New Insight into the Mechanism for the Removal of Methylene Blue by Hydrotalcite-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of nZVI@H
2.3. Materials Characterization
2.4. Batch Experiments
2.5. Isothermal Equation
- The Langmuir model represents a monolayer adsorption equilibrium on the surface of a homogeneous medium and can be described in linearized form by Equation (3):
- 2.
- The Freundlich model describes multilayer adsorption processes on material interfaces. The linearized form of the Freundlich model can be described by Equation (4) [26]:
2.6. Adsorption Kinetics
2.7. nZVI@H Reusability and Stability Study
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Investigation of the Properties of nZVI@H
3.2. Removal of MB
4. Analysis of Factors
4.1. Effect of pH
4.2. Effect of Initial Concentration
4.3. Effect of Dosage
4.4. Effect of Temperature
4.5. Isothermal Equation Analysis
4.6. Adsorption Kinetic Analysis
4.7. Reusability and Stability of nZVI@H
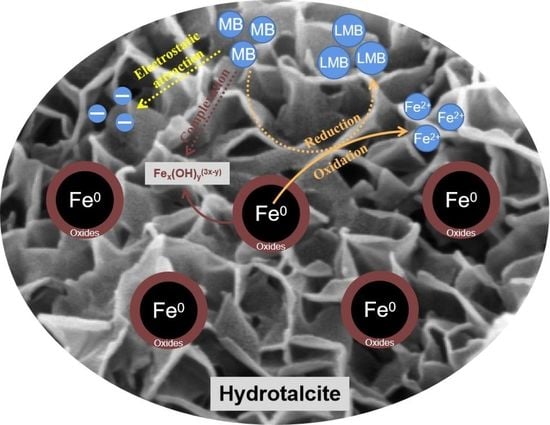
4.8. MB Removal Mechanisms
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Approval
References
- Li, H.; Budarin, V.L.; Clark, J.H.; North, M.; Wu, X. Rapid and efficient adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution by hierarchically porous, activated starbons®: Mechanism and porosity dependence. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Li, M.; Yu, M.; Huang, J.; Xu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Song, P.; Xu, R. A novel approach for methylene blue removal by calcium dodecyl sulfate enhanced precipitation and microbial flocculant GA1 flocculation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, M.; Özdemir, Y.; Alkan, M. Adsorption kinetics and mechanism of cationic methyl violet and methylene blue dyes onto sepiolite. Dyes Pigments 2007, 75, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadillah, G.; Saleh, T.A.; Wahyuningsih, S.; Putri, E.; Febrianastuti, S. Electrochemical removal of methylene blue using alginate-modified graphene adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashkoor, F.; Nasar, A. Magsorbents: Potential candidates in wastewater treatment technology–A review on the removal of methylene blue dye. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 500, 166408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniuk, M.; Oleszczuk, P.; Ok, Y.S. Review on nano zerovalent iron (nZVI): From synthesis to environmental applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Liu, R.; Wu, H.; Liu, Z.; Sun, X.; Tao, C. Adsorption of methylene blue on modified electrolytic manganese residue: Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and mechanism analysis. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 82, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhadria, N.; Hachemaoui, M.; Zaoui, F.; Mokhtar, A.; Boukreris, S.; Attar, T.; Belarbi, L.; Boukoussa, B. Catalytic Reduction of Methylene Blue Dye by Copper Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Cluster Sci. 2021, 33, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Wu, Y. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange by Fe2O3−Fe3O4 Nanoparticles and Fe2O3−Fe3O4−Montmorillonite Nanocomposites. Clean-Soil Air Water 2017, 45, 1600472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koya, A.N.; Zhu, X.; Ohannesian, N.; Yanik, A.A.; Alabastri, A.; Proietti Zaccaria, R.; Krahne, R.; Shih, W.; Garoli, D. Nanoporous Metals: From Plasmonic Properties to Applications in Enhanced Spectroscopy and Photocatalysis. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 6038–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi-Khosroshahi, H.; Edalati, K.; Wu, J.; Nakashima, Y.; Arita, M.; Ikoma, Y.; Sadakiyo, M.; Inagaki, Y.; Staykov, A.T.; Yamauchi, M.; et al. High-pressure zinc oxide phase as visible-light-active photocatalyst with narrow band gap. J. Mater. Chem. 2017, 5, 20298–20303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, E.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Mehrani, Z.; Asgharinezhad, A.A. The efficient removal of methylene blue from water samples using three-dimensional poly (vinyl alcohol)/starch nanofiber membrane as a green nanosorbent. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 35071–35081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Benjwal, P.; Singh, M.; Kar, K.K. Graphene oxide (rGO)-metal oxide (TiO2 /Fe3O4) based nanocomposites for the removal of methylene blue. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 439, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, P.; Chen, J.; Zhang, R.; Huang, J.; Xu, W.; Xiao, S. Immobilization of nZVI particles on cotton fibers for rapid decolorization of organic dyes. Cellulose 2021, 28, 7925–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Hassan, A.K.; Hamad, A.H.; Shther, D.E. Treatment of Contaminated Water with Industrial Dyes by Using Nano Zero Valent Iron (NZVI) and Supported on Pillared Clay. Adv. Anal. Chem. 2019, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, P.