Anaerobic Treatment of Concentrated Black Water in a UASB Reactor at a Short HRT
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| CSTR [13] | Accumulation system [10] | UASB-septic tank [10,23] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 37 | 20 | 15 | 25 |
| Total COD removal (%) | 61 | 80 | 61 | 78 |
| HRT (d) | 20 | 150 | 30 | 30 |
| SRT (d) | 20 | 150 | >365 | >365 |
| Volume required (L/p) | 140 | 1.0*103 | n.d. | 200 |
| Methanisation* (%) | 60 | 58 | 39 | 60 |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Black water collection
2.2. UASB reactor
2.3. Design of the UASB reactor

| Unit | Remarks | Initial design of UASB reactor | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SRT | d | Minimum value at 25 °C | 75 |
| C | gCOD/L | CODtotal in the influent | 12 |
| SS | - | CODss/CODt influent | 0.78 |
| X | gCOD/L | Sludge concentration in the reactor | 28 |
| R | - | Fraction of CODss removed | 0.9 |
| H | - | Level of hydrolysis | 0.7 |
| HRT | d | 6.9 |
2.4. Analyses and measurements
2.5. Calculations
3. Results
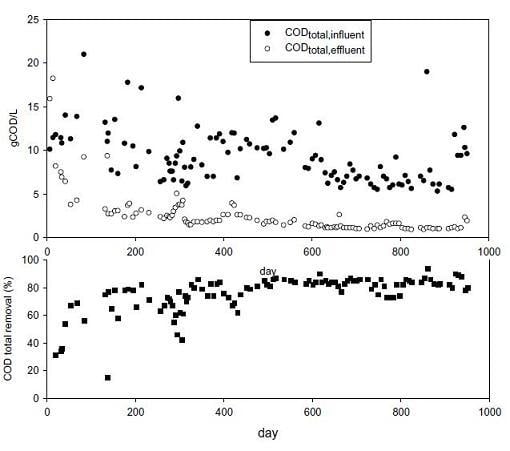
3.1. Performance of the UASB reactor
| Day 1 – 518 | Day 519 – 951 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | Influent | s.d. | Influent | s.d. | |
| pH | - | 8.8 | 0.22 | 8.6 | 0.53 |
| CODtotal | [gCOD/L] | 9.8 | 2.6 | 7.7 | 2.5 |
| CODSS | [gCOD/L] | 5.1 | 2.7 | 4.9 | 2.0 |
| CODcolloidal | [gCOD/L] | 1.3 | 0.42 | 0.5 | 0.22 |
| CODsoluble | [gCOD/L] | 3.4 | 0.47 | 2.3 | 0.81 |
| VFA | [gCOD/L] | 1.5 | 0.48 | 1.2 | 0.89 |
| HCO3- | [gC/L] | 1.2 | 0.37 | 0.67 | 0.20 |
| TN | [gN/L] | 1.9 | 0.19 | 1.2 | 0.18 |
| NH4-N | [gN/L] | 1.4 | 0.15 | 0.85 | 0.15 |
| TP | [gP/L] | 0.22 | 0.067 | 0.15 | 0.064 |
| TP soluble | [gP/L] | 0.090 | 0.0087 | 0.057 | 0.018 |
| PO4-P | [gP/L] | 0.079 | 0.0085 | 0.054 | 0.027 |


3.2. Sludge bed development


3.3. COD mass balance

3.4. Effluent composition
| Day 1 – 518 | Day 519 – 951 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | UASB effluent | s.d. | UASB effluent | s.d. | |
| pH | - | 7.6 | 0.13 | 7.4 | 0.17 |
| CODtotal | [gCOD/L] | 2.4 | 0.84 | 1.2 | 0.34 |
| CODSS | [gCOD/L] | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.10 | 0.08 |
| CODcolloidal | [gCOD/L] | 0.53 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.07 |
| CODsoluble | [gCOD/L] | 1.5 | 0.39 | 0.90 | 0.21 |
| VFA | [gCOD/L] | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.14 | 0.18 |
| BOD5 | [g/L] | 0.87 | 0.24 | 0.48 | 0.06 |
| HCO3- | [gC/L] | 1.4 | 0.14 | 0.87 | 0.10 |
| TN | [gN/L] | 1.8 | 0.22 | 1.2 | 0.12 |
| NH4-N | [gN/L] | 1.5 | 0.19 | 1.0 | 0.18 |
| TP | [gP/L] | 0.13 | 0.015 | 0.094 | 0.018 |
| TP soluble | [gP/L] | 0.103 | 0.010 | 0.070 | 0.011 |
| PO4-P | [gP/L] | 0.092 | 0.011 | 0.069 | 0.013 |
4. Discussion
4.1. Removal efficiency of the UASB reactor
| Unit | UASB reactor This research | UASB-septic tank [10,23] | Pilot plant UASB-septic tank [20] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influent | - | Black water, vacuum toilets, DESAR pilot plant Sneek, Filtered with a coarse filter | Black water, vacuum toilets, Wageningen University | Black water, vacuum toilets, DESAR pilot plant Sneek |
| Reactor volume | L | 50 | 200 | 7400 |
| Up flow velocity | Cm/h | 0.76 | 0.23 | 0.42 |
| Loading rate | kgCOD/m3/d | 1.0 | 0.42 | 0.36 |
| HRT | Days | 8.7 (0.96) | 29 | 30 |
| SRT | Days | 254 | >365 | >365 |
| CODtotal removal | % | 78 (9%) | 78 | 87 |
| CODSS removal | % | 93 (11%) | 94 | 95 |
| Methane production | L CH4/p/d | 10 | 142.0 | 13 |
| m3 CH4/m3 BW | 1.8 | 2.0 | 2.1 |
4.2. Design of the UASB reactor

