Removal Mechanism and Effective Current of Electrocoagulation for Treating Wastewater Containing Ni(II), Cu(II), and Cr(VI)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Metal Removal of EC System
2.2. Adsorption Isotherms of Metal Ions
2.3. Adsorption Experiments in an EC System
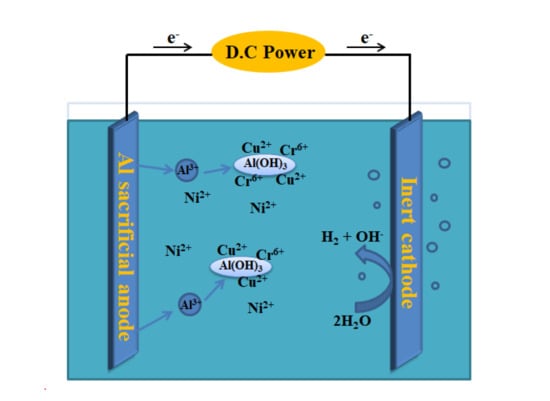
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorption of Ni(II), Cu(II), and Cr(VI)
3.2. Competitive Adsorption
3.3. Direct EC Treatment
3.4. Treatment of Electroplating Wastewater
4. Conclusions
- For individual ions, adsorption of Ni(II) and Cu(II) by Al(OH)3 coagulant can be described by the Langmuir isotherm, while Cr(VI) adsorption fits the Freundlich isotherm better.
- Treating a single heavy metal of wastewater, the removal mechanism of the EC process is the adsorption reaction.
- Under the coexisting condition, the Ni(II) and Cu(II) will compete for the same active sites on the Al(OH)3 surface and Cu(II) suppresses Ni(II) adsorption.
- Treating the coexisting heavy metals, Ni(II) removal not only associates with adsorption but also with the coprecipitation. In contrast, Cr(VI) does not compete with other metal ions for the same type of adsorption sites.
- Whether single or coexisting conditions, the adsorption capacity of heavy metals onto Al(OH)3 coagulants can be used to compute the necessary current to effectively remove heavy metals in the EC system.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Development Document for the Proposed Effluent Limitations Guidelines and Standards for the Metal Products and Machinery Point Source Category; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Chan, G.Y.S.; Lo, W.H.; Babel, S. Physico–chemical treatment techniques for wastewater laden with heavy metals. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 118, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Development Document for Effluent Limitations Guidelines and Standards for the Metal Finishing Point Source Category; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1983.
- Yang, C.L.; Kravets, G. Removal of chromium from abrasive blast media by leaching and electrochemical precipitation. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2000, 50, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.L.; Dluhy, R. Electrochemical generation of aluminum sorbent for fluoride adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 94, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.L.; McGarrahan, J. Electrochemical coagulation for textile effluent decolorization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 127, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.H.; Chen, L.; Yang, C.L. Electrochemical decomposition of reactive blue 19. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2011, 28, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.L.; Kravets, G. Removal of cadmium in leachate from waste alumina beads using electrochemical technology. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2002, 189, 827–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Yang, C.L. Electrochemical treatment of Cr-containing aqueous solutions. Hazardous Materials and Wastewater; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.H.; Chen, L.; Yang, C.L. Effect of anions on electrochemical coagulation for cadmium removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 65, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.L.; Beltran, M.R.; Kravets, G. Heavy Metal Ion Removal and Wastewater Treatment by Influence of Magnetic and Electrical Fields; US Air Force: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Oden, M.K.; Sari-Erkan, H. Treatment of metal plating wastewater using iron electrode byelectrocoagulation process: Optimization and process performance. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 119, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shannag, M.; Al-Qodah, Z.; Bani-Melhem, K.; Qtaishat, M.R.; Alkasrawi, M. Heavy metal ions removal from metal plating wastewater using electrocoagulation: Kinetic study and process performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doggaz, A.; Attour, A.; Mostefa, M.L.P.; Come, K.; Tlili, M.; Lapicque, F. Removal of heavy metals by electrocoagulation from hydrogenocarbonatecontainingwaters: Compared cases of divalent iron and zinc cations. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 29, 100796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, X.; Cao, G.; Liu, S.; Duan, Z.; Song, S.; Song, M.; Zhang, M. Optimization and assessment of Feeelectrocoagulation for theremoval of potentially toxic metals from real smelting wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 218, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Aji, B.; Yavuz, Y.; Savas-Koparal, A. Electrocoagulation of heavy metals containing model wastewater using monopolar iron electrodes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 86, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbal, F.; Camcı, S. Copper, chromium and nickel removal from metal plating wastewater by electrocoagulation. Desalination 2011, 269, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidmann, I.; Calmano, W. Removal of Zn(II), Cu(II), Ni(II), Ag(I) and Cr(VI) present in aqueous solutions by aluminum electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhoum, N.; Monser, L.; Bellakhal, N.; Belgaied, J.E. Treatment of electroplating wastewater containing Cu(II), Zn(II) and Cr(VI) by electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 112, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbal, F.; Camcı, S. Comparison of Electrocoagulation and chemical coagulation for heavy metal removal. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2010, 33, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Kim, T.K.; Zoh, K.D. Removal mechanism of heavy metal (Cu, Ni, Zn, and Cr) in the presence of cyanide during electrocoagulation using Fe and Al electrodes. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, K.S.; Al-Saati, N.H.; Alquzweeni, S.S.; Zubaidi, S.L.; Kot, P.; Kraidi, L.; Hussein, A.H.; Alkhaddar, R.; Shaw, A.; Alwash, R.; et al. Decolourization of dye solutions by electrocoagulation: An investigation of the effect of operational parameters. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 584, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, K.S.; Hussein, A.H.; Zubaidi, S.L.; Kot, P.; Kraidi, L.; Alkhaddar, R.; Shaw, A.; Alwash, R. Effect of initial pH value on the removal of reactive black dye from water by electrocoagulation (EC) method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1294, 072017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, K.S.; AlKhaddar, R.; Shaw, A.; Kot, P.; Al-Jumeily, D.; Alwash, R.; Aljefery, M.H. Electrocoagulation as an Eco-Friendly River Water Treatment Method. Advances in Water Resources Engineering and Management; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 219–235. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S.; Greenberg, A.E. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.H.; Chang Chien, S.W.; Dong, C.D.; Chen, C.W.; Huang, C.H.; Shen, S.Y. The coinage refractory wastewater treated by electrocatalytic-membrane process (ECMP) integrated with chemical-or electro-coagulation techniques. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 125, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatsios, E.; Hahladakis, J.N.; Gidarakos, E. Optimization of electrocoagulation (EC) process for the purification of a real industrial wastewater from toxic metals. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 154, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.Y.; Lee, J.U.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, K.W. Competitive adsorption characteristics of Co2+, Ni2+, and Cr3+ by IRN-77 cation exchange resin in synthesized wastewater. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussa, D.T.; El-Naas, M.H.; Nasser, M.; Al-Marri, M.J. A comprehensive review ofelectrocoagulation for water treatment: Potentials and challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 186, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahreen, A.; Jami, M.S.; Ali, F. Role of electrocoagulation in wastewater treatment: A developmental review. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.-H.; Shen, S.-Y.; Dong, C.-D.; Kumar, M.; Chang, J.-H. Removal Mechanism and Effective Current of Electrocoagulation for Treating Wastewater Containing Ni(II), Cu(II), and Cr(VI). Water 2020, 12, 2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092614
Huang C-H, Shen S-Y, Dong C-D, Kumar M, Chang J-H. Removal Mechanism and Effective Current of Electrocoagulation for Treating Wastewater Containing Ni(II), Cu(II), and Cr(VI). Water. 2020; 12(9):2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092614
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chien-Hung, Shan-Yi Shen, Cheng-Di Dong, Mohanraj Kumar, and Jih-Hsing Chang. 2020. "Removal Mechanism and Effective Current of Electrocoagulation for Treating Wastewater Containing Ni(II), Cu(II), and Cr(VI)" Water 12, no. 9: 2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092614
APA StyleHuang, C. -H., Shen, S. -Y., Dong, C. -D., Kumar, M., & Chang, J. -H. (2020). Removal Mechanism and Effective Current of Electrocoagulation for Treating Wastewater Containing Ni(II), Cu(II), and Cr(VI). Water, 12(9), 2614. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092614