Benefits, Inconveniences, and Facilities of the Application of Rain Gardens in Urban Spaces from the Perspective of Climate Change—A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Climate Change Effects, Prediction and Climate Models
1.2. Climate Change Effects, Mitigation and the Aim of the Work
2. Rain Gardens: Definitions and Nomenclature; Classification: Similarities and Differences
2.1. Definitions and Nomenclature
2.2. Classification of Rain Gardens
3. Benefits of Using Rain Gardens
3.1. A Holistic Approach to the Issue
3.2. Participation in Rainwater Management
3.3. Economic Issues
3.4. Role in Water Protection
3.5. Benefits for the Ecosystem and Biodiversity
3.6. Rain Gardens as Multifunctional Solutions—Benefits for Society
3.7. Other Benefits
4. Inconveniences in the Application of Rain Gardens
4.1. Adopted Assumptions
4.2. Land Area Demand
4.3. Limitations of Use
4.4. Possible Problems at the Design and Construction Stage
4.5. Economic Issues
4.6. Maintenance of Rain Gardens
4.7. Social Problems
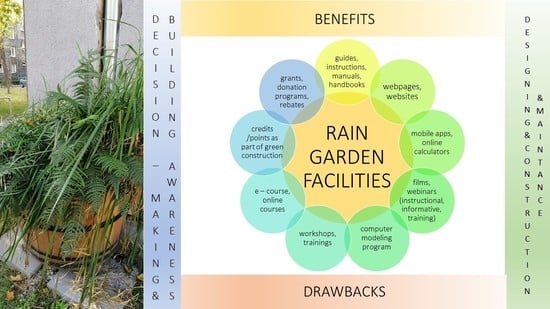
5. Facilities for the Application of Rain Gardens
5.1. Definition and Classification of Facilities
- Computer programs (including mobile applications);
- Special guides, manuals, and instructions;
- Workshops and training;
- Videos and webinars (instructional, training, informative);
- Websites and web pages;
- E-courses, online courses;
- Co-financing programs and rebates (etc.) solutions.
5.2. Computer Programs and Other Tools
5.2.1. Specialized Solutions
5.2.2. Solutions for Ordinary Users (Non-Specialists)
5.3. Internet Resources
5.4. Workshops, Subsidies, and Other Programs and Actions
5.5. Multi-Criteria Building Assessment Systems
6. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: https://cordex.org/about/what-is-regional-downscaling (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Available online: https://klimada2.ios.gov.pl/metodyka-opracowania-projekcji-klimatycznych (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Available online: https://euro-cordex.net/060374/index.php.en (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Available online: https://euro-cordex.net/060378/index.php.en (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Team Work, Plan Adaptacji Miasta Krakowa do Zmian Klimatu do Roku 2030. Available online: https://www.bip.krakow.pl (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Available online: https://www.wody.gov.pl/aktualnosci/1991-aktualna-sytuacja-hydrologiczno-meteorologiczna (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Available online: https://twitter.com/IMGWmeteo/status/1423701727497359364 (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Morash, J.; Wright, A.; LeBleu, C.; Meder, A.; Kessler, R.; Brantley, E.; Howe, J. Increasing sustainability of residential areas using rain gardens to improve pollutant capture, biodiversity and ecosystem resilience. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Available online: https://www.epa.gov/soakuptherain/soak-rain-rain-gardens (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Available online: https://www.susdrain.org/delivering-suds/using-suds/suds-components/infiltration/rain-gardens.html (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Raingardens–Factsheet 2014, Natural Resources Conservation Service–Caribbean Area, United States Department of Agriculture, NRCS USDA. 2014. Available online: www.nrcs.usda.gov (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Available online: https://www.epa.gov/green-infrastructure/what-green-infrastructure#raingardens (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Available online: https://www.teraz-srodowisko.pl/slownik-ochrona-srodowiska/definicja/ogrod-deszczowy.html (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Available online: https://www.groundwater.org/action/home/raingardens.html (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Wojciechowska, E.; Gajewska, M.; Żurkowska, N.; Surówka, M.; Obarska–Pempkowiak, H. Zrównoważone Systemy Gospodarowania Wodą Deszczową; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Gdańskiej: Gdańsk, Poland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shafique, M.; Kim, R. Retrofitting the Low Impact Development practices into developed urban areas including barriers and potential solution. Open Geosci. 2017, 9, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Ye, Z.; Shibata, S. Assessment of rain garden effects for the management of urban storm runoff in Japan. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burszta–Adamiak, E. Wybrane Zagadnienia Związane z Projektowaniem i Eksploatacją Systemów Alternatywnych; Wody opadowe a zjawiska ekstremalne; Łomotowski, J., Ed.; Wydawnictwo Seidel-Przywecki: Józefosław, Poland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Królikowska, J.; Królikowski, A. Wody Opadowe. Odprowadzanie, Zagospodarowanie, Podczyszczanie i Wykorzystanie; Wydawnictwo Seidel–Przywecki Sp. z o.o.: Józefosław, Poland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Secino, B.J.; Merchant, B.P.; Marsan, C.B.; Racine, R.K. Stormwater Runoff Reduction on the Worcester Polytechnic Institute Campus. 2018. Available online: https://digitalcommons.wpi.edu/iqp-all/5205 (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Szpakowski, W.; Rayss, J.; Lademann, D. Ogród Deszczowy w 5 Krokach; Gdańskie Wody Sp. z o.o.: Gdańsk, Poland, 2018; Available online: http://www.gdmel.pl/dla-inwestorow-gdmel/poradnik-ogrod-deszczowy-w-5-krokach (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://sendzimir.org.pl/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/broszura-ogrod-deszczowy-w-gruncie.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Kukadia, J.; Lundholm, M.; Russell, I. Designing Rain Gardens: A Practical Guide, Urban Design London. Available online: https://www.urbandesignlondon.com/documents/85/UDL_Rain_Gardens_for_web_0vwx1Ls.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Franke, T.; Adlong, M. Rainscape Project Design for Homes & Schools WaterWise Rainscape Rebate Class, 5 September 2015. Available online: https://www.austintexas.gov/sites/default/files/files/Watershed/Project-design-presentation-02-09-2017w.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- The Fact Sheet, CLASIC Tool Overview, The Water Research Foundation, April 2021. Available online: https://www.waterrf.org (accessed on 6 November 2021).
- DeBusk, K.; Wynn, T. Storm-water bioretention for runoff quality and quantity mitigation. J. Environ. Eng. 2011, 137, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.R.; Ismail, Z.; Niksokhan, M.H.; Dayarian, M.A.; Ramli, A.H.; Shirazi, S.M. A quantity–quality model to assess the effects of source control stormwater management on hydrology and water quality at the catchment scale. Water 2019, 11, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, R.; Hunt, W. Underdrain configuration to enhance bioretention exfiltration to reduce pollutant loads. J. Environ. Eng. 2011, 137, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.raingardennetwork.com/benefits-of-planting-rain-gardens (accessed on 6 November 2021).
- Austin Water, WaterWise Rainscape Rebate Residential &School. Available online: https://www.austintexas.gov/sites/default/files/files/Water/Conservation/Rebates_and_Programs/WaterWiseRainscapeRebate.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://www.wfos.krakow.pl/program-priorytetowy-moja-woda (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Godyń, I.; Grela, A.; Stajno, D.; Tokarska, P. Sustainable rainwater management concept in a housing estate with a financial feasibility assessment and motivational rainwater fee system efficiency analysis. Water 2020, 12, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siwiec, E.; Erlandsen, A.; Vennemo, H. City greening by rain gardens-costs and benefits. Environ. Prot. Nat. Resour./Ochr. Sr. I Zasobów Nat. 2018, 29, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckart, K.; McPhee, Z.; Bolisetti, T. Performance and implementation of low impact development: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 413–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, F.; Woodson, D.; LaChance, C.H.; York, C.H. Stormwater Management: Rain Gardens, The Texas A&M AgriLife Extension. 2012. Available online: https://www.ugra.org/images/pdf/TAMUraingardenManualB6247.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://nemo.uconn.edu/raingardens/index.htm (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Hathaway, J.M.; Hunt, W.F.; Jadlocki, S. Indicator bacteria removal in storm-water best management practices in Charlotte, North Carolina. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 135, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, W.F.; Smith, J.T.; Jadlocki, S.J.; Hathaway, J.M.; Eubanks, P.R. Pollutant removal and peak flow mitigation by a bioretention cell in urban Charlotte, N.C. J. Environ. Eng. 2008, 134, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beautiful, Hard Working Rain Gardens, an Outreach & Communications How-to Guide, Resource Media 2013. Available online: https://www.resource-media.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/09/Rain-Garden-Outreach-Communications-How-to-Guide-general.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Trojanowska, M. Health-promoting places: Rain gardens and sustainable water management. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 960, 022025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LEED v4 for Building Design and Construction Updated with Addenda on July 25, 2019. Available online: https://www.usgbc.org/resources/leed-v4-building-design-and-construction-current-version (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- BREEAM International New Construction 2016 Technical Manual Document Reference: SD233 Version: 2016 Issue: 2.0. Available online: https://www.breeam.com/BREEAMInt2016SchemeDocument/content/resources/output/10_pdf/a4_pdf/nc_pdf_printing/sd233_nc_int_2016_print.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://www.horstexcavating.com/news-and-blog/are-rain-gardens-a-good-solution-for-stormwater-management/ (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Rain Gardens, Absorb Water, Reduce Runoff, Prevent Flooding, United States Department of Agriculture, USDA, Natural Resources Conservation Service, NRCS. 2009. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/nrcs142p2_011366.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/null/?cid=nrcs142p2_008528 (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Rain gardens. Iowa Rain Garden. Design and Installation Manual, the Iowa Stormwater Partnership, Iowa Department of Agriculture and Land Stewardship-Division of Soil Conservation (IDALS-DSC). 2008. Available online: https://www.iowadnr.gov/portals/idnr/uploads/water/watershed/files/raingardens.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Creating Your Rain Garden. How to Do Anything, The Watershed Alliance of South-Eastern PA. Available online: https://pecpa.org/wp-content/uploads/Water-Resources-Create-Your-Rain-Garden.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Andreoletti, J.; Melvin, E.; Hulett, N.; Niles, M.; Hipes, D.; Doerner, K.; Farmer, A.; Forrer, K.; Hanna, B.; Bates, K.; et al. The Vermont Rain Garden Manual, Winooski Natural Resources Conservation District; University of Vermont Extension: Burlington, VT, USA. Available online: https://www.uvm.edu/seagrant/sites/default/files/uploads/publication/VTRainGardenManual_Full.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://www.rhs.org.uk/garden-features/rain-gardens (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Rain Gardens, A Beautiful Contribution for Cleaner Water, Chester Ridley Crum Watersheds Association, LWV, Nether Providence Township, Blue Trillium. Available online: https://www.malvern.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/crcraingardensbrochure2010.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Dietz, M.; Filchak, K. Rain Gardens, A Design Guide for Homeowners in Connecticut. In Helping to Improve Water Quality in Your Community; University of Connecticut, College of Agriculture and Natural Resources, Cooperative Extension System, CT USA. Available online: https://nemo.uconn.edu/publications/rain_garden_broch.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Hinman, C. (Principal Author), Rain Garden Handbook for Western Washington, A Guide for Design, Maintenance, and Installation, Department of Ecology State of Washington, Washington State University Extension, June 2013. Available online: https://apps.ecology.wa.gov/publications/documents/1310027.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://www.mass.gov/guides/about-dig-safe (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Cost Calculator. Available online: https://nemo.uconn.edu/raingardens/calculator.htm (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Rain Garden. Available online: https://www.malvern.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/Raingdns.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://nemo.uconn.edu/raingardens/maintenance.htm (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://www.mywatersheds.org/rain-garden-101 (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Bertolotto, C.S.; Clark, A. (Principal Authors), Rain garden and bioretention literature review: An assessment of functional parameters, BMPs and landowner perspectives, Washington State Department of Ecology Regional Stormwater Monitoring Program, February 2017. Available online: https://www.ezview.wa.gov/Portals/_1962/Documents/SAM/RainGarden-Bioretention%20Literature%20Review%202017.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Rossman, L.A. Storm Water Management Model User’s Manual Version 5.1, National Risk Management Research Laboratory, Office of Research and Development, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, EPA/600/R-14/413b Revised September 2015. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2019-02/documents/epaswmm5_1_manual_master_8-2-15.pdf (accessed on 6 November 2021).