| UASB reactor full scale | ||
|---|---|---|
| SRT | (d) | 75 |
| C | COD concentration in the influent (gCOD/L) | 16.1a |
| SS | CODss/CODt influent (-) | 0.75a |
| X | sludge concentration in the reactor (gCOD/L) | 34.2 |
| R | fraction of CODss removed (-) | 0.93 |
| H | fraction of removed solids which is hydrolyzed (-) | 0.49 |
| HRT | (d) | 12.6 |
| V | (L/p) | 63 |
| Loading rate | (kgCOD/m3/d) | 1.3 |
4.3. Fate of nutrients and further treatment
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Hernandez Leal, L.; Zeeman, G.; Temmink, H.; Buisman, C. Characterisation and biological treatment of greywater. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 56, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Otterpohl, R.; Albold, A.; Oldenburg, M. Source control in urban sanitation and waste management: ten systems with reuse of resources. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawa-Roeleveld, K.; Zeeman, G. Anaerobic treatment in decentralised and source-separation-based sanitation concepts. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2006, 5, 115–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeman, G.; Lettinga, G. The role of anaerobic digestion of domestic sewage in closing the water and nutrient cycle at community level. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraete, W.; Morgan-Sagastume, F.; Aiyuk, S.; Waweru, M.; Rabaey, K.; Lissens, G. Anaerobic digestion as a core technology in sustainable management of organic matter. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Driver, J.; Lijmbach, D.; Steen, I. Why recover phosphorus for recycling, and how? Environ. Technol. 1999, 20, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.; Pronk, W.; Larsen, T.A. Treatment processes for source-separated urine. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3151–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halalsheh, M.; Abu Ghunmi, L.; Al-Alami, N.; Fayyad, M. Fate of pathogens in tomato plants and soil irrigated with secondary treated wastewater. In Proceedings of the Sanitation Challenge, Wageningen, The Netherlands, May 2008; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Huibers, F.P.; van Lier, J.B. Use of wastewater in agriculture: the water chain approach. Irrig. Drain. 2005, 42, S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawa-Roeleveld, K.; Elmitwalli, T.; Zeeman, G. Enhanced primary treatment of concentrated black water and kitchen residues within DESAR concept using two types of anaerobic digesters. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Berg, W.J. KNN Advies, Efficiency of combined heat and power. Personal communication, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- CBS-Statline. Energy balance, energy consumption of households. 2006. http://statline.cbs.nl/StatWeb/publication/?VW=T&DM=SLNL&PA=70846ned&D1=0-1,3-4,30-33&D2=30&D3=5&D4=a&HD=080606-2108&HDR=T&STB=G3: (accessed on 6 June 2008).
- Wendland, C.; Deegener, S.; Behrendt, J.; Toshev, P.; Otterpohl, R. Anaerobic digestion of blackwater from vacuum toilets and kitchen refuse in a continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR). Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeeman, G.; Kujawa, K.; De Mes, T.; Hernandez, L.; de Graaff, M.S.; Mels, A.; Meulman, B.; Temmink, H.; Buisman, C.; van Lier, J.; Lettinga, G. Anaerobic treatment as a core technology for energy, nutrients and water recovery from source separated domestic waste(water). Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeeman, G.; Sanders, W. Potential of anaerobic digestion of complex waste(water). Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kujawa-Roeleveld, K. Anaerobic treatment of concentrated wastewater in DESAR concepts; 2005-14; Stowa: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Halalsheh, M.; Koppes, J.; den Elzen, J.; Zeeman, G.; Fayyad, M.; Lettinga, G. Effect of SRT and temperature on biological conversions and the related scum-forming potential. Water Res. 2005, 39, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Burton, F.L.; Stensel, H.D. Wastewater Engineering - Treatment and Reuse, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Luostarinen, S.; Sanders, W.; Kujawa-Roeleveld, K.; Zeeman, G. Effect of temperature on anaerobic treatment of black water in UASB-septic tank systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meulman, B.; Zeeman, G.; Buisman, C.J.N. Treatment of concentrated black water on pilot scale: options and challenges. In Proceedings of the Sanitation Challenge, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 19-21 May 2008; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Koster, I.W.; Koomen, E. Ammonia inhibition of maximum growth rate of hydrogenotrophic methanogens at various pH-levels and temperatures. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1988, 28, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeman, G.; Kujawa, K.; Meulman, B.; Kwant, F. Full scale demonstration of vacuum collection, transport & treatment of black water. In Poster presentation at the Advanced Sanitation Conference, Aachen, Germany, March 2007.
