Ammonium Recovery from Synthetic Wastewaters by Using Zeolitic Mixtures: A Desorption Batch-Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Inizio Modulo
2. Materials and Methods
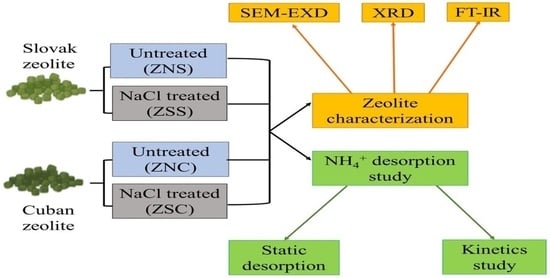
2.1. Tested Zeolites
2.2. NH4+ Adsorption-Desorption by Zeolitic Mixtures
2.3. Desorption Kinetics
2.4. Theory: Kinetic Models
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. BET, XRD, SEM-EDX, and ATR-FTIR Characterization of Tested Zeolites
3.2. NH4+ Desorption
3.3. NH4+ Desorption Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guida, S.; Potter, C.; Jefferson, B.; Soares, A. Preparation and Evaluation of Zeolites for Ammonium Removal from Municipal Wastewater through Ion Exchange Process. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojjati-Najafabadi, A.; Esfahani, P.N.; Davar, F.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Vasseghian, Y. Adsorptive removal of malachite green using novel GO@ZnO-NiFe2O4-αAl2O3 nanocomposites. Chem. Engin. J. 2023, 471, 144485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Joo, S.W.; Hojjati-Najafabadi, A.; Xie, H.; Wu, Y.; Mashifana, T.; Vasseghian, Y. Latest advances in layered covalent organic frameworks for water and wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2023, 329, 138580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Nawaz, T.; Beaudry, J. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Recovery from Wastewater. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Butterly, C.; Zhang, W.; He, J.; Chen, D. Adsorbent Materials for Ammonium and Ammonia Removal: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscarella, S.M.; Badalucco, L.; Laudicina, V.A.; Mannina, G. Chapter 5—Zeolites for the Nutrient Recovery from Wastewater. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Mannina, G., Pandey, A., Sirohi, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- Guaya, D.; Mendoza, A.; Valderrama, C.; Farran, A.; Sauras-Yera, T.; Cortina, J.L. Use of Nutrient-Enriched Zeolite (NEZ) from Urban Wastewaters in Amended Soils: Evaluation of Plant Availability of Mineral Elements. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.L.; Tanner, C.C.; Lahav, O.; Green, M.; Cyrus, J.S.; Reddy, G.B.; Abdusattar, T.; Hadi, A.; Kurniawan, T.; Dimova, G.; et al. The Application Effects of Natural Zeolite on Soil Runoff, Soil Drainage and Some Chemical Soil Properties in Arid Land Area. Desalination 2011, 34, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Guaya, D.; Valderrama, C.; Farran, A.; Sauras, T.; Cortina, J.L. Valorisation of N and P from Waste Water by Using Natural Reactive Hybrid Sorbents: Nutrients (N,P,K) Release Evaluation in Amended Soils by Dynamic Experiments. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widiastuti, N.; Wu, H.; Ang, H.M.; Zhang, D. Removal of Ammonium from Greywater Using Natural Zeolite. Desalination 2011, 277, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Khan, N.; Kim, G.H.; Harris, J.; Longhurst, P.; Bolan, N.S. Zeolite for Nutrient Stripping from Farm Effluents. In Environmental Materials and Waste: Resource Recovery and Pollution Prevention; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 569–589. [Google Scholar]
- Nakhli, S.A.A.; Delkash, M.; Bakhshayesh, B.E.; Kazemian, H. Application of Zeolites for Sustainable Agriculture: A Review on Water and Nutrient Retention. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, K.; Reddy, D.D. Zeolites and Their Potential Uses in Agriculture. Adv. Agron. 2011, 113, 219–241. [Google Scholar]
- Polat, E.; Karaca, M.; Demir, H.; Onus, A.N. Use of Natural Zeolite (Clinoptilolite) in Agriculture. J. Fruit Ornam. Plant Res. 2004, 12, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Langwaldt, J. Ammonium Removal from Water by Eight Natural Zeolites: A Comparative Study. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 2166–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, G.; Alduina, R.; Badalucco, L.; Barbara, L.; Capri, F.C.; Cosenza, A.; Di Trapani, D.; Gallo, G.; Laudicina, V.A.; Muscarella, S.M.; et al. Water Resource Recovery Facilities (WRRFs): The Case Study of Palermo University (Italy). Water 2021, 13, 3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Campos Bernardi, A.C.; Anchão Oliviera, P.P.; de Melo Monte, M.B.; Souza-Barros, F. Brazilian Sedimentary Zeolite Use in Agriculture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 167, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliu, T.D.; Oladoja, N.A. Nutrient Recovery from Wastewater and Reuse in Agriculture: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2299–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canellas, J. Tertiary Ammonium Removal with Zeolites. Ph.D. Thesis, Cranfield University, Cranfield, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Koon, J.H.; Kaufman, W.J. Ammonia Removal from Municipal Wastewaters by Ion Exchange. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1975, 47, 448–465. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, C.J.; Shyu, H.Y.; Xaba, L.; Bair, R.; Yeh, D.H. Performance and Onsite Regeneration of Natural Zeolite for Ammonium Removal in a Field-Scale Non-Sewered Sanitation System. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zeng, L.; Li, X.; Park, H. Removal of Ammonium from RO Permeate of Anaerobically Digested Wastewater by Natural Zeolite. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 3169–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscarella, S.M.; Laudicina, V.A.; Cano, B.; Badalucco, L.; Conte, P.; Mannina, G. Recovering Ammonium by Treated and Untreated Zeolitic Mixtures: A Comprehensive Experimental and Modelling Study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2023, 349, 112434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvaney, R.L.; Sparks, D.L. Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 3. Chemical Methods; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; pp. 1123–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Largitte, L.; Pasquier, R. A Review of the Kinetics Adsorption Models and Their Application to the Adsorption of Lead by an Activated Carbon. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 109, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesinghe, D.T.N.; Dassanayake, K.B.; Sommer, S.G.; Jayasinghe, G.Y.; Scales, P.J.; Chen, D. Ammonium Removal from High-Strength Aqueous Solutions by Australian Zeolite. J. Environ. Sci. Health. A Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2016, 51, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrappa, K.; Kumar, B.V.S. Characterization of Zeolites by Infrared Spectroscopy. Asian J. Chem. 2007, 19, 4933–4935. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani, A.R.; Mahvi, A.H. Use of Ion Exchange for Removal of Ammonium: A Biological Regeneration of Zeolite. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2004, 8, 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Q.; Dhar, B.R.; Elbeshbishy, E.; Lee, H.S. Ammonium Nitrogen Removal from the Permeates of Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactors: Economic Regeneration of Exhausted Zeolite. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 2008–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neag, E.; Șenilă, M.; Török, A.I.; Roman, M.; Puskás, F. Regeneration and reuse of natural zeolite for ammonium removal. In Proceedings of the International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference: SGEM, Albena, Bulgaria, 30 June–6 July 2019; Volume 19, pp. 651–656. [Google Scholar]
- Conte, P. Effects of Ions on Water Structure: A Low-Field 1H T1 NMR Relaxometry Approach. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2015, 53, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Monomodal Pseudo-First-Order | R2 | χ2 | Offset | qe1 | qe2 | k1 | k2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZNS | 0.983 | 0.47 | 22.8 ± 0.3 | 5.7 ± 0.3 | - | 0.33 ± 0.04 | - |
| ZSS | 0.975 | 1.37 | 23.8 ± 0.4 | 6.1 ± 0.4 | - | 0.3 ± 0.1 | - |
| ZNC | 0.987 | 1.98 | 23.2 ± 0.1 | 9 ± 1 | - | 0.8 ± 0.1 | - |
| ZSC | 0.952 | 7.77 | 27 ± 1 | 11 ± 1 | - | 0.25 ± 0.04 | - |
| Bimodal Pseudo-First-Order | R2 | χ2 | Offset | qe1 | qe2 | k1 | k2 |
| ZNS | 0.977 | 0.64 | 23 ± 3 | 1 ± 2 | 5 ± 2 | 0.03 ± 0.3 | 0.4 ± 0.2 |
| ZSS | 0.994 | 0.34 | 24.1 ± 0.2 | 5 ± 1 | 3 ± 1 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 3 ± 2 |
| ZNC | 0.991 | 1.36 | 23.8 ± 0.3 | 7 ± 2 | 4 ± 3 | 1.5 ± 1.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 |
| ZSC | 0.937 | 10.34 | 28 ± 5 | 8 ± 11 | 5 ± 8 | 0.4 ± 0.5 | 0.1 ± 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muscarella, S.M.; Laudicina, V.A.; Badalucco, L.; Conte, P.; Mannina, G. Ammonium Recovery from Synthetic Wastewaters by Using Zeolitic Mixtures: A Desorption Batch-Study. Water 2023, 15, 3479. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193479
Muscarella SM, Laudicina VA, Badalucco L, Conte P, Mannina G. Ammonium Recovery from Synthetic Wastewaters by Using Zeolitic Mixtures: A Desorption Batch-Study. Water. 2023; 15(19):3479. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193479
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuscarella, Sofia Maria, Vito Armando Laudicina, Luigi Badalucco, Pellegrino Conte, and Giorgio Mannina. 2023. "Ammonium Recovery from Synthetic Wastewaters by Using Zeolitic Mixtures: A Desorption Batch-Study" Water 15, no. 19: 3479. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193479
APA StyleMuscarella, S. M., Laudicina, V. A., Badalucco, L., Conte, P., & Mannina, G. (2023). Ammonium Recovery from Synthetic Wastewaters by Using Zeolitic Mixtures: A Desorption Batch-Study. Water, 15(19), 3479. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193479