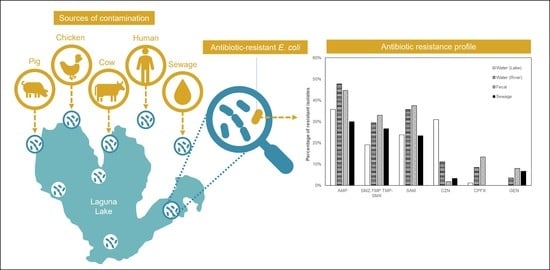
Multiple Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolates from Fecal and Water Sources in Laguna Lake, Philippines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Types and Origins of E. coli Isolates
2.3. Antibiotic Resistance Assay (ARA) Using VITEK 2®
2.4. MAR Indexing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antibiogram Profiles
3.2. MAR Index and Co-Occurence of Antibiotic Resistance
4. Discussion
4.1. High-Risk Sources of Fecal Contamination
4.2. Multidrug Resistance in E. coli
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cordero, J.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; García-Fernández, C.; Capita, R. Microbial load and antibiotic resistance patterns of Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis isolates from the meat of wild and domestic pigeons. Foods 2019, 8, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singer, A.C.; Shaw, H.; Rhodes, V.; Hart, A. Review of antimicrobial resistance in the environment and its relevance to environmental regulators. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chavoshani, A.; Hashemi, M.; Mehdi Amin, M.; Ameta, S.C. Pharmaceuticals as emerging micropollutants in aquatic environments. In Micropollutants and Challenges; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 35–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, D.; He, S.; Ye, H.; Zhang, L.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shu, L.; Chen, S. Prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli in drinking water sources in Hangzhou City. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döhla, M.; Sib, E.; Dericks, B.; Grobe, S.; Behringer, K.; Frechen, M.; Simon, K.; Färber, H.; Lenz, F.; Parcina, M.; et al. Assessment of the prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and the concentration of antibiotics in EU bathing waters in western Germany. Expo. Health 2019, 12, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance 2014; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, J.K.; Pinyon, J.L.; Anantham, S.; Hall, R.M. Commensal Escherichia coli of healthy humans: A reservoir for antibiotic-resistance determinants. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malema, M.S.; Abia, A.L.K.; Tandlich, R.; Zuma, B.; Kahinda, J.-M.M.; Ubomba-Jaswa, E. Antibiotic-resistant pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from rooftop rainwater-harvesting tanks in the Eastern Cape, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larsson, D.G.J.; Andremont, A.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Brandt, K.K.; de Roda Husman, A.M.; Fagerstedt, P.; Fick, J.; Flach, C.-F.; Gaze, W.H.; Kuroda, M.; et al. Critical knowledge gaps and research needs related to the environmental dimensions of antibiotic resistance. Environ. Int. 2018, 117, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ana, K.M.S.; Espino, M.P. Occurrence and distribution of hormones and bisphenol A in Laguna Lake, Philippines. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 127122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador-Membreve, D.M.; Rivera, W.L. Predominance of blaTEM and tetA genes in antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli isolates from Laguna Lake, Philippines. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2021, 11, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntabugi, K.M.-M.; Manegabe, B.J.; Dewar, J.B.; Simbahan, J.F.; Flavier, M.E.; Sekomo, C.B. Synergistic increase in antibiotic resistance with tolerance to cadmium and lead in environmental bacteria isolated from the San Cristobal River, Laguna De Bay, Philippines. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 78, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, P.G.; Zara, E.S.; Paraoan, C.E.M.; Dimasupil, M.A.Z.; Abello, J.J.M.; Santos, I.T.G.; Rivera, W.L. Antibiotic resistance and extended-spectrum beta-lactamase production of Escherichia coli isolated from irrigation waters in selected urban farms in Metro Manila, Philippines. Water 2018, 10, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LLDA (Laguna Lake Development Authority). LLDA Quarterly Monitoring Report: Laguna Lake and Tributary Rivers. October to December 2018. Available online: https://llda.