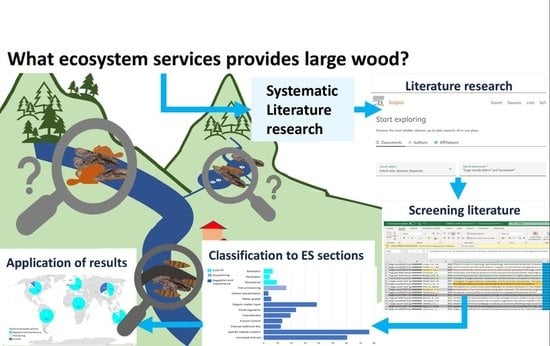
Ecosystem Services of Large Wood: Mapping the Research Gap
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- To describe the current state of ecosystem services and large wood
- To identify the possible knowledge gap between ecosystem services and large wood
- To transform primary data from the literature to classified ecosystem services
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation for a Systematic Literature Research
2.2. Key Terms of the Search
2.3. Search of the Literature
2.4. Process of Elaboration of the Data
2.5. Ecosystem Services Classification
3. Results
3.1. Results of the Search of Eligible Articles
3.2. General Results and Geographical Aspects of the Systematic Literature Research
3.3. Results of the Key Area and Specific Area of Research
3.4. Transformation of Information into ES Classification
4. Discussion
4.1. Systematic Literature Review Process
4.2. The Current State of the Relationship between ES and LW
4.3. Process of Classification of ES Provided by LW
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wohl, E. Bridging the gaps. An overview of wood across time and space in diverse rivers. Geomorphology 2017, 279, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, F.J.; Gregory, S.V.; Iroumé, A.; Ruiz-Villanueva, V.; Wohl, E. Reflections on the history of research on large wood in rivers. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 46, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohl, E.; Cenderelli, D.A.; Dwire, K.A.; Ryan-Burkett, S.E.; Young, M.K.; Fausch, K.D. Large in-stream wood studies: A call for common metrics. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 35, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.P.; Gehrke, P.C.; Jansen, J.D.; Abbe, T.B. Experimental reintroduction of woody debris on the Williams River, NSW: Geomorphic and ecological responses. River Res. Appl. 2004, 20, 513–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cordova, J.M.; Rosi-Marshall, E.J.; Yamamuro, A.M.; Lamberti, G.A. Quantity, controls and functions of large woody debris in Midwestern USA streams. River Res. Appl. 2007, 23, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galia, T. Controls on log step occurrence in steep headwater streams draining Carpathian managed forests. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elosegi, A.; Flores, L.; Díez, J. The importance of local processes on river habitat characteristics: A Basque stream case study. Limnetica 2011, 30, 183–196. Available online: https://www.limnetica.com/documentos/limnetica/limnetica-30-2-p-183.pdf. (accessed on 24 May 2021).
- Nichols, R.A.; Ketcheson, G.L. A Two-Decade Watershed Approach to Stream Restoration Log Jam Design and Stream Recovery Monitoring: Finney Creek, Washington. JAWRA 2013, 49, 1367–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entrekin, S.A.; Tank, J.L.; Rosi-Marshall, E.J.; Hoellein, T.J.; Lamberti, G.A. Response of secondary production by macroinvertebrates to large wood addition in three Michigan streams. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 1741–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.B.; Breneman, D.H.; Richards, C. Macroinvertebrate community structure and function associated with large wood in low gradient streams. Riv. Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines-Young, R.; Potschin, M.B. Common International Classification of Ecosystem Services (CICES) V5.1 and Guidance on the Application of the Revised Structure; Fabis Consulting Ltd.: Nottingham, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski, R.C.; Gurnell, A.M.; Burgess-Gamble, L.; England, J.; Holland, D.; Klaar, M.J.; Morrissey, I.; Uttley, C.; Wharton, G. The current state of the use of large wood in river restoration and management. Water Environ. J. 2019, 33, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.P.; Jiang, B.; Kinzig, A.P.; Lee, K.N.; Ouyang, Z.; Knops, J. Linking ecosystem characteristics to final ecosystem services for public policy. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jesson, J.; Matheson, L.; Lacey, F. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques, 1st ed.; Sage Publications: London, UK, 2011; p. 192. ISBN 978-1848601543. [Google Scholar]
