Microscale Constructed Wetlands with Different Particulate Matters in their Substrates Exhibit Opposite Nitrogen Removal Performances
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Particulate Matters
2.2. Experimental Setup and Operation
2.3. Water Quality Determination
2.4. Calculation Method of N Balance in CWs
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Measurement
2.6. Composition of Accumulated Solids
2.7. Determination of Permeability Coefficient
2.8. Microbial Analysis
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
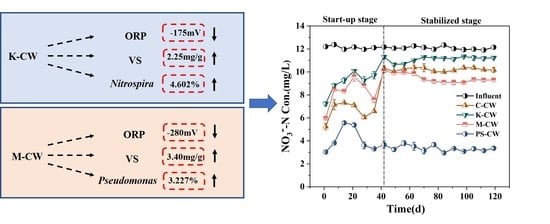
3.1. Nitrogen Removal Performance
3.2. Particle Size Distribution and Composition of Accumulated Solids in CWs
3.3. Physiochemical Characteristics of the CW Substrates
3.4. Key Enzyme Activities Related to Nitrogen Transformation
3.5. Microbial Community Structure in Different PM-Addition CWs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Zhang, J.; Fan, J.; Yang, T.; Sun, S. A study of ferric-carbon micro-electrolysis process to enhance nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiency in subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Constructed Wetlands Treatment of Municipal Wastewaters; Office of Research and Development: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2000. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyNET.exe/30004TBD.TXT?ZyActionD=ZyDocument&Client=EPA&Index=1995+Thru+1999&Docs=&Query=&Time=&EndTime=&SearchMethod=1&TocRestrict=n&Toc=&TocEntry=&QField=&QFieldYear=&QFieldMonth=&QFieldDay=&IntQFieldOp=0&ExtQFieldOp=0&XmlQuery=&File=D%3A%5Czyfiles%5CIndex%20Data%5C95thru99%5CTxt%5C00000016%5C30004TBD.txt&User=ANONYMOUS&Password=anonymous&SortMethod=h%7C-&MaximumDocuments=1&FuzzyDegree=0&ImageQuality=r75g8/r75g8/x150y150g16/i425&Display=hpfr&DefSeekPage=x&SearchBack=ZyActionL&Back=ZyActionS&BackDesc=Results%20page&MaximumPages=1&ZyEntry=1&SeekPage=x&ZyPURL (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Pedescoll, A.; Samsó, R.; Romero, E.; Puigagut, J.; García, J. Reliability, repeatability and accuracy of the falling head method for hydraulic conductivity measurements under laboratory conditions. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 754–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.; Griffin, P.; Cooper, P. Factors affecting the longevity of sub-surface horizontal flow systems operating as tertiary treatment for sewage effluent. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselles-Osorio, A.; Puigagut, J.; Segú, E.; Vaello, N.; Granés, F.; García, D.; García, J. Solids accumulation in six full-scale subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, P.; Dotro, G.; Nivala, J.; García, J. Clogging in subsurface-flow treatment wetlands: Occurrence and contributing factors. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Huang, L.; Liang, Y.; Xiang, H.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Q.; Hou, J.; Chen, Y. Response of microbes to biochar strengthen nitrogen removal in subsurface flow constructed wetlands: Microbial community structure and metabolite characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Matos, M.P.; Von Sperling, M.; de Matos, A.T. Clogging in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands: Influencing factors, research methods and remediation techniques. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio Technol. 2018, 17, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ji, M.; Zhuang, L.; Nie, L.; Liu, Z. Effects of solids accumulation and plant root on water flow characteristics in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, D.-y.; Xiao, K.; Guan, J.; Xie, Y.F.; Wang, X.-m.; Waite, T.D. Role of adsorption in combined membrane fouling by biopolymers coexisting with inorganic particles. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 226–234. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.-s.; Sim, K.; Kang, D.-H.; Youn, H.J. Application of Inorganic Particles Modified with Polyvinylamine to Produce Antibacterial Paper. BioResources 2018, 13, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitis, V.; Haught, R.C.; Clark, R.M.; Rothenberg, G. Assessing the removal of inorganic colloids and Cryptosporidium parvum from drinking water. J. Environ. Monit. 2002, 4, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Xie, H.; Häggblom, M.; Liang, S.; Hu, Z. Inorganic particle accumulation promotes nutrient removal of vertical flow constructed wetlands: Mechanisms and implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Luo, S.; Yu, B.; Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. A comparative analysis for the development and recovery processes of different types of clogging in lab-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 24073–24083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lianfang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Wei, T. Clogging processes caused by biofilm growth and organic particle accumulation in lab-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 750–757. [Google Scholar]
