A Review of SWAT Model Application in Africa
Abstract
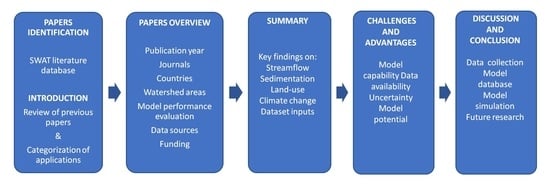
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of Reviewed Papers (Year, Journals, Countries, Data Sources and Funding)
3. Summaries of SWAT Model Application
3.1. Applications Considering Water Resources and Streamflow Simulations
3.2. Applications Considering Erosion and Sedimentation Related Studies
3.3. Applications Considering Land Use Management and Agricultural Related Context
3.4. Applications Considering a Climate Change Context
3.5. Applications Considering Model Parameterization and Dataset Inputs
4. Challenges and Advantages of the SWAT Model Application
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Data Source | Number |
|---|---|
| Landsat/satellite sources | 54 |
| Own development/local sources | 35 |
| Global Land Cover Characterization (GLCC) database | 27 |
| Derived from previous studies | 13 |
| Food and Agriculture Organization Africover land cover dataset | 12 |
| Water and Land Resource Centre (WLRC) | 2 |
| Soil Conservation Research Programme (SCRP) | 2 |
| International Soil Reference and Information Centre (ISRIC) | 2 |
| Agriculture Research Council - Institute of Soil, Climate and Water | 1 |
| Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectro-radiometer (MODIS) | 1 |
| IMPETUS database 250 m resolution | 1 |
| Centre for Mapping and Remote Sensing | 1 |
| International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) | 1 |
| Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer derived by the USGS | 1 |
| Climate Change Initiative Land Cover (CCI-LC) | 1 |
| Data Source | Number |
|---|---|
| FAO soil data base | 66 |
| Soil and Terrain Database | 27 |
| Local sources | 23 |
| Derived from previous studies | 21 |
| Harmonized Digital Soil map of the World (HWSD) | 9 |
| WaterBase | 1 |
| IRD (French National Research Institute for Sustainable Development) | 1 |
| Soil and Water Conservation Agency from Landsat Thematic Mapper | 1 |
| International Soil Reference and Information Centre | 1 |
| Data Source | Number |
|---|---|
| Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) | 52 |
| Developed from previous studies/own sources/local | 31 |
| Advanced Space borne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) | 24 |
| United States Geological Survey (USGS) | 20 |
| HydroSHEDS | 7 |
| CGIAR Consortium for Spatial Information website | 6 |
| SPOT-5/6 (Satellite Pour l’Observation de la Terre) DEM | 3 |
| Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) | 2 |
| International Water Management Institute (IWMI) | 1 |
| Institute of Soil, Climate and Water (ISCW) | 1 |
| Source | Number |
|---|---|
| International Funding (European Union) | 67 |
| African/Continental | 25 |
| International Funding (North America) | 18 |
| Collaborative funding | 11 |
| International funding (Asia) | 8 |
References
- Krysanova, V.; White, M. Advances in Water Resources Assessment with SWAT—An Overview. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Al-Asadi, K. Evaluating the Effect of Numerical Schemes on Hydrological Simulations: HYMOD as A Case Study. Water 2019, 11, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large Area Hydrologic Modeling and Assessment Part I: Model Development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassman, P.; Reyes, M.; Green, C.; Arnold, J. The Soil and Water Assessment Tool: Historical Development, Applications, and Future Research Directions. Trans. ASAE 2007, 50, 1211–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mutenyo, I.; Nejadhashemi, P.A.; Woznicki, S.A.; Giri, S. Evaluation of Swat Performance on a Mountainous Watershed in Tropical Africa. Hydrol. Curr. Res. 2013, S14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Griensven, A.; Ndomba, P.; Yalew, S.; Kilonzo, F. Critical Review of SWAT Applications in the Upper Nile Basin Countries. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3371–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CARD SWAT Literature Database 2019. Available online: https://www.card.iastate.edu/swat_articles/readme/ (accessed on 31 July 2019).