- Mengist, W.; Soromessa, T.; Legese, G. Ecosystem services research in mountainous regions: A systematic literature review on current knowledge and research gaps. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Villanueva, V.; Piégay, H.; Gurnell, A.M.; Marston, R.A.; Stoffel, M. Recent advances quantifying the large wood dynamics in river basins: New methods and remaining challenges. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 611–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- England, J.; Dobbek, L.; Finn Leeming, B.; Gurnell, A.M.; Wharton, G. Restoration of a chalk stream using wood: Assessment of habitat improvements using the Modular River Survey. Water Environ. J. 2019, 33, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elosegi, A.; Elorriaga, C.; Flores, L.; Martí, E.; Díez, J. Restoration of wood loading has mixed effects on water, nutrient, and leaf retention in Basque mountain streams. Fresh. Sci. 2016, 35, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tullos, D.; Walter, C. Fish use of turbulence around wood in winter: Physical experiments on hydraulic variability and habitat selection by juvenile coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2014, 98, 115–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piégay, H.; Gregory, K.J.; Bondarev, V.; Chin, A.; Dahlstrom, N.; Elosegi, A.; Gregory, S.V.; Joshi, V.; Mutz, M.; Rinaldi, M.; et al. Public Perception as a Barrier to Introducing Wood in Rivers for Restoration Purposes. Environ. Manag. 2005, 36, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keys, T.A.; Govenor, H.; Jones, C.N.; Hession, W.C.; Hester, E.T.; Scott, D.T. Effects of large wood on floodplain connectivity in a headwater Mid-Atlantic stream. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 118, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deane, A.; Norrey, J.; Coulthard, E.; McKendry, D.C.; Dean, A.P. Riverine large woody debris introduced for natural flood management leads to rapid improvement in aquatic macroinvertebrate diversity. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 163, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, A.; Daniels, M.D.; Urban, M.A.; Piégay, H.; Gregory, K.J.; Bigler, W.; Butt, A.Z.; Grable, J.L.; Gregory, S.V.; Lafrenz, M.; et al. Perceptions of Wood in Rivers and Challenges for Stream Restoration in the United States. Environ. Manag. 2008, 41, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, I.J.; Gergel, S.E.; Bennett, E.M. Seeing the forest for its multiple ecosystem services: Indicators for cultural services in heterogeneous forests. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 71, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disman, M. Jak se vyrábí sociologická znalost: Příručka pro uživatele, 4th ed.; Karolinum: Prague, Czech Republic, 2011; p. 372. ISBN 9788024619668. [Google Scholar]
- Vihervaara, P.; Rönkä, M.; Walls, M. Trends in Ecosystem Service Research: Early Steps and Current Drivers. AMBIO 2010, 39, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Villanueva, V.; Díez-Herrero, A.; García, J.A.; Ollero, A.; Piégay, H.; Stoffel, M. Does the public’s negative perception towards wood in rivers relate to recent impact of flooding experiencing? Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plummer, M.L. Assessing benefit transfer for the valuation of ecosystem services. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maraseni, T.N.; Mitchell, C. An assessment of carbon sequestration potential of riparian zone of Condamine Catchment, Queensland, Australia. Land Use Policy 2016, 54, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña, V.; Díez, J.R.; Flores, L.; Meleason, M.; Elosegi, A.; Jones, J. Does it make economic sense to restore rivers for their ecosystem services? J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; de Groot, R.; Braat, L.; Kubiszewski, I.; Fioramonti, L.; Sutton, P.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M. Twenty years of ecosystem services: How far have we come and how far do we still need to go? Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Lay, Y.; Piégay, H.; Gregory, K.; Chin, A.; Dolédec, S.; Elosegi, A.; Mutz, M.; Wyżga, B.; Zawiejska, J. Variations in Cross-Cultural Perception of Riverscapes in Relation to In-Channel Wood. Trans. Inst. Br. Geogr. 2008, 33, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Stage | Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Defined research question | i. To describe the current state of ES and LW. |
| ii. Classification of data from the literature database for ES classification. | |
| iii. To identify a possible gap between ES and LW. | |
| Design the plan of the research | i. To prepare key terms for the research. |
| ii. To identify possible limitations of the research. | |
| Search for the literature | i. Search of the literature using key terms. |
| Criteria of search | i. Apply PRISMA protocol and exact criteria to gain eligible literature. |
| Results | i. Apply quality assessment to the database of the literature |
| ii. Transformation of data for ES classification | |
| Discussion and publication | i. Synthesis of the data and publication to contribute to the research on LW and ES. |
| Name of Ecosystem Service | The Presence of LW Enable/Enhance | Section | CICES Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased channel heterogeneity | Channel heterogeneity by amount and orientation of LW | Regulation and maintenance | 5.2.2.1 |
