Detection and Attribution of Runoff Reduction of Weihe River over Different Periods during 1961–2016
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. Meteorological Data and Runoff
2.2.2. Land Surface Characteristics
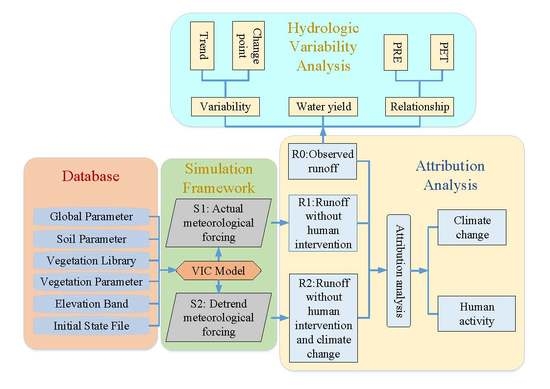
3. Methodology
3.1. Variable Infiltration Capacity (VIC) Model
3.2. Runoff Variability Detection Analysis
3.2.1. The Partial Correlation Method
3.2.2. Time-Varying Analysis with Moving Time Window Method
3.3. Runoff Variation Attribution Method
4. Results
4.1. Performance of the VIC Model
4.2. Climate Change over the Weihe River Basin
4.3. Vegetation Change over the Weihe River Basin
4.4. Variability of Runoff during 1961–2016
4.5. Changes in Precipitation-Runoff Relationship
4.6. Contributions of Climate Change and Human Activity on Runoff Variation
5. Discussion
5.1. Impact of Climate Change
5.2. Impact of Human Activity
5.3. Limitations and Further Scope
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farley, K.A.; Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. Effects of afforestation on water yield: A global synthesis with implications for policy. Glob. Chang. Boil. 2005, 11, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Sohl, T.L.; Young, C.J. Projecting the land cover change and its environmental impacts in the Cedar River Basin in the Midwestern United States. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 024025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Rustomji, P.; Hairsine, P. Responses of streamflow to changes in climate and land use/cover in the Loess Plateau, China. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.J.; Adhikari, P.; Li, L.; Su, F. Quantitative assessment of climate change and human impacts on long-term hydrologic response: A case study in a sub-basin of the Yellow River, China. Int. J. Clim. 2009, 30, 2130–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Tian, P.; Mu, X.; Jiao, J.; Wang, F.; Gao, P. Quantifying the impact of climate variability and human activities on streamflow in the middle reaches of the Yellow River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Jiang, G.; Wei, Y.; Mu, X.; Wang, F.; Zhao, G.; Sun, W. Streamflow regimes of the Yanhe River under climate and land use change, Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 29, 2402–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Cheng, W.; Fu, B.; Lü, Y. The role of climatic and anthropogenic stresses on long-term runoff reduction from the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 571, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, S.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z.; Lü, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; et al. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Shi, C.-X. Effects of climatic factors and human activities on runoff of the Weihe River in recent decades. Quat. Int. 2012, 282, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Li, Y.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, A. Dynamic changes of sediment load and water discharge in the Weihe River, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jin, W.; Guo, A. Spatiotemporal Impacts of Climate, Land Cover Change and Direct Human Activities on Runoff Variations in the Wei River Basin, China. Water 2016, 8, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, L.; Duan, K. What is the main driving force of hydrological cycle variations in the semiarid and semi-humid Weihe River Basin, China? Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 684, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, H.; Yeh, P.J.-F.; Knouft, J.H. Modeling the potential impacts of climate change on streamflow in agricultural watersheds of the Midwestern United States. J. Hydrol. 2013, 491, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zou, X.; Gao, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Tang, D.; Wang, T.; Wu, X. Quantifying the anthropogenic and climatic contributions to changes in water discharge and sediment load into the sea: A case study of the Yangtze River, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 536, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.; Tao, F. Contributions of climate change and human activities to runoff change in seven typical catchments across China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 605, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hejazi, M. Quantifying the relative contribution of the climate and direct human impacts on mean annual streamflow in the contiguous United States. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Yang, D.; Yang, H.; Lei, H. Attribution analysis based on the Budyko hypothesis for detecting the dominant cause of runoff decline in Haihe basin. J. Hydrol. 2014, 510, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, G.; Wang, S.; Jiao, L.; Wu, X.; Fu, B. The effects of vegetation on runoff and soil loss: Multidimensional structure analysis and scale characteristics. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 28, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Istanbulluoglu, E.; Bai, T.; Huang, Q.; Yang, D.; Huang, S. Impact of climate change and human activities on runoff in the Weihe River Basin, China. Quat. Int. 2015, 380, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Zhang, L.; McVicar, T.R.; Chille, B.; Gau, P. Analysis of the impact of conservation measures on stream flow regime in catchments of the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 2124–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.J.; Zheng, F.-L. Impacts of land use change and climate variability on hydrology in an agricultural catchment on the Loess Plateau of China. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.M.; Sun, G.; Fu, B.J.; Su, C.H.; Liu, Y.; Lamparski, H. Regional effects of vegetation restoration on water yield across the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 2617–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, L.; Potter, N.; Cowan, T.; Cai, W. Long-term streamflow trends in the middle reaches of the Yellow River Basin: Detecting drivers of change. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 30, 1315–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Charles, S.P.; Chiew, F.H.S. A two-parameter climate elasticity of streamflow index to assess climate change effects on annual streamflow. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVicar, T.R.; Li, L.T.; Van Niel, T.G.; Zhang, L.; Li, R.; Yang, Q.K.; Zhang, X.P.; Mu, X.M.; Wen, Z.M.; Liu, W.Z.; et al. Developing a decision support tool for China’s re-vegetation program: Simulating regional impacts of afforestation on average annual streamflow in the Loess Plateau. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 251, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; McVicar, T.R.; Guo, J.; Tang, Y.; Yao, A. Isolating the impacts of climate change and land use change on decadal streamflow variation: Assessing three complementary approaches. J. Hydrol. 2013, 507, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Liang, W.; Jiang, X. Determining the hydrological responses to climate variability and land use/cover change in the Loess Plateau with the Budyko framework. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 557, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, M.; Bernhofer, C. Applying simple water-energy balance frameworks to predict the climate sensitivity of streamflow over the continental United States. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 2531–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X. Advances in separating effects of climate variability and human activity on stream discharge: An overview. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 71, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q. Attribution of Runoff Change for the Xinshui River Catchment on the Loess Plateau of China in a Changing Environment. Water 2016, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Liang, S.; Yao, Y.; Jia, K.; Meng, S.; Li, J. Detection and attribution of changes in hydrological cycle over the Three-North region of China: Climate change versus afforestation effect. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 203, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Kang, T.; Bu, J.; Chen, J.; Gao, Y. Evaluating the Impacts of Climate Change and Vegetation Restoration on the Hydrological Cycle over the Loess Plateau, China. Water 2019, 11, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Z.; Yuan, F.; Duan, Q.; Zheng, J.; Liang, M.; Chen, F. Regional Parameter Estimation of the VIC Land Surface Model: Methodology and Application to River Basins in China. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Q.; Oki, T.; Kanae, S.; Hu, H. Hydrological Cycles Change in the Yellow River Basin during the Last Half of the Twentieth Century. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 1790–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saxton, K.E.; Rawls, W.J. Soil Water Characteristic Estimates by Texture and Organic Matter for Hydrologic Solutions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Myneni, R.; Glassy, J.M.; Dedieu, G.; Running, S.W. Prototyping of MODIS LAI and FPAR algorithm with LASUR and LANDSAT data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2387–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Z.; Bi, J.; Pan, Y.; Ganguly, S.; Anav, A.; Xu, L.; Samanta, A.; Piao, S.L.; Nemani, R.; Myneni, R. Global Data Sets of Vegetation Leaf Area Index (LAI)3g and Fraction of Photosynthetically Active Radiation (FPAR)3g Derived from Global Inventory Modeling and Mapping Studies (GIMMS) Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI3g) for the Period 1981 to 2011. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 927–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Wood, E.F.; Burges, S.J. A simple hydrologically based model of land surface water and energy fluxes for general circulation models. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1994, 99, 14415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wood, E.F.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Surface soil moisture parameterization of the VIC-2L model: Evaluation and modification. Glob. Planet. Chang. 1996, 13, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Xie, Z. A new surface runoff parameterization with subgrid-scale soil heterogeneity for land surface models. Adv. Water Resour. 2001, 24, 1173–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijssen, B.; Schnur, R.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Global Retrospective Estimation of Soil Moisture Using the Variable Infiltration Capacity Land Surface Model, 1980–1993. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 1790–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.H.; Liu, Q.; Su, F.G. An Application of the VIC-3L Land Surface Model with the New Surface Runoff Model in Simulating Streamflow for the Yellow River Basin. In GIS and Remote Sensing in Hydrology, Water Resources and Environment; Chen, Y.B., Ed.; International Assn of Hydrological Sciences: Wallingford, UK, 2004; pp. 