- Gassman, P.W.; Sadeghi, A.M.; Srinivasan, R. Applications of the SWAT Model Special Section: Overview and Insights. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Fohrer, N. SWAT2000: Current Capabilities and Research Opportunities in Applied Watershed Modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, D.K.; Bera, M. Watershed-Scale Hydrologic and Nonpoint-Source Pollution Models: Review of Applications. Trans. ASAE 2004, 47, 789–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harper, D.M.; Brierley, B.; Ferguson, A.J.D.; Phillips, G. The Ecological Bases for Lake and Reservoir Management. In Proceedings of the Ecological Bases for Management of Lakes and Reservoirs Symposium, Leicester, UK, 19–22 March 1996; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013. ISBN 978-94-017-3282-6. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.L.; Gassman, P.W.; Srinivasan, R.; Arnold, J.G.; Yang, X. A Review of SWAT Studies in Southeast Asia: Applications, Challenges and Future Directions. Water 2019, 11, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Almeida Bressiani, D.; Gassman, P.W.; Fernandes, J.G.; Garbossa, L.H.P.; Srinivasan, R.; Bonumá, N.B.; Mendiondo, E.M. Review of Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) Applications in Brazil: Challenges and Prospects. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2015, 8, 9–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaibou Begou, J.; Jomaa, S.; Benabdallah, S.; Bazie, P.; Afouda, A.; Rode, M. Multi-Site Validation of the SWAT Model on the Bani Catchment: Model Performance and Predictive Uncertainty. Water 2016, 8, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessie, M.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Pauwels, V.R.N.; Admasu, T.; Poesen, J.; Adgo, E.; Deckers, J.; Nyssen, J. Analyzing Runoff Processes through Conceptual Hydrological Modeling in the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 5149–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milzow, C.; Krogh, P.E.; Bauer-Gottwein, P. Combining Satellite Radar Altimetry, SAR Surface Soil Moisture and GRACE Total Storage Changes for Hydrological Model Calibration in a Large Poorly Gauged Catchment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1729–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nkiaka, E.; Nawaz, N.R.; Lovett, J.C. Evaluating Global Reanalysis Datasets as Input for Hydrological Modelling in the Sudano-Sahel Region. Hydrology 2017, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Setegn, S.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Melesse, A.M.; Dargahi, B. SWAT Model Application and Prediction Uncertainty Analysis in the Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakrishnan, R.; Srinivasan, R.; Santhi, C.; Arnold, J.G. Advances in the Application of the SWAT Model for Water Resources Management. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehew, A.E.; Milewski, A.; Soliman, F. Reconstructing an Extreme Flood from Boulder Transport and Rainfall-Runoff Modelling: Wadi Isla, South Sinai, Egypt. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2010, 70, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeba, D.; Kansal, M.L.; Sen, S. Economic Evaluation of the Proposed Alternatives of Inter-Basin Water Transfer from the Baro Akobo to Awash Basin in Ethiopia. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 2, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouessar, M.; Bruggeman, A.; Abdelli, F.; Mohtar, R.H.; Gabriels, D.; Cornelis, W.M. Modelling Water-Harvesting Systems in the Arid South of Tunisia Using SWAT. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 2003–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sultan, M.; Metwally, S.; Milewski, A.; Becker, D.; Ahmed, M.; Sauck, W.; Soliman, F.; Sturchio, N.; Yan, E.; Rashed, M.; et al. Modern Recharge to Fossil Aquifers: Geochemical, Geophysical, and Modeling Constraints. J. Hydrol. 2011, 403, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosase, E.; Ahiablame, L.; Srinivasan, R. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Blue Water in the Limpopo River Basin, Southern Africa: A Case Study. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2019, 19, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeba, D.; Kansal, M.; Sen, S. Assessment of Water Scarcity and Its Impacts on Sustainable Development in Awash Basin, Ethiopia. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuol, J.; Abbaspour, K.C.; Srinivasan, R.; Yang, H. Estimation of Freshwater Availability in the West African Sub-Continent Using the SWAT Hydrologic Model. J. Hydrol. 2008, 352, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faramarzi, M.; Abbaspour, K.C.; Ashraf Vaghefi, S.; Farzaneh, M.R.; Zehnder, A.J.B.; Srinivasan, R.; Yang, H. Modeling Impacts of Climate Change on Freshwater Availability in Africa. J. Hydrol. 