3D Characterization of Pore Structure and Pore Scale Seepage Simulation of Sandstone Based on Computational Tomography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Three-Dimensional (3D) Microstructure of Sandstone Based on CT
2.1. Preparation of Sandstone CT Samples
2.2. CT Scanning of Sandstone Samples
2.3. Sandstone CT Image Processing and 3D Reconstruction
3. Characteristics of Pore Structure in Sandstone
3.1. Porosity
3.2. Coordination Number, Pore Size, and Pore Throat Radius Distribution
4. Numerical Simulation of Fluid Flow
4.1. Model Description
4.2. Seepage Velocity and Streamline Distribution
4.3. Permeability of Sandstone
5. Conclusions
- (a)
- The porosity of coarse sandstone, medium sandstone, and fine sandstone are 16.43%, 12.03%, and 11.64%, respectively. The porosity of medium sandstone and fine sandstone is relatively similar, but the average pore radius, pore throat radius, and coordination number of medium sandstone are slightly larger than those of fine sandstone, which is conducive to fluid flow in fine sandstone.
- (b)
- The distribution pattern of pore structure characteristics in coarse sandstone, medium sandstone, and fine sandstone is consistent with pore size following a lognormal distribution and pore throat radius following a Weibull distribution. And the unconnected pores of the three types of sandstones are all less than 0.5%, indicating that the unconnected pores of sandstones can be ignored.
- (c)
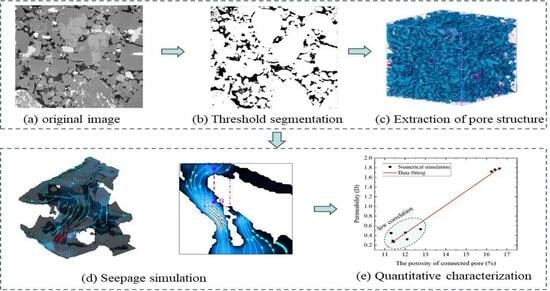
- The fluid flow process in sandstone was reproduced through numerical simulation, and the flow velocity significantly increased at the pore throat. And the complexity of the pore structure increased the path of fluid flow and reduced the permeability of sandstone.
- (d)
- The permeability and porosity of sandstone are generally linearly related and have a high correlation. However, there is a significant difference in permeability and porosity in low-permeability sandstone samples, and pore structure characteristic parameters are needed to assist in determining the permeability of pores.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chi, P.; Sun, J.; Yan, W.; Luo, X. Multiscale fusion of tight sandstone digital rocks using attention-guided generative adversarial network. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 160, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qin, W.; Jin, A.; Wu, H.; Chen, Z. Research and analysis of the impact of the pore structure on the mechanical properties and fracture mechanism of sandstone. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 107753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Xie, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Yue, W. Characterization of pore structure of tight sandstone reservoirs based on fractal analysis of NMR echo data. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 81, 103483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Luo, Z.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, N.; Ren, D.; Cao, Y. Numerical modeling and analysis of the matrix acidizing process in fractured sandstone rocks with the Extended–FEM. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2023, 220, 111215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Xia, Y.; Qiao, J.; Chen, J.; Zeng, J.; Cai, J. Modeling of multiphase flow in low permeability porous media: Effect of wettability and pore structure properties. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gao, Y.; Wan, Y.; Su, Y.; An, S.; Sun, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Liu, L.; et al. Influence of stress sensitivity on microscopic pore structure and fluid flow in porous media. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 36, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Liu, J.; Song, R.; Song, Y. Study on Permeability Stress-Sensitivity in Seepage-Geomechanical Coupling of Fractured Deep Tight Sandstone Gas Reservoirs. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, S.; Liu, H.; Mao, H.; Shi, X.; Qiu, X.; Liu, M.; Min, Z.; Song, Y.; Wei, X. Numerical Tracking of Natural Gas Migration in Underground Gas Storage with Multilayered Sandstone and Fault-Bearing Caprocks. Energies 2023, 16, 4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Tang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. Characterization of Extra Low-Permeability Conglomerate Reservoir and Analysis of Three-Phase Seepage Law. Processes 2023, 11, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manwart, C.; Aaltosalmi, U.; Koponen, A.; Hilfer, R.; Timonen, J. Lattice-Boltzmann and finite-difference simulations for the permeability for three-dimensional porous media. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 66, 016702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Wang, Y.; Chung, T.; Armstrong, R.T.; McClure, J.E.; Mostaghimi, P. Computations of permeability of large rock images by dual grid domain decomposition. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 126, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristinof, R.; Ranjith, P.G.; Choi, S.K. Finite element simulation of fluid flow in fractured rock media. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 60, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, P.; López-Querol, S. Generalized unconfined seepage flow model using displacement-based formulation. Eng. Geol. 2013, 166, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, L.R.; Wilson, A.M. Comparison of four numerical models for simulating seepage from salt marsh sediments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 69, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borujeni, A.T.; Lane, N.M.; Thompson, K.; Tyagi, M. Effects of image resolution and numerical resolution on computed permeability of consolidated packing using LB and FEM pore-scale simulations. Comput. Fluids 2013, 88, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Ayatollahi, S. A new wormhole mechanistic model for radial acid flow geometry using novel 3D flow correlations. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 230, 212176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; He, L.; Li, J.; Zou, C.; Shao, C. Permeability prediction for porous sandstone using digital twin modeling technology and Lattice Boltzmann method. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 142, 104695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Ge, L.; Hu, F.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Xu, H.; Lu, S.; Xue, Q. Pore-scale characterization of tight sandstone in Yanchang Formation Ordos Basin China using micro-CT and SEM imaging from nm- to cm-scale. Fuel 2017, 209, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, A.; Ayatollahi, S.; Kharrat, R.; Dashti, N. Estimation of 3-D pore network coordination number of rocks from watershed segmentation of a single 2-D image. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 94, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, A.; Jamshidi, S.; Salehi, S. An automated simple algorithm for realistic pore network extraction from micro-tomography images. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2014, 123, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamani, H.; Rabbani, A.; Russell, K.P.; Zydney, A.L.; Gomez, E.D.; Hattrick-Simpers, J.; Werber, J.R. Data-science-based reconstruction of 3-D membrane pore structure using a single 2-D micrograph. J. Memb. Sci. 2023, 678, 121673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durr, N.; Sauer, M.; Hiermaier, S. A numerical study on mesoscale simulation of quartzite and sandstone under shock loading. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2017, 108, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakirov, T.R.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Yuan, C. Characterization of dynamic adsorption regimes in synthetic and natural porous structures using lattice Boltzmann simulations. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 189, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhao, H.; Ning, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Q. Permeability prediction of numerical reconstructed multiscale tight porous media using the representative elementary volume scale lattice Boltzmann method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 118, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Dong, Y.; Deng, H.; Elsworth, D. High-resolution characterization of nanoparticle transport in heterogeneous porous media via low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Hou, Z.; Liu, Q.; Fu, F. Reconstruction of three-dimension digital rock guided by prior information with a combination of InfoGAN and style-based GAN. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Sun, W.; Ji, W.; Zhang, R.; Du, K.; Zhang, S.; Ren, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X. Effects of pore-throat structure on gas permeability in the tight sandstone reservoirs of the Upper Triassic Yanchang formation in the Western Ordos Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 162, 602–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Kuru, E.; Gingras, M.; Iremonger, S. CT-CFD integrated investigation into porosity and permeability of neat early-age well cement at downhole condition. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 205, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, A. Superpixels pore network extraction for geological tomography images. Adv. Water Resour. 2023, 182, 104582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhian, D.; Azin, R.; Ranjbar, A. Application of medical and dental CT-Scan technologies for determining porosity distribution of the Persian Gulf coastal zone and Zagros basin core samples. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 150, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Su, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y. Micro-CT characterization on pore structure evolution of low-permeability sandstone under acid treatment. Appl. Geochem. 2023, 152, 105633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, B.; Mitra, S.K.; Vick, D. Understanding the micro structure of Berea Sandstone by the simultaneous use of micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) and focused ion beam-scanning electron microscopy (FIB-SEM). Micron 2011, 42, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Kogure, T.; Nishizawa, O.; Xue, Z. Different flow behavior between 1-to-1 displacement and co-injection of CO2 and brine in Berea sandstone: Insights from laboratory experiments with X-ray CT imaging. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2017, 66, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, M.; Jing, X.; Xiao, W.; Cui, Q. Influence mechanism of pore-scale anisotropy and pore distribution heterogeneity on permeability of porous media. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khishvand, M.; Akbarabadi, M.; Piri, M. Micro-scale experimental investigation of the effect of flow rate on trapping in sandstone and carbonate rock samples. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 94, 379–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.; Guo, J.; Yao, N.; Fan, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, P. Experimental Investigation on Post-Peak Permeability Evolution Law of Saturated Sandstone under Various Cyclic Loading–Unloading and Confining Pressure. Water 2022, 14, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Dang, Y.; Chao, Z. Analysis of the Hydromechanical Properties of Compact Sandstone and Engineering Application. Water 2023, 15, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Niu, F.; Liu, M.; Luo, J. Evolution characteristics of freeze–thaw-induced sandstone damage under water immersion conditions in Changdu, Tibet, China. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2024, 217, 104013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lai, J.; Bai, G.; Pang, X.; Ma, X.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Fan, X. Comparison of fractal models using NMR and CT analysis in low permeability sandstones. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 112, 104069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Yao, S.; Xiao, H.; Cao, J.; Hu, W.; Sun, L.; Tao, K.; Liu, X. Pore structure and connectivity of tight sandstone reservoirs in petroleum basins: A review and application of new methodologies to the Late Triassic Ordos Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 129, 105084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, E.; Muggeridge, A.; Jones, A.; Krevor, S. Pore structure and wetting alteration combine to produce the low salinity effect on oil production. Fuel 2023, 332, 126155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Nos. | Sandstone Types | Sample Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| 1# | coarse sandstone | |
| 2# | coarse sandstone | |
| 3# | coarse sandstone | |
| 4# | middle sandstone | |
| 5# | middle sandstone | |
| 6# | middle sandstone | |
| 7# | fine sandstone | |
| 8# | fine sandstone | |
| 9# | fine sandstone |
| Nos. | Symbol | Value | Unit | Physical Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 1000 | density | ||
| 2# | 0.001 | viscosity | ||
| 3# | 0.01 | inlet velocity |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, K.; Li, K.; Ji, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, K.; Chen, X. 3D Characterization of Pore Structure and Pore Scale Seepage Simulation of Sandstone Based on Computational Tomography. Water 2024, 16, 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16071022
Zhu K, Li K, Ji Y, Li X, Liu X, Liu K, Chen X. 3D Characterization of Pore Structure and Pore Scale Seepage Simulation of Sandstone Based on Computational Tomography. Water. 2024; 16(7):1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16071022
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Kaipeng, Kai Li, Yadong Ji, Xiaolong Li, Xuan Liu, Kaide Liu, and Xuandong Chen. 2024. "3D Characterization of Pore Structure and Pore Scale Seepage Simulation of Sandstone Based on Computational Tomography" Water 16, no. 7: 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16071022
APA StyleZhu, K., Li, K., Ji, Y., Li, X., Liu, X., Liu, K., & Chen, X. (2024). 3D Characterization of Pore Structure and Pore Scale Seepage Simulation of Sandstone Based on Computational Tomography. Water, 16(7), 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16071022