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z. Removal of high concentration p-nitrophenol in aqueous solution by zero valent iron with ultrasonic irradiation (US-ZVI). J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution using bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 363, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messele, S.A.; Soares, O.S.; Órfão, J.J.; Bengoa, C.; Stüber, F.; Fortuny, A.; Fabregat, A.; Font, J. Effect of activated carbon surface chemistry on the activity of ZVI/AC catalysts for Fenton-like oxidation of phenol. Catal. Today 2015, 240, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, S.; Lei, H.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W. Enhanced separation of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) using polyacrylamide: Performance, characterization and implication. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zheng, X. Enhanced removal of pentachlorophenol by a novel composite: Nanoscale zero valent iron immobilized on organobentonite. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3744–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, P.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Wen, T.; Jehan, R.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Recent advances in layered double hydroxide-based nanomaterials for the removal of radionuclides from aqueous solution. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Fan, Q.; Pan, D.; Li, J.; Chi, F.; Xie, Y.; Yu, S.; Xiao, C.; et al. Synthesis of novel nanomaterials and their application in efficient removal of radionuclides. Sci. China Chem. 2019, 62, 933–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanjit, S.; Kashihara, M.; Nakayama, A.; Shrestha, L.K.; Ariga, K.; Namba, K. Highly active and reusable hydrotalcite-supported Pd(0) catalyst for Suzuki coupling reactions of aryl bromides and chlrides. Tetrahedron 2017, 74, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, A.; Mostafa, M.K.; Nasr, M. Regression analysis and artificial intelligence for removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using nanoscale zero-valent iron. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 16, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Liang, J.; Xue, Y. Ultrasound-assisted electrodeposition synthesis of nZVI-Pd/AC toward reductive degradation of methylene blue. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 67098–67107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, S.; Sohrabi, M.R. Removal of methylene blue, a basic dye, from aqueous solutions using nano-zerovalent iron. Water Sci. Technol. A J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2014, 70, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarekegn, M.M.; Balakrishnan, R.M.; Hiruy, A.M.; Dekebo, A.H. Removal of methylene blue dye using nano zerovalent iron, nanoclay and iron impregnated nanoclay–A comparative study. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 30109–30131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tang, J.; Tang, J.; Li, X. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by sewage sludge-derived biochar: Adsorption kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalvaç, G.M.; Bayrak, B. Use of natural and effective mandarin peel in the elimination of malachite green from the aqueous media: Adsorption properties, kinetics and thermodynamics. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 177, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, G.; Bayrak, B. The synthesis of biochar-supported nano zero-valent iron composite and its adsorption performance in removal of malachite green. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2021, 12, 4785–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somsesta, N.; Sricharoenchaikul, V.; Aht-Ong, D. Adsorption removal of methylene blue onto activated carbon/cellulose biocomposite films: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 240, 122221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temel, F.; Turkyilmaz, M.; Kucukcongar, S. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by silica gel supported calix[4]arene cage: Investigation of adsorption properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 125, 109540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.M.