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/dox/waterqualityrpt/2020//Updates/2020q4.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Labrador, K.L.; Nacario, M.A.G.; Malajacan, G.T.; Abello, J.J.M.; Galarion, L.H.; Rensing, C.; Rivera, W.L. Selecting rep-PCR markers to source track fecal contamination in Laguna Lake, Philippines. J. Water Health 2019, 18, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dela Peña, L.B.R.O.; Labrador, K.L.; Nacario, M.A.G.; Bolo, N.R.; Rivera, W.L. Microbial source tracking of fecal contamination in Laguna Lake, Philippines using the library-dependent method, rep-PCR. J. Water Health 2021, 19, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calayag, A.M.B.; Paclibare, P.A.P.; Santos, P.D.; Bautista, C.A.C.; Rivera, W.L. Molecular characterization and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella enterica from swine slaughtered in two different types of Philippine abattoir. Food Microbiol. 2017, 65, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, M.; Esteve, C.; Alcaide, E. Multiresistant waterborne pathogens isolated from water reservoirs and cooling systems. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrat, R.R.C.; Sorokina, M.; Andrade, B.; Goris, T.; Dávila, A.M.R. Global ocean resistome revealed: Exploring antibiotic resistance gene abundance and distribution in TARA Oceans samples. GigaScience 2020, 9, giaa046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnisz, M.; Kiedrzyńska, E.; Kiedrzyński, M.; Korzeniewska, E.; Czatzkowska, M.; Koniuszewska, I.; Jóźwik, A.; Szklarek, S.; Niestępski, S.; Zalewski, M. The impact of WWTP size and sampling season on the prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater and the river system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Guan, F.; Chen, B.; Luo, P.; Guo, C.; Wu, G.; Ye, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Fang, H. Spatial and seasonal variations of antibiotic resistance genes and antibiotics in the surface waters of Poyang Lake in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagher, L.A.; Hassan, J.; Kharroubi, S.; Jaafar, H.; Kassem, I.I. Nationwide assessment of water quality in rivers across Lebanon by quantifying fecal indicators densities and profiling antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talukdar, P.K.; Rahman, M.; Rahman, M.; Nabi, A.; Islam, Z.; Hoque, M.; Endtz, H.; Islam, M.A. Antimicrobial resistance, virulence factors and genetic diversity of Escherichia coli isolates from household water supply in Dhaka, Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Watanabe, N.; Xiao, C.; Harter, T.; McCowan, B.; Liu, Y.; Atwill, E.R. Antibiotic-resistant E. coli in surface water and groundwater in dairy operations in northern California. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 186, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, A.Q.; Verma, M.; Hsu, L.Y.; Legido-Quigley, H. An analysis of national action plans on antimicrobial resistance in Southeast Asia using a governance framework approach. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2021, 7, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swatantra, S.; Shukla, S.; Tandia, N.; Nitesh, K.; Paliwal, R. Antibiotic residues: A global challenge. Pharma Sci. Monit. 2014, 5, 184–197. [Google Scholar]
- Zellweger, R.M.; Carrique-Mas, J.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Day, N.P.J.; Thwaites, G.E.; Baker, S.; Ashley, E.; de Balogh, K.; Baird, K.; Basnyat, B.; et al. A current perspective on antimicrobial resistance in Southeast Asia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2963–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; LaPara, T.M. The effects of subtherapeutic antibiotic use in farm animals on the proliferation and persistence of antibiotic resistance among soil bacteria. ISME J. 2007, 1, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Food and Drug Administration. CVM Updates-CVM Reports on Antimicrobials Sold or Distributed for Food Producing Animals; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2010.