2013, 480, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessesse, B.; Bewket, W.; Bräuning, A. Model-Based Characterization and Monitoring of Runoff and Soil Erosion in Response to Land Use/Land Cover Changes in the Modjo Watershed, Ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunink, J.E.; Niadas, I.A.; Antonaropoulos, P.; Droogers, P.; de Vente, J. Targeting of Intervention Areas to Reduce Reservoir Sedimentation in the Tana Catchment (Kenya) Using SWAT. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melaku, N.D.; Renschler, C.S.; Holzmann, H.; Strohmeier, S.; Bayu, W.; Zucca, C.; Ziadat, F.; Klik, A. Prediction of Soil and Water Conservation Structure Impacts on Runoff and Erosion Processes Using SWAT Model in the Northern Ethiopian Highlands. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 1743–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemann, T.; Zeleke, G.; Amsler, C.; Giovanoli, L.; Suter, H.; Roth, V. Modelling the Effect of Soil and Water Conservation on Discharge and Sediment Yield in the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 73, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aga, A.O.; Chane, B.; Melesse, A.M. Soil Erosion Modelling and Risk Assessment in Data Scarce Rift Valley Lake Regions, Ethiopia. Water 2018, 10, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gathagu, J.N.; Sang, J.K.; Maina, C.W. Modelling the Impacts of Structural Conservation Measures on Sediment and Water Yield in Thika-Chania Catchment, Kenya. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesuf, H.M.; Assen, M.; Alamirew, T.; Melesse, A.M. Modeling of Sediment Yield in Maybar Gauged Watershed Using SWAT, Northeast Ethiopia. CATENA 2015, 127, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbahi, M.; Benabdallah, S.; Boussema, R. Assessment of Soil Erosion Risk Using SWAT Model. Arab. J. Geosci. 2012, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfahunegn, G.B.; Vlek, P.L.G.; Tamene, L. Management Strategies for Reducing Soil Degradation through Modeling in a GIS Environment in Northern Ethiopia Catchment. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2012, 92, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betrie, G.D.; Mohamed, Y.A.; van Griensven, A.; Srinivasan, R. Sediment Management Modelling in the Blue Nile Basin Using SWAT Model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khelifa, W.B.; Hermassi, T.; Strohmeier, S.; Zucca, C.; Ziadat, F.; Boufaroua, M.; Habaieb, H. Parameterization of the Effect of Bench Terraces on Runoff and Sediment Yield by Swat Modeling in a Small Semi-Arid Watershed in Northern Tunisia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 1568–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndomba, P.; Mtalo, F.; Killingtveit, Å. A Guided SWAT Model Application on Sediment Yield Modeling in Pangani River Basin: Lessons Learnt. J. Urban Environ. Eng. 2008, 2, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettam, A.; Taleb, A.; Sauvage, S.; Boithias, L.; Belaidi, N.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.M. Modelling Hydrology and Sediment Transport in a Semi-Arid and Anthropized Catchment Using the SWAT Model: The Case of the Tafna River (Northwest Algeria). Water 2017, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mwangi, J.; Shisanya, C.; Gathenya, J.; Namirembe, S.; Moriasi, D. A Modeling Approach to Evaluate the Impact of Conservation Practices on Water and Sediment Yield in Sasumua Watershed, Kenya. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 70, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyandye, C.; Worqlul, A.; Martz, L.; Muzuka, A. The Impact of Future Climate and Land Use/Cover Change on Water Resources in the Ndembera Watershed and Their Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies. Environ. Syst. Res. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martine, N.; D’Urso, G.; Immerzeel, W.W. Adaptive Simulation of the Impact of Changes in Land Use on Water Resources in the Lower Aswa Basin. J. Agric. Eng. 2013, 43, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mwangi, H.M.; Julich, S.; Patil, S.D.; McDonald, M.A.; Feger, K.-H. Modelling the Impact of Agroforestry on Hydrology of Mara River Basin in East Africa. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 3139–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duku, C.; Zwart, S.J.; Hein, L. Modelling the Forest and Woodland-Irrigation Nexus in Tropical Africa: A Case Study in Benin. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 230, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melesse, A.M.; McClain, M.; Wang, X.; Abira, M.; Mutayoba, W. Modeling the Impact of Land-Cover and Rainfall Regime Change Scenarios on the Flow of Mara River, Kenya. World Environ. Water Resour. Congr. 