- Available online: https://www.epa.gov/water-research/storm-water-management-model-swmm (accessed on 6 November 2021).
- Bąk, J. Modelling the relationship between LID practices and the runoff of rainwater through the example of rainfall data for Krakow. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 45, 00008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/wizards/giwiz/index.cfm (accessed on 6 November 2021).
- Available online: https://www.epa.gov/water-research/green-infrastructure-modeling-toolkit (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://gifmod.com/about (accessed on 6 November 2021).
- A Simple Model for Hydraulic Performance Model of a Rain Garden—Example 8. Available online: https://gifmod.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Example_8__Rain_Garden.pdf (accessed on 6 November 2021).
- Available online: https://gifmod.com/worked-examples (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Alikhani, J.; Nietch, C.; Jacobs, S.; Shuster, B.; Massoudieh, A. Modeling and design scenario analysis of long-term monitored bioretention system for rainfall-runoff reduction to combined sewer in Cincinnati, OH. J. Sustain. Water Built Environ. 2020, 6, 040190161–401901617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://clasic.erams.com (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://nemo.uconn.edu/tools/app/raingarden.htm (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://rgapp.nemo.uconn.edu/index.html (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Earth–Wise Guide to Rain Gardens. Keeping Water on the Land, Fact Sheet: Six Easy Steps to Build a Rain Garden. Available online: https://www.austintexas.gov/sites/default/files/files/Watershed/growgreen/factsheets/raingarden_factsheet.pdf (accessed on 6 November 2021).
- Bannerman, R.; Considine, E. A How-to Manual for Homeowners, Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources DNR Publication PUB-WT-776 2003, University of Wisconsin–Extension UWEX Publication. Available online: https://www.chicagobotanic.org/downloads/wed/WI_DNR_homeowners.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Bray, R.; Gedge, D.; Grant, G.; Leuthvilay, L. Rain Garden Guide, RESET Development. Available online: https://raingardens.info/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/UKRainGarden-Guide.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Gleason, J. Rain Gardens in Austin, 2012 Landscape Professional Training Presentation (Video). Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P794yLA5Zx4 (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://www.nativeplantsalvage.org/rain-garden-webinar (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://www.uaex.uada.edu/media-resources/news/2021/may2021/05-07-2021-Ark-rain-garden-webinar.aspx (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://tpwd.texas.gov/education/water-education/texaswatersprogram/Texaswaters specialist (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://www.citizensolution.org/online-courses (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/klimat/moja-woda-20--wez-5000-zl-i-oszczedzaj-wode (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://www.krakow.pl/aktualnosci/251098,2163,komunikat,ogrody_deszczowe_przy_budynkach_komunalnych.html?_ga=2.105735875.1728608664.1627885211-1450375323.1626697872 (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Available online: https://zbk-krakow.pl/aktualnosci_ogolne/251062,1999,komunikat,ogrody_deszczowe_przy_budynkach_komunalnych_.html (accessed on 20 November 2021).



| Benefits | Drawbacks | Facilities |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bąk, J.; Barjenbruch, M. Benefits, Inconveniences, and Facilities of the Application of Rain Gardens in Urban Spaces from the Perspective of Climate Change—A Review. Water 2022, 14, 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071153
Bąk J, Barjenbruch M. Benefits, Inconveniences, and Facilities of the Application of Rain Gardens in Urban Spaces from the Perspective of Climate Change—A Review. Water. 2022; 14(7):1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071153
Chicago/Turabian StyleBąk, Joanna, and Matthias Barjenbruch. 2022. "Benefits, Inconveniences, and Facilities of the Application of Rain Gardens in Urban Spaces from the Perspective of Climate Change—A Review" Water 14, no. 7: 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071153
APA StyleBąk, J., & Barjenbruch, M. (2022). Benefits, Inconveniences, and Facilities of the Application of Rain Gardens in Urban Spaces from the Perspective of Climate Change—A Review. Water, 14(7), 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14071153