- Seeley, M.E.; Song, B.; Passie, R.; Hale, R.C. Microplastics affect sedimentary microbial communities and nitrogen cycling. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, L.; Cheng, Z.; Yao, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wang, L.; Sun, H. LDPE microplastics affect soil microbial communities and nitrogen cycling. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, W.G. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Zhu, J. Optimization of methane production in anaerobic co-digestion of poultry litter and wheat straw at different percentages of total solid and volatile solid using a developed response surface model. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2016, 51, 325–334. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10934529.2015.1109395 (accessed on 1 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Huang, J.; Han, T.; Yan, C.; Cao, C.; Cao, M. Comprehensive metagenomic and enzyme activity analysis reveals the negatively influential and potentially toxic mechanism of polystyrene nanoparticles on nitrogen transformation in constructed wetlands. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.; Liang, S. Enhanced triclosan and nutrient removal performance in vertical up-flow constructed wetlands with manganese oxides. Water Res. 2018, 143, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, B.; Li, Q.; Liu, N.; Xia, B.; Zhu, L.; Qu, K. Toxicities of polystyrene nano-and microplastics toward marine bacterium Halomonas alkaliphila. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.-H.; He, P.-J.; Shao, L.-M. Characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) fractions from excess sludges and their effects on bioflocculability. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3193–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Piwpuan, N.; Arias, C.A.; Headley, T.; Brix, H. Can root exudates from emergent wetland plants fuel denitrification in subsurface flow constructed wetland systems? Ecol. Eng. 2013, 61, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; He, Q.; Liu, T.; Zheng, F.; Mei, H.; Chen, M.; Liu, G.; Vymazal, J.; Chen, Y. Impact of microplastics on the treatment performance of constructed wetlands: Based on substrate characteristics and microbial activities. Water Res. 2022, 217, 118430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Jaroudi, S.; Ul-Hamid, A.; Al-Gahtani, M. Failure of crude oil pipeline due to microbiologically induced corrosion. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Huang, J.; Zeng, G.; Gu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Tang, B.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Shi, L. Exploiting extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) controlling strategies for performance enhancement of biological wastewater treatments: An overview. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, L.; Cao, J.; Feng, Q.; Fang, F.; Chen, Y. Inhibition of 1, 4-dioxane on the denitrification process by altering the viability and metabolic activity of Paracoccus denitrificans. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 27274–27282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHEN, L.; HUANG, F.; Zhang, C.; Liu, F.; Lang, H. Effect of norfloxacin on denitrification process in groundwater: Evidence for denitrifying enzyme activity. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2020, 40, 2496–2501. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, L.; Wang, P.; Hou, J.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, T. Distinct community structure and microbial functions of biofilms colonizing microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2395–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Jia, W.; Qin, X. LDPE microplastic films alter microbial community composition and enzymatic activities in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussud, C.; Meistertzheim, A.; Conan, P.; Pujo-Pay, M.; George, M.; Fabre, P.; Coudane, J.; Higgs, P.; Elineau, A.; Pedrotti, M. Evidence of niche partitioning among bacteria living on plastics, organic particles and surrounding seawaters. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, N.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, W.; Ma, Y.; Niu, Z. Colonization characteristics of bacterial communities on plastic debris influenced by environmental factors and polymer types in the Haihe Estuary of Bohai Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10763–10773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, L.; Xie, H.; Zhang, S.; Hu, Z.; Liang, S.; Zhang, J. Microscale Constructed Wetlands with Different Particulate Matters in their Substrates Exhibit Opposite Nitrogen Removal Performances. Water 2023, 15, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030434
Cui L, Xie H, Zhang S, Hu Z, Liang S, Zhang J. Microscale Constructed Wetlands with Different Particulate Matters in their Substrates Exhibit Opposite Nitrogen Removal Performances. Water. 2023; 15(3):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030434
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Lele, Huijun Xie, Shiwen Zhang, Zhen Hu, Shuang Liang, and Jian Zhang. 2023. "Microscale Constructed Wetlands with Different Particulate Matters in their Substrates Exhibit Opposite Nitrogen Removal Performances" Water 15, no. 3: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030434
APA StyleCui, L., Xie, H., Zhang, S., Hu, Z., Liang, S., & Zhang, J. (2023). Microscale Constructed Wetlands with Different Particulate Matters in their Substrates Exhibit Opposite Nitrogen Removal Performances. Water, 15(3), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030434