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann, D.; NolteHolube, R.; Raschke, E. A large-scale horizontal routing model to be coupled to land surface parametrization schemes. Tellus Ser. a-Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 1996, 48, 708–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Nan, H.; Huntingford, C.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Sitch, S.; Peng, S.; Ahlström, A.; Canadell, J.G.; Cong, N.; et al. Evidence for a weakening relationship between interannual temperature variability and northern vegetation activity. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.; Song, X.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Wang, F.; Zhao, G. Spatiotemporal vegetation cover variations associated with climate change and ecological restoration in the Loess Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 209, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Liang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yan, J.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Mo, X. Separating Vegetation Greening and Climate Change Controls on Evapotranspiration trend over the Loess Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, T. Evidence for intensification of the global water cycle: Review and synthesis. J. Hydrol. 2006, 319, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D.; Farnsworth, K.; Jones, P.; Xu, K.; Smith, L. Climatic and anthropogenic factors affecting river discharge to the global ocean, 1951–2000. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 62, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Mu, X.; Li, R.; Fleskens, L.; Stringer, L.C.; Ritsema, C.J. Co-evolution of soil and water conservation policy and human–environment linkages in the Yellow River Basin since 1949. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 508, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, W.; Miao, C. Hydrogeomorphic Ecosystem Responses to Natural and Anthropogenic Changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 45, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, S.; Mayor, A.G.; Bourakhouadar, J.; Bellot, J. Plant Spatial Pattern Predicts Hillslope Runoff and Erosion in a Semiarid Mediterranean Landscape. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L.; Jiao, L.; Wang, C. Reducing soil erosion by improving community functional diversity in semi-arid grasslands. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 52, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Y. Quantitative estimation on contributions of climate changes and human activities to decreasing runoff in Weihe River Basin, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.; Xu, Z.; Yao, W.; Jin, S.; Xiao, P.; Ran, D. Assessing the effects of changes in land use and climate on runoff and sediment yields from a watershed in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 544, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, J.; Lu, C.X.; Niu, J.; Gao, Y. Attribution of Runoff Reduction in the Juma River Basin to Climate Variation, Direct Human Intervention, and Land Use Change. Water 2018, 10, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Liang, W.; Fu, B.J.; Lu, Y.H.; Fu, S.Y.; Wang, S.; Su, H.M. Vegetation changes in recent large-scale ecological restoration projects and subsequent impact on water resources in China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-J.; Tang, Q.; Pan, M.; Tang, Y. A Long-Term Land Surface Hydrologic Fluxes and States Dataset for China. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 2067–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Catchment | River | Gauge Station | Longitude | Latitude | Area(km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WH1 | Jinghe | Zhangjiashan | 108°36′ | 34°38′ | 43,216 |
| WH2 | Upper reach | Linjiacun | 107°03′ | 34°23′ | 30,661 |
| WH3 | Middle and lower reaches | Huaxian | 109°46′ | 34°35′ | 32,621 |
| Scenario | Vegetation Parameter | Forcing Data | Impacts |
|---|---|---|---|
| S0: Observed runoff (R0) | / | / | Climate change and human activity |
| S1: Simulated runoff (R1) | Maryland Land Cover 1 km | actual | Climate change |
| S2: Simulated runoff (R2) | Maryland Land Cover 1 km | detrended | None |
| Basin | Mean (108 m3) | Trend (108 m3·year−1) | Variation (108 m3) | Rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | Before | After | |||
| WH | 77.52 | 44.85 | −0.9882 | 0.8175 * | −32.68 | −42.15 |
| WH1 | 14.72 | 7.61 | −0.1250 | −0.3619 ** | −7.12 | −48.34 |
| WH2 | 21.89 | 9.19 | −0.5015 ** | −0.0386 | −12. 71 | −58.04 |
| WH3 | 42.09 | 27.42 | −0.1919 | 0.9414 ** | −14.67 | −34.84 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Kang, T.; Bu, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y. Detection and Attribution of Runoff Reduction of Weihe River over Different Periods during 1961–2016. Water 2020, 12, 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051416
Yang S, Kang T, Bu J, Chen J, Wang Z, Gao Y. Detection and Attribution of Runoff Reduction of Weihe River over Different Periods during 1961–2016. Water. 2020; 12(5):1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051416
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shuai, Tingting Kang, Jingyi Bu, Jiahao Chen, Zhipeng Wang, and Yanchun Gao. 2020. "Detection and Attribution of Runoff Reduction of Weihe River over Different Periods during 1961–2016" Water 12, no. 5: 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051416
APA StyleYang, S., Kang, T., Bu, J., Chen, J., Wang, Z., & Gao, Y. (2020). Detection and Attribution of Runoff Reduction of Weihe River over Different Periods during 1961–2016. Water, 12(5), 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12051416