- Aarestrup, F. Sustainable farming: Get pigs off antibiotics. Nature 2012, 486, 465–466 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, D.A.; Zhao, S.; Tong, E.; Ayers, S.; Singh, A.; Bartholomew, M.J.; McDermott, P.F. Antimicrobial drug resistance in Escherichia coli from humans and food animals, United States, 1950–2002. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calayag, A.M.B.; Widmer, K.W.; Rivera, W.L. Antimicrobial susceptibility and frequency of bla and qnr genes in Salmonella enterica isolated from slaughtered pigs. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, L.J.; Sala-Comorera, L.; Martin, N.A.; Nolan, T.M.; Stephens, J.H.; Gitto, A.; O’Hare, G.M.; O’Sullivan, J.J.; Meijer, W.G. Correlation between antimicrobial resistance and faecal contamination in small urban streams and bathing waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 140242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, A.J.; Micalizzi, G.B.; Graham, G.M.; Bates, J.B.; Costanzo, S.D. Antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli in wastewaters, surface waters, and oysters from an urban riverine system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5667–5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Huang, L.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Mao, D.; Luo, Y. Discharge of KPC-2 genes from the WWTPs contributed to their enriched abundance in the receiving river. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sayah, R.S.; Kaneene, J.B.; Johnson, Y.; Miller, R. Patterns of antimicrobial resistance observed in Escherichia coli isolates obtained from domestic-and wild-animal fecal samples, human septage, and surface water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dela Peña, L.B.R.O.; Vejano, M.R.A.; Rivera, W.L. Molecular surveillance of Cryptosporidium spp. for microbial source tracking of fecal contamination in Laguna Lake, Philippines. J. Water Health 2021, 19, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odonkor, S.T.; Addo, K.K. Prevalence of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from drinking water sources. Int. J. Microbiol. 2018, 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Obolski, U.; Dellus-Gur, E.; Stein, G.Y.; Hadany, L. Antibiotic cross-resistance in the lab and resistance co-occurrence in the clinic: Discrepancies and implications in E. coli. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 40, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A. Plasmids and the spread of resistance. Int. J. Med Microbiol. 2013, 303, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázár, V.; Nagy, I.; Spohn, R.; Csörgő, B.; Györkei, Á.; Nyerges, A.; Horváth, B.; Vörös, A.; Busa-Fekete, R.; Hrtyan, M.; et al. Genome-wide analysis captures the determinants of the antibiotic cross-resistance interaction network. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aly, S.M.; Albutti, A. Antimicrobials use in aquaculture and their public health impact. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2014, 5, 1. [Google Scholar]



| Sample Type | Name of Site | Latitude | Longitude | E. coli Isolates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lake Stations | East Bay (LS2) | 14.267958 | 121.341787 | 28 |
| West Bay (LS5) | 14.486943 | 121.139375 | 28 | |
| South Bay (LS8) | 14.209662 | 121.239543 | 28 | |
| Tributaries | Bagumbayan River (TR1) | 14.484974 | 121.060856 | 28 |
| Mangangate River (TR2) | 14.430198 | 121.045141 | 28 | |
| Sapang Baho River (TR3) | 14.576433 | 121.099633 | 28 | |
| Tunasan River (TR4) Biñan River (TR5) | 14.385343 | 121.050977 | 28 | |
| 14.3317 | 121.085 | 28 | ||
| Pila River (TR6) | 14.2453 | 121.3554 | 28 | |
| San Cristobal River (TR7) | 14.2197 | 121.1392 | 28 | |
| Sta. Rosa River (TR8) | 14.3094 | 121.101 | 28 | |
| Fecal | Cattle | - | - | 28 |
| Poultry | - | - | 28 | |
| Swine | - | - | 28 | |
| Human | - | - | 28 | |
| Sewage | - | - | 30 | |
| Total | 450 |
| Name of Antibiotic | Resistant n (%) | Intermediate n (%) | Susceptible n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ampicillin | 178 (39.6) | 18 (4.0) | 254 (56.4) |
| Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole | 127 (28.2) | 0 | 323 (71.8) |
| Ampicillin/Sulbactam | 52 (11.5) | 97 (21.6) | 301 (66.9) |
| Cefazolin | 52 (11.6) | 2 (0.4) | 396 (88.0) |
| Ciprofloxacin | 29 (6.4) | 6 (1.3) | 415 (92.2) |
| Gentamicin | 18 (4.0) | 1 (0.2) | 431 (95.8) |
| Tobramycin | 6 (1.3) | 10 (2.2) | 434 (96.4) |
| Nitrofurantoin | 6 (1.3) | 39 (8.7) | 405 (90.0) |
| Ceftriaxone | 5 (1.1) | 1 (0.2) | 444 (98.7) |
| Aztreonam | 5 (1.1) | 0 | 445 (98.9) |
| Cefepime | 4 (0.9) | 0 | 446 (99.1) |
| Piperacillin/Tazobactam | 2 (0.4) | 3 (0.7) | 445 (98.9) |
| Ertapenem | 2 (0.4) | 0 | 448 (99.6) |
| Meropenem | 2 (0.4) | 0 | 448 (99.6) |
| Amikacin | 0 | 0 | 450 (100.0) |
| Tigecycline | 0 | 0 | 450 (100.0) |
| Number (Percentage) of Antibiotic Resistant E. coli Isolates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | AMP | SXT | SAM | CFZ | CIP | GEN |
| LS2 | 10 (35.7) | 7 (25.0) | 8 (28.6) | 6 (21.4) | 0 | 0 |
| LS5 | 11 (39.3) | 4 (14.3) | 8 (28.6) | 13 (46.4) | 0 | 0 |
| LS8 | 9 (32.1) | 5 (17.9) | 4 (14.3) | 7 (25.0) | 1 (3.6) | 0 |
| TR1 | 8 (28.6) | 5 (17.9) | 7 (25.0) | 0 | 1 (3.6) | 0 |
| TR2 | 11 (39.3) | 6 (21.4) | 7 (25.0) | 3 (10.7) | 2 (7.1) | 1 (3.6) |
| TR3 | 10 (35.7) | 8 (28.6) | 10 (35.7) | 3 (10.7) | 8 (28.6) | 2 (7.1) |
| TR4 | 11 (39.3) | 4 (14.3) | 8 (28.6) | 3 (10.7) | 2 (7.1) | 0 |
| TR5 | 19 (67.9) | 8 (28.6) | 11 (39.3) | 8 (28.6) | 3 (10.7) | 1 (3.6) |
| TR6 | 20 (71.4) | 14 (50.0) | 13 (46.4) | 6 (21.4) | 0 | 2 (7.1) |
| TR7 | 15 (53.6) | 10 (35.7) | 13 (46.4) | 1 (3.6) | 2 (7.1) | 2 (7.1) |
| TR8 | 13 (46.4) | 11 (39.3) | 11 (39.3) | 1 (3.6) | 1 (3.6) | 0 |
| Total | 137 (44.5) | 82 (26.6) | 100 (32.5) | 51 (16.5) | 20 (6.5) | 8 (2.6) |
| Number (Percentage) of Antibiotic Resistant E. coli Isolates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fecal Source | AMP | SXT | SAM | CFZ | CIP | GEN |
| Chicken | 19 (67.9) | 19 (67.9) | 16 (57.1) | 0 | 12 (42.9) | 3 (10.7) |
| Cow | 9 (32.1) | 6 (21.4) | 9 (32.1) | 0 | 0 | 2 (7.1) |
| Pig | 12 (42.9) | 10 (35.7) | 11 (39.3) | 0 | 1 (3.6) | 2 (7.1) |
| Human | 10 (35.7) | 2 (7.1) | 6 (21.4) | 2 (7.1) | 2 (7.1) | 2 (7.1) |
| Sewage | 9 (30) | 8 (26.7) | 7 (23.3) | 1 (3.3) | 0 | 2 (6.7) |
| Total | 59 (41.5) | 45 (31.7) | 49 (34.5) | 3 (2.1) | 15 (10.6) | 11 (7.7) |
| Antibiotic | β-Lactams | Non-β-Lactams | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penicillin | Cephalo- Sporin | Mono- Bactam | Aminoglycoside | Fluoroqui- Nolone | Others | ||||||
| AMP | SAM | TZP | CFZ | CRO | ATM | GEN | TOB | CIP | NIT | SXT | |
| AMP | |||||||||||
| SAM | *** | ||||||||||
| TZP | - | - | |||||||||
| CFZ | *** | - | - | ||||||||
| CRO | - | - | - | *** | |||||||
| ATM | - | - | - | *** | *** | ||||||
| GEN | *** | *** | - | - | - | - | |||||
| TOB | *** | *** | - | - | - | - | *** | ||||
| CIP | ** | *** | - | - | - | - | *** | *** | |||
| NIT | *** | *** | - | *** | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| TMP | *** | *** | - | - | - | - | *** | *** | *** | - | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
dela Peña, L.B.R.O.; Nacario, M.A.G.; Bolo, N.R.; Rivera, W.L. Multiple Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolates from Fecal and Water Sources in Laguna Lake, Philippines. Water 2022, 14, 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14091517
dela Peña LBRO, Nacario MAG, Bolo NR, Rivera WL. Multiple Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolates from Fecal and Water Sources in Laguna Lake, Philippines. Water. 2022; 14(9):1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14091517
Chicago/Turabian Styledela Peña, Laurice Beatrice Raphaelle O., Mae Ashley G. Nacario, Nicole R. Bolo, and Windell L. Rivera. 2022. "Multiple Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolates from Fecal and Water Sources in Laguna Lake, Philippines" Water 14, no. 9: 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14091517
APA Styledela Peña, L. B. R. O., Nacario, M. A. G., Bolo, N. R., & Rivera, W. L. (2022). Multiple Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolates from Fecal and Water Sources in Laguna Lake, Philippines. Water, 14(9), 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14091517