- Kujawa-Roeleveld, K.; Fernandes, T.; Wiryawan, Y.; Tawfik, A.; Visser, M.; Zeeman, G. Performance of UASB septic tank for treatment of concentrated black water within DESAR concept. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- APHA. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Batstone, D.J. Mathematical modelling of anaerobic reactors treating domestic wastewater: Rational criteria for model use. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2006, 5, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorter, K. Black water production at the Decentralized Sanitation and Reuse demonstration project in Sneek, the Netherlands. personal communication, 17 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 85th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lettinga, G.; Hulshoff Pol, L.W. UASB-process design for various types of wastewaters. Water Sci. Technol. 1991, 24, 87–107. [Google Scholar]
- Vinnerås, B.; Björklund, A.; Jönsson, H. Thermal composting of faecal matter as treatment and possible disinfection method - laboratory-scale and pilot-scale studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 88, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winker, M.; Vinnerås, B.; Muskolus, A.; Arnold, U.; Clemens, J. Fertiliser products from new sanitation systems: Their potential values and risks. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, A. The quest for sustainable nitrogen removal technologies. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van der Star, W.R.L.; Abma, W.R.; Blommers, D.; Mulder, J.W.; Tokutomi, T.; Strous, M.; Picioreanu, C.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Startup of reactors for anoxic ammonium oxidation: Experiences from the first full-scale anammox reactor in Rotterdam. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4149–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Graaff, M.S.; Zeeman, G.; Temmink, H.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Buisman, C.J.N. Combined anaerobic treatment and autotrophic nitrogen removal from black water. In IWA 2nd Specialized Conference Nutrient Management in Wastewater Treatment Processes, Krakow, Poland, September 2009.
- Vlaeminck, S.E.; Terada, A.; Smets, B.F.; van der Linden, D.; Boon, N.; Verstraete, W.; Carballa, M. Nitrogen removal from digested black water by one-stage partial nitritation and anammox. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5035–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlinger, K.N.; Young, T.M.; Schroeder, E.D. Predicting struvite formation in digestion. Water Res. 1998, 32, 3607–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Voorthuizen, E.; Zwijnenburg, A.; van der Meer, W.; Temmink, H. Biological black water treatment combined with membrane separation. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4334–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordell, D.; Drangert, J.-O.; White, S. The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Global Environ. Change 2009, 19, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, Y.; Fujii, M. Three years experience of operating and selling recovered struvite from full-scale plant. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
De Graaff, M.S.; Temmink, H.; Zeeman, G.; Buisman, C.J.N. Anaerobic Treatment of Concentrated Black Water in a UASB Reactor at a Short HRT. Water 2010, 2, 101-119. https://doi.org/10.3390/w2010101
De Graaff MS, Temmink H, Zeeman G, Buisman CJN. Anaerobic Treatment of Concentrated Black Water in a UASB Reactor at a Short HRT. Water. 2010; 2(1):101-119. https://doi.org/10.3390/w2010101
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Graaff, Marthe S., Hardy Temmink, Grietje Zeeman, and Cees J. N. Buisman. 2010. "Anaerobic Treatment of Concentrated Black Water in a UASB Reactor at a Short HRT" Water 2, no. 1: 101-119. https://doi.org/10.3390/w2010101
APA StyleDe Graaff, M. S., Temmink, H., Zeeman, G., & Buisman, C. J. N. (2010). Anaerobic Treatment of Concentrated Black Water in a UASB Reactor at a Short HRT. Water, 2(1), 101-119. https://doi.org/10.3390/w2010101