. Ammonium-Nitrogen (NH4+-N) Removal from Groundwater by a Dropping Nitrification Reactor: Characterization of NH4+-N Transformation and Bacterial Community in the Reactor. Water 2020, 12, 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020599
Maharjan AK, Kamei T, Amatya IM, Mori K, Kazama F, Toyama T. Ammonium-Nitrogen (NH4+-N) Removal from Groundwater by a Dropping Nitrification Reactor: Characterization of NH4+-N Transformation and Bacterial Community in the Reactor. Water. 2020; 12(2):599. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020599
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaharjan, Amit Kumar, Tatsuru Kamei, Iswar Man Amatya, Kazuhiro Mori, Futaba Kazama, and Tadashi Toyama. 2020. "Ammonium-Nitrogen (NH4+-N) Removal from Groundwater by a Dropping Nitrification Reactor: Characterization of NH4+-N Transformation and Bacterial Community in the Reactor" Water 12, no. 2: 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020599
APA StyleMaharjan, A. K., Kamei, T., Amatya, I. M., Mori, K., Kazama, F., & Toyama, T. (2020). Ammonium-Nitrogen (NH4+-N) Removal from Groundwater by a Dropping Nitrification Reactor: Characterization of NH4+-N Transformation and Bacterial Community in the Reactor. Water, 12(2), 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020599