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, Y.Y. Preparation and characterization of NZVI–MCM-48 mesoporous molecular sieves and its mechanism for treatment of methylene blue wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 52, 4520–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfatah, A.M.; Fawzy, M.; Eltaweil, A.S.; El-Khouly, M.E. Green Synthesis of Nano-Zero-Valent Iron Using Ricinus Communis Seeds Extract: Characterization and Application in the Treatment of Methylene Blue-Polluted Water. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 25397–25411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aoh, H.A.; Mihaina, I.A.; Alsharif, M.A.; Darwish, A.A.; Rashad, M.M.; Mustafa, S.K.; Aljohani, M.M.; Al-Duais, M.A.; Alshehri, H. Removal of methylene blue from synthetic wastewater by the selected metallic oxides nanoparticles adsorbent: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2020, 207, 1719–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; López-Valdivieso, A.; Zhang, T.; Mwamulima, T.; Zhang, X.; Song, S.; Peng, C. Preparation of microscale zero-valent iron-fly ash-bentonite composite and evaluation of its adsorption performance of crystal violet and methylene blue dyes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 20050–20062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang, M.; Gao, B.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H. Synthesis, characterization, and dye sorption ability of carbon nanotube–biochar nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robati, D.; Mirza, B.; Ghazisaeidi, R.; Rajabi, M.; Moradi, O.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V. Adsorption behavior of methylene blue dye on nanocomposite multi-walled carbon nanotube functionalized thiol (MWCNT-SH) as new adsorbent. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 216, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albadarin, A.B.; Collins, M.N.; Naushad, M.; Shirazian, S.; Walker, G.; Mangwandi, C. Activated lignin-chitosan extruded blends for efficient adsorption of methylene blue. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, W. Effect of a magnetic field on the adsorptive removal of methylene blue onto wheat straw biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 206, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Kurokawa, T.; Suzuki, M.; Takagi, M.; Kawase, Y. Removal of cationic dye methylene blue by zero-valent iron: Effects of pH and dissolved oxygen on removal mechanisms. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2015, 50, 1057–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Sample | Hydrotalcite | nZVI | nZVI@H |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface area m2·g−1 | 31.2 | 11.6 | 28.7 |
| T (°C) | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax (mg·g−1) | B (L·mg−1) | R2 | Kf ((mg·g−1)/(L·mg−1)1/n) | n−1 (mg·L−1) | R2 | |
| 20 | 79.897 | 2.638 | 0.9914 | 73.394 | 0.0552 | 0.7543 |
| 40 | 80.189 | 6.313 | 0.9960 | 74.290 | 0.0416 | 0.7607 |
| 60 | 81.024 | 20.985 | 0.9988 | 75.872 | 0.0273 | 0.8145 |
| CMB (mg·L−1) | Qe,exp (mg·g−1) | Quasi First-Order Kinetics Equation | Quasi Second-Order Kinetics Equation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe,cal (mg·g−1) | k1 (min−1) | R2 | Qe,cal (mg·g−1) | k2 (g·mg−1·min−1) | R2 | ||
| 40 | 79.7 | 43.1 | 0.172 | 0.937 | 79.4 | 0.097 | 0.986 |
| 100 | 191.0 | 121.1 | 0.185 | 0.959 | 190.8 | 0.035 | 0.988 |
| 200 | 368.8 | 250.9 | 0.188 | 0.962 | 369.1 | 0.019 | 0.991 |
| Diffusion Model | Main Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| kd(mg·(g·min1/2)−1) | C (mg·g−1) | R2 | |
| Boundary layer diffusion | 42.79 | 1.20 | 0.973 |
| Intraparticle diffusion | 3.48 | 59.01 | 0.917 |
| Adsorption equilibrium | 0.69 | 73.92 | 0.976 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, B.; Shen, W.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, F. New Insight into the Mechanism for the Removal of Methylene Blue by Hydrotalcite-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron. Water 2023, 15, 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15010183
Fan J, Zhang B, Zhu B, Shen W, Chen Y, Zeng F. New Insight into the Mechanism for the Removal of Methylene Blue by Hydrotalcite-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron. Water. 2023; 15(1):183. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15010183
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Jiaqi, Bo Zhang, Bohong Zhu, Weili Shen, Yuan Chen, and Fanjun Zeng. 2023. "New Insight into the Mechanism for the Removal of Methylene Blue by Hydrotalcite-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron" Water 15, no. 1: 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15010183
APA StyleFan, J., Zhang, B., Zhu, B., Shen, W., Chen, Y., & Zeng, F. (2023). New Insight into the Mechanism for the Removal of Methylene Blue by Hydrotalcite-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron. Water, 15(1), 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15010183