Degradation of 2-Naphthol in Aqueous Solution by Electro-Fenton System with Cu-Supported Stainless Steel Electrode
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Reagents and Materials
2.2. Experimental Apparatus
2.3. Reaction Device
2.4. Preparation of Modified Electrode
2.5. Methods of Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Electrode
3.2. The Influence of Various Factors on 2-Naphthol Degradation
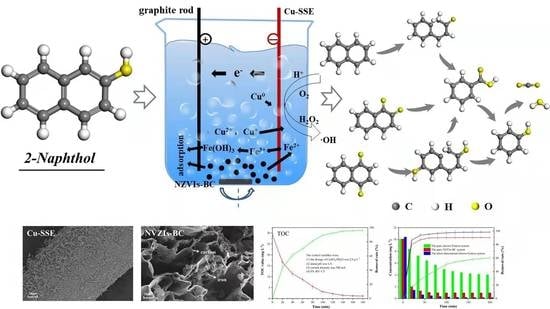
3.3. The Degradation Pathway of 2-Naphthol
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- SEM-EDS and XPS test results show that a dense copper coating was formed on the stainless steel surface by the PED process.
- (2)
- CV and EIS test results show that copper modification helps to improve the electrochemical performance of stainless steel electrodes.
- (3)
- NZVIs-BC was prepared by the impregnation-pyrolysis method, giving it a larger specific surface area and a higher pHpzc. The specific surface area of the NZVIs-BC was 218.4 m2 g−1. The pHpzc of the NZVIs-BC was about 10.50, which helped to adsorb weakly acidic 2-naphthol.
- (4)
- NZVIs-BC could act synergistically with the EF system, thereby improving the removal rate of 2-naphthol in aqueous solution.
- (5)
- Under certain conditions (a ratio of FS to RS of 1:5, a dosage of CuSO4•5H2O of 2.0 g L−1, an initial pH of 2-naphthol wastewater of 6.5, and a current intensity of 300 mA), the removal rate of 2-naphthol could reach 93.82% within 40 min, the removal rate of TOC could reach 96.05% within 200 min, which indicated that the 2-naphthol was well mineralized by the 3D-EF system.
- (6)
- Naphthalene, benzoic acid, 1, 2-naphthalenedione, β-naphthoquinone, phenol, aromatic hydrocarbon were the main degradation products of 2-naphthol, the toxicity of 2-naphthol wastewater had also been reduced.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAS | Atomic absorption spectroscopy |
| AOPs | Advanced oxidation process |
| BET | Brunauer−Emmett−Teller, specific surface area test |
| Cu-SSE | Cu-supported stainless steel electrode |
| CV | Cyclic voltammetry |
| EDS | Energy dispersive spectrometer |
| EF | Electro-Fenton |
| EIS | Electrochemica l impedance spectroscopy |
| EPD | Electrophoretic deposition |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
| FS | FeSO4•5H2O |
| GEP | Galvanostatic electro-deposition |
| LC-MS | Liquid chromatography−mass spectrometry |
| NZVIs | Nano zero-valent iron |
| NZVIs-BC | Nano zero-valent iron-supported biochar |
| PAHs | Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| PED | Potentiostatic electro-deposition |
| pHpzc | Point of zero charges |
| POPs | Persistent organic pollutants |
| ROPs | Refractory organic pollutants |
| RS | Rice straw |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| SSWM | Stainless steel wire mesh |
| TOC | Total organic carbon |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| 3D-EF | Three-dimensional electro-Fenton |
References
- Wang, X.; Chen, Q. Influencing factors of 2-naphthol degradation in water by biofilm-electrode method. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2017, 38, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, N.; Huynh, N.; Le, M.; Vo, K.; Vo, D. Fabrication of Ag-photodeposited TiO2/cordierite honeycomb monolith photoreactors for 2-naphthol degradation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 2628–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, S.; Lian, B.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y. Biodegradation of 2-naphthol and its metabolites by coupling Aspergillus niger with Bacillus subtilis. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Fang, L.; Liu, B.; Qiu, F. Adsorption properties of polystyrene divinyl benzene resin to phenol and 2-naphthol. Chin. J. Process Eng. 2015, 15, 781–787. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Wei, C.; Wu, C.; Ren, Y.; Diao, C.; Guan, Q.; Yan, B.; Peng, P.; Fu, J. Identification, property and degradation of organic compounds in coking wastewater during treatment processes. Environ. Chem. 2012, 31, 1480–1486. [Google Scholar]
- Edvinas, K.; Dainius, M.; Martynas, T.; Dalia, J.; Inga, R.; Jolanta, S.; Viktoras, R.; Jonas, B. Decomposition of 2-naphthol in water using a non-thermal plasma reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Huang, W.; Ma, Z.; Lu, Y.; Shen, X. A novel approach for removing 2-naphthol from wastewater using immobilized organo-bentonite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 252–253, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Xu, G.; Jiang, L.; Hu, X.; Xu, J.; Xie, X.; Li, A. Amphiphilic hyper-crosslinked porous cyclodextrin polymer with high specific surface area for rapid removal of organic micropollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 123015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, S.; Lian, B. Synergistic degradation of 2-naphthol by Fusarium proliferatum and Bacillus subtilis in wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, K.; Ganesh, S.; Balendu, S.; Ram, S.; Birendra, N. A novel comparative study of modified carriers in moving bed biofilm reactor for the treatment of wastewater. Process Optim. Kinet. Study. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzouk, B.; Yakoubi, M.; Zongo, I.; Leclerc, J.; Paternotte, G.; Pontvianne, S.; Lapicque, F. Effect of modification of textile wastewater composition on electrocoagulation efficiency. Desalination 2011, 275, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Lee, C.; Javed, H.; Yu, P.; Kim, J.; Alvarez, P. Easily recoverable, micrometer-sized TiO2 hierarchical spheres decorated with cyclodextrin for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of organic micropollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12402–12411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynas, T.; Edvinas, K.; Dalia, J.; Viktoras, R.; Dainius, M. Ozone-UV-catalysis based advanced oxidation process for wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 17584–17597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gu, L.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, N.; Li, C.; Tao, H.; Wen, H.; Zhang, D. Pyrolytic temperature dependent conversion of sewage sludge to carbon catalyst and their performance in persulfate degradation of 2-naphthol. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 324, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Meas, A.; Shan, S.; Yang, R.; Gai, X. Production and optimization of bamboo hydrochars for adsorption of Congo red and 2-naphthol. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 207, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enric, B.; Ignasi, S.; Mehmet, O. Electro-Fenton process and related electrochemical technologies based on Fenton’s reaction chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 6570–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bury, N.; Mumford, K.; Stevens, G. The electro-Fenton regeneration of granular activated carbons: degradation of organic contaminants and the relationship to the carbon surface. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, F.; Wen, R.; Zhang, H.; Elumalai, P.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Huang, M.; Ying, G. Heterogeneous electro-Fenton using three-dimension NZVI-BC electrodes for degradation of neonicotinoid wastewater. Water Res. 2020, 128, 115975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Ahmed, M.; Wang, H.; Jin, Y. Treatment of landfill leachate RO concentration by iron–carbon micro–electrolysis (ICME) coupled with H2O2 with emphasis on convex optimization method. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2019, 31, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Gao, Y.; Yan, D.; Xu, H.; Wang, J. Degradation characteristics of color index direct blue 15 dye using iron-carbon micro-electrolysis coupled with H2O2. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, M.; Yu, X.; Ma, L.; Yu, F. Modified iron-carbon as heterogeneous electro-Fenton catalyst for organic pollutant degradation in near neutral pH condition: Characterization, degradation activity and stability. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 160, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M. Synthesis of magnetic carbon nanotube and photocatalytic dye degradation ability. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 5595–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Ha, J.; Shin, N.; Kim, Y.; Choi, J. Self-activated anodic nanoporous stainless steel electrocatalysts with high durability for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 364, 137315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q. Electrochemical Preparation of Ni-Fe-Mo-Cu on Nickel Foamed Cathode for High-Efficiency HER. New Chem. Mater. 2019, 47, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Tan, Q.; Zhu, M.; Li, Y. Reduction of nitrobenzene wastewater by electrolysis using stainless steel brush as cathode. J. Chang. Inst. Technol. 2014, 28, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Wei, D.; Wen, J. Highly Efficient COX-free Hydrogen Production on ZIF-derived Carbon-based Ru-Co Bimetallic Catalyst. Guangzhou Chem. Ind. 2021, 49, 38–42, 129. [Google Scholar]
- Call, D.; Merrill, M.; Logan, B. High surface area stainless steel brushes as cathodes in microbial electrolysis cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2179–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Qiu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Deng, F.; Ma, F. Utilization of response surface modeling to optimize hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radicals generation by electro-Fenton with copper-foam as cathode. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2018, 12, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, L. Treatment of wastewater containing high-concentration dimethyl phthalate by Fenton oxidation under Cu2+ catalysis. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2014, 8, 2789–2794. [Google Scholar]