2008, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; You, L.; Takeshima, H. Invest in Small-Scale Irrigated Agriculture: A National Assessment on Potential to Expand Small-Scale Irrigation in Nigeria. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 193, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GITHUI, F.; Mutua, F.; Bauwens, W. Estimating the Impacts of Land-Cover Change on Runoff Using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT): Case Study of Nzoia Catchment, Kenya. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyamfi, C.; Ndambuki, J.M.; Salim, R.W. Hydrological Responses to Land Use/Cover Changes in the Olifants Basin, South Africa. Water 2016, 8, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashaw, T.; Tulu, T.; Argaw, M.; Worqlul, A.W. Modeling the Hydrological Impacts of Land Use/Land Cover Changes in the Andassa Watershed, Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1394–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woldesenbet, T.A.; Elagib, N.A.; Ribbe, L.; Heinrich, J. Hydrological Responses to Land Use/Cover Changes in the Source Region of the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 724–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabiri, G.; Leemhuis, C.; Diekkrüger, B.; Näschen, K.; Steinbach, S.; Thonfeld, F. Modelling the Impact of Land Use Management on Water Resources in a Tropical Inland Valley Catchment of Central Uganda, East Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 1052–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, H.; Lemma, B.; Gebremariam, E. Identifying Sustainability Challenges on Land and Water Uses: The Case of Lake Ziway Watershed, Ethiopia. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 88, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gathagu, J.N.; Mourad, K.A.; Sang, J. Effectiveness of Contour Farming and Filter Strips on Ecosystem Services. Water 2018, 10, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wambura, F.J.; Dietrich, O.; Graef, F. Analysis of Infield Rainwater Harvesting and Land Use Change Impacts on the Hydrologic Cycle in the Wami River Basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 203, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welderufael, W.A.; Woyessa, Y.E.; Edossa, D.C. Impact of Rainwater Harvesting on Water Resources of the Modder River Basin, Central Region of South Africa. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 116, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dile, Y.T.; Karlberg, L.; Daggupati, P.; Srinivasan, R.; Wiberg, D.; Rockström, J. Assessing the Implications of Water Harvesting Intensification on Upstream-Downstream Ecosystem Services: A Case Study in the Lake Tana Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.; Zehnder, A.; Jewitt, G.; Yang, H. Water Availability, Demand and Reliability of In Situ Water Harvesting in Smallholder Rain-Fed Agriculture in the Thukela River Basin, South Africa. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, H.; You, L.; Wielgosz, B.; Ringler, C. Estimating the Potential for Expanding Smallholder Irrigation in Sub-Saharan Africa. Agric. Water Manag. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, H.; Lemma, B. SWAT Based Hydrological Assessment and Characterization of Lake Ziway Sub-Watersheds, Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 13, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossa, A.Y.; Diekkrüger, B.; Giertz, S.; Steup, G.; Sintondji, L.O.; Agbossou, E.K.; Hiepe, C. Modeling the Effects of Crop Patterns and Management Scenarios on N and P Loads to Surface Water and Groundwater in a Semi-Humid Catchment (West Africa). Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 115, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, G.T.; Teshale, E.Z.; Yu, B.; Rutherfurd, I.D.; Jeong, J. Streamflow and Sediment Yield Prediction for Watershed Prioritization in the Upper Blue Nile River Basin, Ethiopia. Water 2017, 9, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Githui, F.; Gitau, W.; Mutua, F.; Bauwens, W. Climate Change Impact on SWAT Simulated Streamflow in Western Kenya. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 1823–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingston, D.; Taylor, R. Projected Impacts of Climate Change on Groundwater and Stormflow in a Humid, Tropical Catchment in the Ugandan Upper Nile Basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2010, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, D.; Alamirew, T.; Kebede, A.; Zeleke, G.; Melesse, A.M. Modeling Climate Change Impact on the Hydrology of Keleta Watershed in the Awash River Basin, Ethiopia. Environ. Model. Assess. 2019, 24, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheer, A.; Lü, H.; Omer, A.; Ali, A.; Abdelgader, A. Impacts of Climate Change under CMIP5 RCP Scenarios on the Streamflow in the Dinder River and Ecosystem Habitats in Dinder National Park, Sudan. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2015, 12, 10157–10195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagena, M.B.; Sommerlot, A.; Abiy, A.Z.; Collick, A.S.; Langan, S.; Fuka, D.R.; Easton, Z.M. Climate Change in the Blue Nile Basin Ethiopia: Implications for Water Resources and Sediment Transport. Clim. Chang. 2016, 139, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingston, D.G.; Taylor, R.G. Sources of Uncertainty in Climate Change Impacts on River Discharge and Groundwater in a Headwater Catchment of the Upper Nile Basin, Uganda. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teklesadik, A.D.; Alemayehu, T.; van Griensven, A.; Kumar, R.; Liersch, S.; Eisner, S.; Tecklenburg, J.; Ewunte, S.; Wang, X. Inter-Model Comparison of Hydrological Impacts of Climate Change on the Upper Blue Nile Basin Using Ensemble of Hydrological Models and Global Climate Models. Clim. Chang. 2017, 141, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, T.; Lettenmaier, D.; Kabat, P. Hydrologic Impacts of Climate Change on the Nile River Basin: Implications of the 2007 IPCC Scenarios. Clim. Chang. 2006, 100, 433–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessu, S.; Melesse, A. Impact and Uncertainties of Climate Change on the Hydrology of the Mara River Basin, Kenya/Tanzania. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notter, B.; Hurni, H.; Wiesmann, U.; Ngana, J. Evaluating Watershed Service Availability under Future Management and Climate Change Scenarios in the Pangani Basin. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts ABC 2013, 61–62, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duku, C.; Zwart, S.J.; Hein, L. Impacts of Climate Change on Cropping Patterns in a Tropical, Sub-Humid Watershed. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danvi, A.; Giertz, S.; Zwart, S.J.; Diekkrüger, B. Rice Intensification in a Changing Environment: Impact on Water Availability in Inland Valley Landscapes in Benin. Water 2018, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Easton, Z.M.; Walter, M.T.; Fuka, D.R.; White, E.D.; Steenhuis, T.S. A Simple Concept for Calibrating Runoff Thresholds in Quasi-Distributed Variable Source Area Watershed Models. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 3131–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, T.; Griensven, A.v.; Woldegiorgis, B.T.; Bauwens, W. An Improved SWAT Vegetation Growth Module and Its Evaluation for Four Tropical Ecosystems. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 4449–4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wambura, F.J.; Dietrich, O.; Lischeid, G. Improving a Distributed Hydrological Model Using Evapotranspiration-Related Boundary Conditions as Additional Constraints in a Data-Scarce River Basin. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 759–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladejana, O.O.; Salami, A.T.; Adetoro, O.-I.O. Hydrological Responses to Land Degradation in the Northwest Benin Owena River Basin, Nigeria. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 225, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, E.D.; Easton, Z.M.; Fuka, D.R.; Collick, A.S.; Adgo, E.; McCartney, M.; Awulachew, S.B.; Selassie, Y.G.; Steenhuis, T.S. Development and Application of a Physically Based Landscape Water Balance in the SWAT Model. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dile, Y.; Karlberg, L.; Srinivasan, R.; Rockström, J. Investigation of the Curve Number Method for Surface Runoff Estimation In Tropical Regions. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2016, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, V.; Nigussie, T.K.; Lemann, T. Model Parameter Transfer for Streamflow and Sediment Loss Prediction with SWAT in a Tropical Watershed. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tessema, S.M.; Lyon, S.W.; Setegn, S.G.; Mörtberg, U. Effects of Different Retention Parameter Estimation Methods on the Prediction of Surface Runoff Using the SCS Curve Number Method. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 3241–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dile, Y.T.; Srinivasan, R. Evaluation of CFSR Climate Data for Hydrologic Prediction in Data-Scarce Watersheds: An Application in the Blue Nile River Basin. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 1226–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolera, M.B.; Chung, I.-M.; Chang, S.W. Evaluation of the Climate Forecast System Reanalysis Weather Data for Watershed Modeling in Upper Awash Basin, Ethiopia. Water 2018, 10, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aouissi, J.; Benabdallah, S.; Lili Chabaâne, Z.; Cudennec, C. Evaluation of Potential Evapotranspiration Assessment Methods for Hydrological Modelling with SWAT—Application in Data-Scarce Rural Tunisia. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 174, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.M.; Pricope, N.G. Increasing the Accuracy of Runoff and Streamflow Simulation in the Nzoia Basin, Western Kenya, through the Incorporation of Satellite-Derived CHIRPS Data. Water 2017, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuka, D.R.; Walter, M.T.; MacAlister, C.; Degaetano, A.T.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Easton, Z.M. Using the Climate Forecast System Reanalysis as Weather Input Data for Watershed Models. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 5613–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Tuo, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, H.; Song, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L.; Mekonnen, D.F. Hydrological Evaluation of Open-Access Precipitation and Air Temperature Datasets Using SWAT in a Poorly Gauged Basin in Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuol, J.; Abbaspour, K.C. Using Monthly Weather Statistics to Generate Daily Data in a SWAT Model Application to West Africa. Ecol. Model. 2007, 201, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitew, M.M.; Gebremichael, M.; Ghebremichael, L.T.; Bayissa, Y.A. Evaluation of High-Resolution Satellite Rainfall Products through Streamflow Simulation in a Hydrological Modeling of a Small Mountainous Watershed in Ethiopia. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaponnière, A.; Boulet, G.; Chehbouni, A.; Aresmouk, M. Understanding Hydrological Processes with Scarce Data in a Mountain Environment. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 1908–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aouissi, J.; Benabdallah, S.; Lili Chabaâne, Z.; Cudennec, C. Valuing Scarce Observation of Rainfall Variability with Flexible Semi-Distributed Hydrological Modelling—Mountainous Mediterranean Context. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moges, M.; Schmitter, P.; Tilahun, S.; Langan, S.; Dagnew, D.; Tadesse, A.; Steenhuis, T. Suitability of Watershed Models to Predict Distributed Hydrologic Response in the Awramba Watershed in Lake Tana Basin. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Griensven, A.; Popescu, I.; Abdelhamid, M.R.; Ndomba, P.M.; Beevers, L.; Betrie, G.D. Comparison of Sediment Transport Computations Using Hydrodynamic versus Hydrologic Models in the Simiyu River in Tanzania. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts ABC 2013, 61–62, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouraoui, F.; Benabdallah, S.; Jrad, A.; Bidoglio, G. Application of the SWAT Model on the Medjerda River Basin (Tunisia). Phys. Chem. Earth Parts ABC 2005, 30, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, J.J.L.; Sumner, P.D.; Lorentz, S.A.; Germishuyse, T. Connectivity Aspects in Sediment Migration Modelling Using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool. Geosciences 2013, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Näschen, K.; Diekkrüger, B.; Leemhuis, C.; Seregina, L.; van der Linden, R. Impact of Climate Change on Water Resources in the Kilombero Catchment in Tanzania. Water 2019, 11, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duku, C.; Rathjens, H.; Zwart, S.J.; Hein, L. Towards Ecosystem Accounting: A Comprehensive Approach to Modelling Multiple Hydrological Ecosystem Services. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4377–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tibebe, D.; Bewket, W. Surface Runoff and Soil Erosion Estimation Using the SWAT Model in the Keleta Watershed, Ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 22, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyeko, M. Hydrologic Modelling of Data Scarce Basin with SWAT Model: Capabilities and Limitations. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliehe, M.; Mulungu, D.M.M. Assessment of Water Availability for Competing Uses Using SWAT and WEAP in South Phuthiatsana Catchment, Lesotho. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts ABC 2017, 100, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen Liechti, T.; Matos, J.; Ferras, D.; Boillat, J.-L.; Schleiss, A. Hydrological Modelling of the Zambezi River Basin Taking into Account Floodplain Behaviour by a Modified Reservoir Approach. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2014, 12, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trambauer, P.; Maskey, S.; Winsemius, H.; Werner, M.; Uhlenbrook, S. A Review of Continental Scale Hydrological Models and Their Suitability for Drought Forecasting in (Sub-Saharan) Africa. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts ABC 2013, 66, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegegne, G.; Park, D.K.; Kim, Y.