Denitrification Assays for Testing Effects of Xenobiotics on Aquatic Denitrification and Their Degradation in Aquatic Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
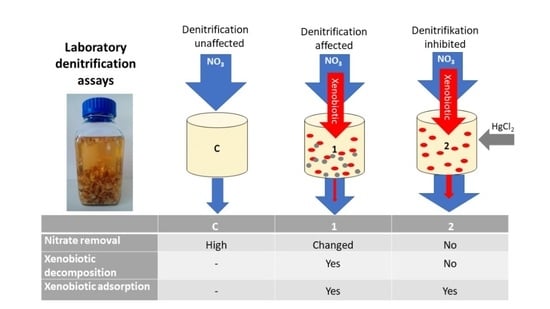
2.1. Design of the Laboratory Denitrification Assays
2.2. Procedure
- (1)
- Initial NO3-N concentrations (pre-test, 20–40 mg L−1; test, 15 and 30 mg L−1) (test conditions: 12.5 g L−1 wood shavings, 10–15 mm fraction, and 0.5 g L−1 NaHCO3);
- (2)
- Concentrations of poplar wood shavings (7.5, 12.5, and 25 g L−1) (test conditions: 10–15 mm fraction, 0.5 g L−1 NaHCO3, and 15 mg L−1 NO3-N);
- (3)
- Fraction of wood shavings (0.5–1.0 cm and 1.0–1.5 cm) (test conditions: 12.5 g L−1 wood shavings, 0.5 g L−1 NaHCO3, and 15 mg L−1 NO3-N);
- (4)
- Concentrations of NaHCO3 (0, 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 g L−1) (test conditions: 12.5 g L−1 wood shavings, 10–15 mm fraction, and 15 mg L−1 NO3-N).
2.3. Validation of Tests with Metolachlor
2.4. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of the SBA and LSA Optimization
3.2. Validation of the Methodology by Testing the Effects of Metolachlor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pina-Ochoa, E.; Alvarez-Cobelas, M. Denitrification in Aquatic Environments: A Cross-System Analysis. Biogeochemistry 2006, 81, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, P.J.; Helton, A.M.; Poole, G.C.; Hall, R.O.; Hamilton, S.K.; Peterson, B.J.; Tank, J.L.; Ashkenas, L.R.; Cooper, L.W.; Dahm, C.N.; et al. Stream Denitrification across Biomes and Its Response to Anthropogenic Nitrate Loading. Nature 2008, 452, 202-U46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, S.E.G.; Mulholland, P.J.; Hamilton, S.K.; Tank, J.L.; Bernot, M.J.; Burgin, A.J.; Crenshaw, C.L.; Dodds, W.K.; Grimm, N.B.; McDowell, W.H.; et al. Cross-Stream Comparison of Substrate-Specific Denitrification Potential. Biogeochemistry 2011, 104, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivett, M.O.; Buss, S.R.; Morgan, P.; Smith, J.W.N.; Bemment, C.D. Nitrate Attenuation in Groundwater: A Review of Biogeochemical Controlling Processes. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4215–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addy, K.; Gold, A.J.; Christianson, L.E.; David, M.B.; Schipper, L.A.; Ratigan, N.A. Denitrifying Bioreactors for Nitrate Removal: A Meta-Analysis. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinto, R.; Weigelhofer, G.; Brito, A.G.; Hein, T. Effects of Dry-Wet Cycles on Nitrous Oxide Emissions in Freshwater Sediments: A Synthesis. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, B.; Sun, X.; Yang, L. Hot Spots and Hot Moments of Nitrogen Removal from Hyporheic and Riparian Zones: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 144168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinay, G.; Gumiero, B.; Tabacchi, E.; Gimenez, O.; Tabacchi-Planty, A.M.; Hefting, M.M.; Burt, T.P.; Black, V.A.; Nilsson, C.; Iordache, V.; et al. Patterns of Denitrification Rates in European Alluvial Soils under Various Hydrological Regimes. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malá, J.; Bílková, Z.; Hrich, K.; Schrimpelová, K.; Kriška, M.; Šereš, M. Sustainability of Denitrifying Bioreactors with Various Fill Media. Plant Soil Environ. 2017, 63, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaynes, D.B.; Kaspar, T.C.; Moorman, T.B.; Parkin, T.B. In Situ Bioreactors and Deep Drain-Pipe Installation to Reduce Nitrate Losses in Artificially Drained Fields. J. Env. Qual. 2008, 37, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robertson, W.D.; Merkley, L.C. In-Stream Bioreactor for Agricultural Nitrate Treatment. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christianson, L.E.; Bhandari, A.; Helmers, M.J. A Practice-Oriented Review of Woodchip Bioreactors for Subsurface Agricultural Drainage. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2012, 28, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigelhofer, G.; Hein, T. Efficiency and Detrimental Side Effects of Denitrifying Bioreactors for Nitrate Reduction in Drainage Water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 13534–13545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgood, Z.; Robertson, W.D.; Schiff, S.L.; Elgood, R. Nitrate Removal and Greenhouse Gas Production in a Stream-Bed Denitrifying Bioreactor. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, L.A.; Robertson, W.D.; Gold, A.J.; Jaynes, D.B.; Cameron, S.C. Denitrifying Bioreactors—An Approach for Reducing Nitrate Loads to Receiving Waters. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1532–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gothwal, R.; Shashidhar, T. Antibiotic Pollution in the Environment: A Review. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2015, 43, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, R.M.; Seibert, D.; Quesada, H.B.; de Jesus Bassetti, F.; Fagundes-Klen, M.R.; Bergamasco, R. Occurrence, Impacts and General Aspects of Pesticides in Surface Water: A Review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 135, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Cheng, R.; Chen, F.; Lin, X.Q.; Yao, X.J.; Liang, B.; Huang, C.; Sun, K.; Wang, A.J. Selective Stress of Antibiotics on Microbial Denitrification: Inhibitory Effects, Dynamics of Microbial Community Structure and Function. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Liu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Lin, X.; Yin, G.; Liu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Lin, X.; et al. Effects of Multiple Antibiotics Exposure on Denitrification Process in the Yangtze Estuary Sediments. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roose-Amsaleg, C.; David, V.; Alliot, F.; Guigon, E.; Crouzet, O.; Laverman, A.M. Synergetic Effect of Antibiotic Mixtures on Soil Bacterial N2O-Reducing Communities. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 1873–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, Ş. Combined Removal of Pesticides and Nitrates in Drinking Waters Using Biodenitrification and Sand Filter System. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause Camilo, B.; Matzinger, A.; Litz, N.; Tedesco, L.P.; Wessolek, G. Concurrent Nitrate and Atrazine Retention in Bioreactors of Straw and Bark Mulch at Short Hydraulic Residence Times. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 55, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesar, A.; Roŝ, M. Long-Term Study of Nitrate, Nitrite and Pesticide Removal from Groundwater: A Two-Stage Biological Process. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 82, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschall, N.; Edwards, M.; Craiovan, E.; Frey, S.K.; Sunohara, M.; Ball, B.; Zoski, E.; Topp, E.; Khan, I.; Clark, I.D.; et al. Amending Woodchip Bioreactors with Water Treatment Plant Residuals to Treat Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Veterinary Antibiotic Compounds in Tile Drainage. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.-J.; Lai, W.W.-P.L.; Tung, H.; Lin, A.Y.-C. Pharmaceutical_anticorrosive Substance Removal by Woodchip Column Reactor.Pdf. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2020, 22, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepine, C.; Christianson, L.; Soucek, D.; McIsaac, G.; Summerfelt, S. Metal Leaching and Toxicity of Denitrifying Woodchip Bioreactor Outflow—Potential Reuse Application. Aquac. Eng. 2021, 93, 102129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhan, Z.E.; Ong, S.K.; Moorman, T.B. Dissipation of Atrazine, Enrofloxacin, and Sulfamethazine in Wood Chip Bioreactors and Impact on Denitrification. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 1816–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, F.; Guan, X. Effects of Norfloxacin on Nitrate Reduction and Dynamic Denitrifying Enzymes Activities in Groundwater. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvězdová, M.; Kosubová, P.; Košíková, M.; Scherr, K.E.; Šimek, Z.; Brodský, L.; Šudoma, M.; Škulcová, L.; Sáňka, M.; Svobodová, M.; et al. Currently and Recently Used Pesticides in Central European Arable Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, C.; Baran, N.; André, L.; Charron, M.; Joulian, C. Side Effects of Pesticides and Metabolites in Groundwater: Impact on Denitrification. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 662727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, P.J.; Christ, S.J.; Parkin, G.F. Kinetics of Alachlor Transformation and Identification of Metabolites Under Anaerobic Conditions. Water Res. 1997, 31, 3107–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.Z.; Yong, M.A.; Wang, S. Denitrification Potential Enhancement by Addition of External Carbon Sources in a Pre-Denitrification Process. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, R.L. Soil Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, M.H.; Harremoës, P. Biological Denitrification of Sewage: A Literature Review. In Proceedings of the Conference on Nitrogen As a Water Pollutant; Jenkins, S.H., Ed.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 509–555. ISBN 978-1-4832-1344-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; He, Q.; Chen, N.; Peng, T.; Feng, C. Denitrification Behavior in a Woodchip-Packed Bioreactor with Gradient Filling for Nitrate-Contaminated Water Treatment. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 154, 107454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensel, H.D.; Loehr, R.C.; Lawrence, A.W. Biological Kinetics of Suspended-Growth Denitrification. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1973, 45, 249–261. [Google Scholar]
- Bolzonella, D.; Innocenti, L.; Pavan, P.; Cecchi, F. Denitrification Potential Enhancement by Addition of Anaerobic Fermentation Products from the Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahdhiri, A.; Lesage, G.; Hannachi, A.; Heran, M. Minimum COD Needs for Denitrification: From Biological Models to Experimental Set-Up. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 61, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, C.; Silverstein, J. Denitrification of High-Nitrate, High-Salinity Wastewater. Water Res. 1999, 33, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Ma, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, Y. Long-Term Effect of PH on Denitrification: High PH Benefits Achieving Partial-Denitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 278, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.P.; Bouwer, E.J. Biodegradation of Aromatic Compounds under Mixed Oxygen/Denitrifying Conditions: A Review. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 18, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Yin, G.; Liu, M.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, J.; Zong, H.; Yang, Y.; Gao, L.; Tong, C. Effects of Sulfamethazine on Denitrification and the Associated N2O Release in Estuarine and Coastal Sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigger, G.T.; Adams, C.D.; Steller, H.K. Diffusion of Oxygen Through Activated Sludge Flocs: Experimental Measurement, Modeling, and Implications for Simultaneous Nitrification and Denitrification. Water Environ. Res. 2007, 79, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, S.M.; Trevors, J.T. Effect of the Herbicide Glyphosate on Nitrification, Denitrification, and Acetylene Reduction in Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1986, 29, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, E.E.; Arli, M.; Uygur, V. Effects of the Herbicide Topogard on Soil Respiration, Nitrification, and Denitrification in Potato-Cultivated Soils Differing in PH. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2004, 39, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouzet, O.; Poly, F.; Bonnemoy, F.; Bru, D.; Batisson, I.; Bohatier, J.; Philippot, L.; Mallet, C. Functional and Structural Responses of Soil N-Cycling Microbial Communities to the Herbicide Mesotrione: A Dose-Effect Microcosm Approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 4207–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessel-Bothe, S.; Pätzold, S.; Klein, C.; Behre, G.; Welp, G. Adsorption von Pflanzenschutzmitteln Und DOC an Saugkerzen Aus Glas Und Keramik. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2000, 163, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowski, L.; Olsson, O.; Leder, C.; Kümmerer, K. A Comparative Assessment of the Transformation Products of S-Metolachlor and Its Commercial Product Mercantor Gold® and Their Fate in the Aquatic Environment by Employing a Combination of Experimental and in Silico Methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 506–507, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment | Description | Additional Reagents Added after 48 h |
|---|---|---|
| C (Control) | Denitrification unaffected | 0.1 mL of pure methanol per L of sample |
| T1 | Xenobiotics affect denitrification; xenobiotics can undergo adsorption and decomposition | 0.1 mL of the tested xenobiotics per L of sample (conc.: 1000 mg L−1 in pure methanol solution) |
| T2 | Inhibitor stops denitrification; xenobiotics can undergo only adsorption | 0.1 mL of the tested xenobiotics per L of sample (conc.: 1000 mg L−1 in pure methanol solution) + 3.8 mL HgCl2 (123.5 mg L−1) |
| Tested Variable | Results |
|---|---|
| Concentration of wood chips: 7.5 (low), 12.5 (mid), 25 g L−1 (high) | COD: high (390 ± 70) > mid (147 ± 5) > low (83 ± 10) rD: high (1.6 ± 0.01) ~ mid (1.3 ± 0.2) ~ low (1.5 ± 0.2) turb: high (20.6 ± 2.8) ~ mid (13.8 ± 4.1) ~ low (7.7 ± 0.3), high > low |
| Concentration of NaHCO3: 0.0 (zero), 0.5 (low), 1.0 (mid), 2.0 g L−1 (high) | pH: zero (6.5 ± 0.2) < low (7.5 ± 0.05) < mid (7.8 ± 0.08) < high (8.2 ± 0.02) rD: zero (0.8 ± 0.1) < low (1.3 ± 0.1) ~ mid (1.2 ± 0.2) ~ high (1.1 ± 0.1) |
| Starting NO3-N: 15 mg L−1 (low), 30 mg L−1 (high) | COD: low (173 ± 12) ~ high (180 ± 14) End NOx-N: low (11.0 ± 0.4) < high (21.5 ± 0.3) rD: low (0.6 ± 0.06) < high (1.2 ± 0.04) |
| Fraction of wood shavings: 5–10 (low), 10–15 mm (high) | COD: high (143 ± 30) ~ low (119 ± 10) rD: high (1.5 ± 0.1) ~ low (1.5 ± 0.3) turb: high (10.1 ± 1.4) ~ low (10.3 ± 1.9) |
| Purging with Ar | DO after 2 days: yes (0.3 ± 0.03) < no (0.8 ± 0.1) DO after 7 days: yes (0.2 ± 0.01) < no (0.4 ± 0.08) rD: yes (0. 6 ± 0.06) < no (1.0 ± 0.17) |
| pH | DO (mg L−1) | COD (mg L−1) | NO2-N (mg L−1) | rD (mg L−1 d−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBA | C | 7.52 | 0.30 | 230 | 0.15 | 2.84 |
| T1 | 7.61 | 0.23 | 230 | 0.15 | 3.56 | |
| T2 | 7.66 | 7.67 | 290 | 0.99 | 0.20 | |
| LSA1 | C | 7.71 | 2.46 | 120 | 0.11 | 1.59 |
| T1 | 7.76 | 2.35 | 100 | 0.07 | 1.68 | |
| T2 | 7.67 | 0.39 | 170 | 0.16 | 0.34 | |
| LSA2 | C | 7.67 | 2.51 | 130 | 0.08 | 1.49 |
| T1 | 7.65 | 1.63 | 140 | 0.16 | 1.55 | |
| T2 | 7.75 | 8.27 | 310 | 0.16 | 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pániková, K.; Weigelhofer, G.; Bílková, Z.; Malá, J. Denitrification Assays for Testing Effects of Xenobiotics on Aquatic Denitrification and Their Degradation in Aquatic Environments. Water 2023, 15, 2536. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142536
Pániková K, Weigelhofer G, Bílková Z, Malá J. Denitrification Assays for Testing Effects of Xenobiotics on Aquatic Denitrification and Their Degradation in Aquatic Environments. Water. 2023; 15(14):2536. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142536
Chicago/Turabian StylePániková, Kristína, Gabriele Weigelhofer, Zuzana Bílková, and Jitka Malá. 2023. "Denitrification Assays for Testing Effects of Xenobiotics on Aquatic Denitrification and Their Degradation in Aquatic Environments" Water 15, no. 14: 2536. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142536
APA StylePániková, K., Weigelhofer, G., Bílková, Z., & Malá, J. (2023). Denitrification Assays for Testing Effects of Xenobiotics on Aquatic Denitrification and Their Degradation in Aquatic Environments. Water, 15(14), 2536. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142536