- Andre, A.; Andre, F. Fe3+ and Cu2+ reduction by phenol derivatives associated with Azure B degradation in Fenton-like reactions. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Das, D.; Mitra, A.; Jena, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Majumder, S. Electrophoretic deposition of ZnFe2O4-carbonaceous composites as promising anode for lithium-ion batteries. Mater. Lett. 2021, 301, 130265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lian, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; He, Z.; Gu, Z. Potentiostatic electrodeposition of self-supported NiS electrocatalyst supported on Ni foam for efficient hydrogen evolution. Mater. Des. 2020, 198, 109316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroslav, M.; Peter, O.; Filip, C.; Patrik, N.; Milan, P.; Ivan, N.; Vlastimil, R.; Juraj, B.; Andrej, V.; Ivan, H. Potentiostatic electrodeposition under light irradiation for preparation of highly photoactive Cu2O for water splitting applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 461, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, K.; Torane, A. Electrodeposition and characterization of pH transformed Cu2O thin films for electrochemical sensor. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Tai, C.; Zou, H.; Guo, Q. A new fluorimetric method for the determination of hydroxyl radical and the scavenging ability of some scavengers. J. Anal. Sci. 2002, 6, 460–462. [Google Scholar]
- Özcan, A.; Şahin, Y.; Koparal, A.; Oturan, M. Carbon sponge as a new cathode material for the electro-Fenton process: Comparison with carbon felt cathode and application to degradation of synthetic dye basic blue 3 in aqueous medium. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2008, 616, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticelli, C.; Fonsati, M.; Meszaros, G.; Trabanelli, G. Copper corrosion in industrial waters-a multimethod analysis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 146, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Yang, C.; Jiang, X.; Dang, Z.; Li, Y. Adsorption and desorption of Cd(II) on amino biochar modified by nano zero valent iron. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 10, 5433–5439. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. Evolution characteristics of micropore and mesopore of different rank coal and cause of their formation. Coal Geol. Explor. 2017, 45, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, X.; Mei, C.; He, L.; He, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wang, C. On the synthesis, characterization and phosphate removal of the biocharbased magnetic composites. J. Saf. Environ. 2017, 17, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, J. Key factors for optimum performance in phosphate removal from contaminated water by a Fe-Mg-La tri-metal composite sorbent. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 445, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Duan, Z.; Qin, R.; Xu, X.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Zhan, F.; He, Y. Enhanced characteristics and mechanism of Cu(II) removal from aqueous solutions in electrocatalytic internal micro-electrolysis fluidized-bed. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, S.; Xu, G.; Wu, Z. Analysis and measures of campaction and passivation in iron carbon micro electrolysis process. China Dye. Finish. 2017, 43, 43–46. [Google Scholar]











| Index | Values |
|---|---|
| Resistivity (μΩ m) | 9.00 |
| Bulk density (g cm−3) | 1.85 |
| Compressive strength (MPa) | 80.27 |
| Ash (‱) | 8.00 |
| Bending strength (MPa) | 43.00 |
| True density (g cm−3) | 2.16 |
| Shore hardness | 47.60 |
| Index | Values |
|---|---|
| Wire diameter (mm) | 23.0 |
| Bulk density (Kg m−3) | 150.0 |
| Specific surface area (m2 m−3) | 320.0 |
| Void fraction (%) | 98.1 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 743.0 |
| Elongation (%) | 43.0 |
| C (‱) | 6.0 |
| Si (‱) | 37.0 |
| Mn (‰) | 10.2 |
| P (‱) | 3.7 |
| S (‱) | 0.8 |
| Cr (%) | 17.2 |
| Ni (‰) | 80.7 |
| Cu (‱) | 21.0 |
| Index | Surface Area (m² g−1) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | Pore Volume (cc g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 218.400 | 3.689 | 0.201 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S.; Shi, L. Degradation of 2-Naphthol in Aqueous Solution by Electro-Fenton System with Cu-Supported Stainless Steel Electrode. Water 2022, 14, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071007
Cheng X, Zhang X, Zhou S, Shi L. Degradation of 2-Naphthol in Aqueous Solution by Electro-Fenton System with Cu-Supported Stainless Steel Electrode. Water. 2022; 14(7):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071007
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Xudong, Xiaoping Zhang, Shaoqi Zhou, and Lin Shi. 2022. "Degradation of 2-Naphthol in Aqueous Solution by Electro-Fenton System with Cu-Supported Stainless Steel Electrode" Water 14, no. 7: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071007
APA StyleCheng, X., Zhang, X., Zhou, S., & Shi, L. (2022). Degradation of 2-Naphthol in Aqueous Solution by Electro-Fenton System with Cu-Supported Stainless Steel Electrode. Water, 14(7), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071007