| Specific habitat creation | Creation of unique habitat | 5.2.2.1 | |
| Channel sediment flux | Controls sediment flux and accumulation | 5.3.1. | |
| Erosion control | Control of possible river reach erosion. | 5.2.1.2 | |
| Invertebrates | A habitat for population of invertebrates | 2.2.2.3 | |
| Flood regulation | Flood risk and regulation | 2.2.1.3 | |
| Organic matter input | An input of organic matter (e.g., DOM) | 5.3.2. | |
| Water quality | A quality of flowing water | 2.2.5.1 | |
| Carbon sequestration | To study a carbon sequestration | 5.1.1.3 | |
| Fish provisioning | A habitat for fish population | Provisioning | 1.1.4.1 |
| Educational | Possibility to study and train knowledge | Cultural | 6.1.2.1 |
| Recreation | Possibility to enjoy free time | 6.1.1.1 | |
| Aesthetics | Experience of beauty of the environment | 3.1.2.4 |
| Name of the Key Term | T | G | A | O | Y | sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| “large wood” & “ecosystem services” | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| “large wood” & “ecosystem” | 170 | 33 | 137 | 1 | 0 | 136 |
| “large wood” & “gaps” | 17 | 3 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 14 |
| “large wood” & “approach” | 115 | 25 | 90 | 4 | 2 | 84 |
| “large wood” & “hazard*” | 55 | 16 | 39 | 0 | 0 | 39 |
| “large wood” & “perception” | 12 | 2 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| “large wood” & “regulation service *” | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| “large wood” & “cultural service *” | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| “large wood” & “provisioning service *” | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| “log jam” & “ecosystem services” | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| “log jam” & “ecosystem” | 22 | 4 | 18 | 0 | 0 | 18 |
| “log jam” & “gaps” | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| “log jam” & “approach” | 11 | 3 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| “log jam” & “hazard” | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| “log jam” & “perception” | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| “log jam” & “regulation service *” | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| “log jam” & “cultural service *” | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| “log jam” & “provisioning service *” | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| “woody debris” & “ecosystem services” | 53 | 7 | 46 | 0 | 0 | 46 |
| “woody debris” & “perception” | 22 | 0 | 22 | 1 | 0 | 21 |
| “woody debris” & “provisioning service *” | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| “woody debris” & “regulation service *” | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| “woody debris” & “cultural service *” | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| “large woody debris” & “ecosystem services” | 4 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| “large woody debris” & “perception” | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| “large woody debris” & “regulation service *” | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| “large woody debris” & “cultural service *” | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| “large woody debris” & “provisioning service *” | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| sum | 499 | 96 | 403 | 6 | 2 | 395 |
| Type of Research | Number of Conducted Research |
|---|---|
| Field inventory | |
| North America | 55 |
| Canada (6), USA (49) | |
| Europe | 64 |
| Greece; Portugal (1), Czechia; Russia (2), Austria; Sweden (3), Switzerland (4), Germany (5), France; Poland (6), Italy; Spain (10), UK (11) | |
| South America | 8 |
| Bolivia (1), Chile (7) | |
| Australia and Oceania | 9 |
| New Zealand (2), Australia (7) | |
| Asia | 9 |
| China; India (2), Japan (6) | |
| Africa | 1 |
| South Africa (1) | |
| Laboratory circumstances | |
| PC Modelling | 5 |
| Laboratory | 11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poledniková, Z.; Galia, T. Ecosystem Services of Large Wood: Mapping the Research Gap. Water 2021, 13, 2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13182594
Poledniková Z, Galia T. Ecosystem Services of Large Wood: Mapping the Research Gap. Water. 2021; 13(18):2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13182594
Chicago/Turabian StylePoledniková, Zuzana, and Tomáš Galia. 2021. "Ecosystem Services of Large Wood: Mapping the Research Gap" Water 13, no. 18: 2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13182594
APA StylePoledniková, Z., & Galia, T. (2021). Ecosystem Services of Large Wood: Mapping the Research Gap. Water, 13(18), 2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13182594