-O. Comparison of Hydrological Models for the Assessment of Water Resources in a Data-Scarce Region, the Upper Blue Nile River Basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 14, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtibaa, S.; Hotta, N.; Irie, M. Analysis of the Efficacy and Cost-Effectiveness of Best Management Practices for Controlling Sediment Yield: A Case Study of the Joumine Watershed, Tunisia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosling, S.N.; Zaherpour, J.; Mount, N.J.; Hattermann, F.F.; Dankers, R.; Arheimer, B.; Breuer, L.; Ding, J.; Haddeland, I.; Kumar, R.; et al. A Comparison of Changes in River Runoff from Multiple Global and Catchment-Scale Hydrological Models under Global Warming Scenarios of 1 °C, 2 °C and 3 °C. Clim. Chang. 2017, 141, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Salah, N.C.; Abida, H. Runoff and Sediment Yield Modeling Using SWAT Model: Case of Wadi Hatab Basin, Central Tunisia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worqlul, A.W.; Ayana, E.K.; Yen, H.; Jeong, J.; MacAlister, C.; Taylor, R.; Gerik, T.J.; Steenhuis, T.S. Evaluating Hydrologic Responses to Soil Characteristics Using SWAT Model in a Paired-Watersheds in the Upper Blue Nile Basin. CATENA 2018, 163, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, J. Applying SWAT to Predict Ortho-Phosphate Loads and Trophic Status in Four Reservoirs in the Upper Olifants Catchment, South Africa. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awotwi, A.; Yeboah, F.; Kumi, M. Assessing the Impact of Land Cover Changes on Water Balance Components of White Volta Basin in West Africa. Water Environ. J. 2015, 29, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danvi, A.; Giertz, S.; Zwart, S.J.; Diekkrüger, B. Comparing Water Quantity and Quality in Three Inland Valley Watersheds with Different Levels of Agricultural Development in Central Benin. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 192, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briak, H.; Moussadek, R.; Aboumaria, K.; Mrabet, R. Assessing Sediment Yield in Kalaya Gauged Watershed (Northern Morocco) Using GIS and SWAT Model. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2016, 4, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lweendo, M.K.; Lu, B.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Xu, W. Characterization of Droughts in Humid Subtropical Region, Upper Kafue River Basin (Southern Africa). Water 2017, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, V.; Donovan, C. Agricultural Statistics in Sub-Saharan Africa: Differences in Institutional Arrangements and Their Impacts on Agricultural Statistics Systems. A Synthesis of Four Country Case Studies; Michigan State University, Department of Agricultural Economics: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieger, K.; Arnold, J.G.; Rathjens, H.; White, M.J.; Bosch, D.D.; Allen, P.M.; Volk, M.; Srinivasan, R. Introduction to SWAT+, A Completely Restructured Version of the Soil and Water Assessment Tool. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 53, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs. World Population Prospects Highlights, 2019 Revision Highlights, 2019 Revision; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-92-1-148316-1. [Google Scholar]
- Agriculture Food and Nutrition for Africa—A Resource Book for Teachers of Agriculture. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/w0078e/w0078e00.htm#TopOfPage (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- Research Institute (IFPRI). East African Agriculture and Climate Change a Comprehensive Analysis; International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schuol, J.; Abbaspour, K.C.; Yang, H.; Srinivasan, R.; Zehnder, A.J.B. Modeling Blue and Green Water Availability in Africa. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, S.J.; Palace, M.W.; Hartter, J.; Diem, J.E.; Chapman, C.A.; Southworth, J. Population pressure and global markets drive a decade of forest cover change in Africa’s Albertine Rift. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 81, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akoko, G.; Le, T.H.; Gomi, T.; Kato, T. A Review of SWAT Model Application in Africa. Water 2021, 13, 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091313
Akoko G, Le TH, Gomi T, Kato T. A Review of SWAT Model Application in Africa. Water. 2021; 13(9):1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091313
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkoko, George, Tu Hoang Le, Takashi Gomi, and Tasuku Kato. 2021. "A Review of SWAT Model Application in Africa" Water 13, no. 9: 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091313
APA StyleAkoko, G., Le, T. H., Gomi, T., & Kato, T. (2021). A Review of SWAT Model Application in Africa. Water, 13(9), 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13091313