Can Continental Shelf River Plumes in the Northern and Southern Gulf of Mexico Promote Ecological Resilience in a Time of Climate Change?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Ecological Resilience and Climate Change
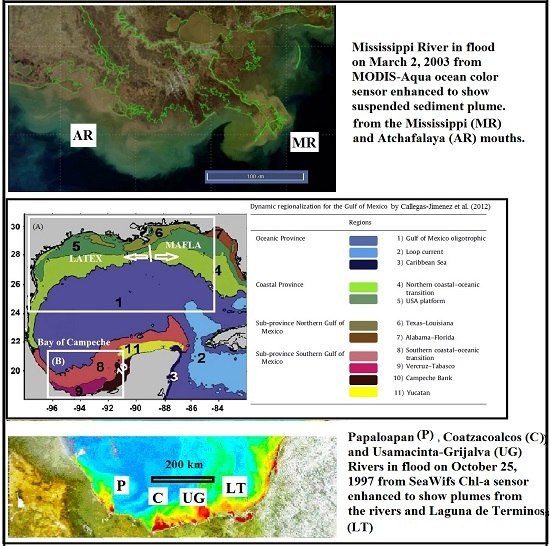
2. Study Sites
2.1. Deltaic Architecture
2.2. Climate Change Effects on River Discharge
3. Synthesis
3.1. Mesoscale Circulation in the Gulf of Mexico
3.2. Plume Dynamics and Coastal Currents
4. Conclusions and Management Implications
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dunn, D.E. Trends in Nutrient Inflows to the Gulf of Mexico from Streams Draining the Conterminous United States, 1972–93; Water-Resources Investigations Report 96-4113; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Yáñez-Arancibia, A.; Day, J.W. The Gulf of Mexico: Towards an integration of coastal management with large marine ecosystem management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2004, 47, 537–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callejas-Jimenez, M.; Santamaria-del-Angel, E.; Gonzalez-Silvera, A.; Millan-Nunez, R.; Cajal-Medrano, R. Dynamic regionalization of the Gulf of Mexico based on normalized radiances (nLw) derived from MODIS-Aqua. Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 37, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tian, H.; Yang, Q.; Yang, J.; Song, X.; Lohrenz, S.E.; Cai, W.J. Long-term trends in evapotranspiration and runoff over the drainage basins of the Gulf of Mexico during 1901–2008. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1988–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Music, B.; Caya, D. Evaluation of the hydrological cycle over the Mississippi River basin as simulated by the Canadian Regional Climate Model (CRCM). J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 969–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbach, P.; Molina, L.; Lucatelli, B.; Roupsard, O.; Ciais, L.; Corrales, L.; Mahe, G. Climatology-based regional modelling of potential vegetation and average annual long-term runoff for Mesoamerica. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 1801–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dagg, M.; Benner, R.; Lohrenz, S.; Lawrence, D. Transformation of dissolved and particulate materials on continental shelves influenced by large rivers: Plume processes. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 833–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signoret, M.; Monreal-Gómez, M.A.; Aldeco, J.; Salas-de-León, D.A. Hydrography, oxygen saturation, suspended particulate matter, and chlorophyll-a fluorescence in an oceanic region under freshwater influence. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 69, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Arancibia, A.; Day, J.W.; Lara-Dominguez, A.L.; Sanchez-Gil, P.; Villalobos, G.J.; Herrera-Silveira, J.A. Ecosystem Functioning: The basis for sustainable management of Terminos Lagoon, Campeche, Mexico. In Gulf of Mexico Origin, Waters and Biota: Ecosystem-Based Management; Day, J.W., Yáñez-Arancibia, A., Eds.; Texas A & M University Press: College Station, TX, USA, 2013; Volume 4, pp. 131–152. [Google Scholar]
- Meade, R.H.; Moody, J.A. Causes for the decline of suspended-sediment discharge in the Mississippi River system, 1940–2007. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Clairain, E.J.; Kemp, G.P.; Laska, S.B.; Mitsch, W.J.; Whigham, D.F. Restoration of the Mississippi Delta: Lessons from hurricanes Katrina and Rita. Science 2007, 315, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couvillion, B.R.; Barras, J.A.; Steyer, G.D.; Sleavin, W.; Fischer, M.; Beck, H.; Trahan, N.; Griffin, B.; Heckman, D. Land Area Change in Coastal Louisiana from 1932 to 2010; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2011.
- Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E.; Wiseman, W.J., Jr. Gulf of Mexico hypoxia, AKA “The dead zone”. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002, 33, 235–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitburg, D.L.; Hondorp, D.W.; Davias, L.A.; Diaz, R.J. Hypoxia, nitrogen, and fisheries: Integrating effects across local and global landscapes. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; DiMarco, S.F.; Jackson, G.A. Relative role of wind forcing and riverine nutrient input on the extent of hypoxia in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernelöv, A. The threats from oil spills: Now, then, and in the future. Ambio 2010, 39, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourafalou, V.H.; Androulidakis, Y.S. Influence of Mississippi River induced circulation on the Deepwater Horizon oil spill transport. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 3823–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, M.L.; Kuenzer, C. Vulnerability assessments of coastal river deltas—Categorization and review. J. Coast. Conserv. 2015, 19, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condrey, R.E.; Hoffman, P.E.; Evers, D.E. The last naturally active delta complexes of the Mississippi River (LNDM): Discovery and implications. In Perspectives on the Restoration of the Mississippi Delta; Day, J.W., Kemp, G.P., Freeman, A.M., Muth, D.P., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 33–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, G.P.; Willson, C.S.; Rogers, J.D.; Westphal, K.A.; Binselam, S.A. Adapting to change in the lowermost Mississippi River: Implications for navigation, flood control and restoration of the delta ecosystem. In Perspectives on the Restoration of the Mississippi Delta; Day, J.W., Kemp, G.P., Freeman, A.M., Muth, D.P., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 51–84. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, J.M. Rising Tide: The Great Mississippi Flood of 1927 and How It Changed America; Simon & Shuster: New York, NY, USA, 1998; p. 528. [Google Scholar]
- Tessler, Z.D.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Grossberg, M.; Gladkova, I.; Aizenman, H.; Syvitski, J.P.M.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E. Profiling risk and sustainability in coastal deltas of the world. Science 2015, 349, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giosan, L.; Syvitski, J.; Constantinescu, S.; Day, J. Climate change: Protect the world’s deltas. Nature 2014, 516, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nittrouer, J.A.; Viparelli, E. Sand as a stable and sustainable resource for nourishing the Mississippi River delta. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, M.D.; Roberts, H.H. The Mississippi Delta Region: Past, present, and future. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2012, 40, 655–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, M.A.; Demas, C.R.; Ebersole, B.A.; Kleiss, B.A.; Little, C.D.; Meselhe, E.A.; Powell, N.J.; Pratt, T.C.; Vosburg, G.M. A water and sediment budget for the lower Mississippi-Atchafalaya River in flood years 2008–2010: Implications for sediment discharge to the oceans and coastal restoration in Louisiana. J. Hydrol. 2012, 432–433, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, J.R.; Leslie, H.M. Resilience to climate change in coastal marine ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2013, 5, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez-Arancibia, A.; Day, J.W.; Reyes, E. Understanding the coastal ecosystem-based management approach in the Gulf of Mexico. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 63, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seijo, J.C.; Caddy, J.F.; Arzapalo, W.W.; Cuevas-Jiminez, A. Considerations for an ecosystem approach to fisheries management in the southern Gulf of Mexico. In Gulf of Mexico Origin, Waters and Biota: Ecosystem-Based Management; Day, J.W., Yáñez-Arancibia, A., Eds.; Texas A & M University Press: College Station, TX, USA, 2013; Volume 4, pp. 319–336. [Google Scholar]
- Rozas, L.P.; Minello, T.J.; Zimmerman, R.J.; Caldwell, P. Nekton populations, long-term wetland loss, and the effect of recent habitat restoration in Galveston Bay, Texas, USA. Mari. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 344, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltz, D.M.; Yáñez-Arancibia, A. Ecosystem-based management of coastal fisheries in the Gulf of Mexico: Environmental and anthropogenic impacts and essential habitat protection. In Gulf of Mexico Origin, Waters and Biota: Ecosystem-Based Management; Day, J.W., Yáñez-Arancibia, A., Eds.; Texas A & M University Press: College Station, TX, USA, 2013; Volume 4, pp. 337–370. [Google Scholar]
- Karnauskas, M.; Schirripa, M.J.; Kelble, C.R.; Cook, G.S.; Craig, J.K. Ecosystems Status Report for the Gulf of Mexico; NOAA National Marine Fisheries Service: Miami, FL, USA, 2013; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Asche, F.; Bennear, L.S.; Oglend, A.; Smith, M.D. US shrimp market integration. Mar. Resour. Econ. 2012, 27, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, J.H., Jr.; Grimes, C.B.; Shaw, R.F. Life history, history, hysteresis, and habitat changes in Louisiana’s coastal ecosystem. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2008, 83, 197–215. [Google Scholar]
- Grimes, C.B. Fishery production and Mississippi River discharge. Fisheries 2001, 26, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Arancibia, A.; Lara-Dominguez, A.L.; Aguirre-Leon, S.; Diaz-Ruiz, S.; Amezcua, F.; Flores, D.; Chavance, P. Ecology of dominant fish populations in tropical estuaries: Environmental factors regulating biological strategies and production. In Fish Community Ecology in Estuaries and Coastal Lagoons: Towards an Ecosystem Integration; Yáñez-Arancibia, A., Ed.; UNAM Press: Mexico City, Mexico, 1985; pp. 311–366. [Google Scholar]
- Deegan, L.A.; Day, J.W.; Gosselink, J.G.; Yáñez-Arancibia, A.; Chavez, G.S.; Sanchez-Gil, P. Relationships among physical characteristics, vegetation distribution and fisheries yield in Gulf of Mexico estuaries. In Estuarine Variability; Wolf, D.A., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 83–100. [Google Scholar]
- Longhurst, A.R.; Pauly, D. Ecology of Tropical Oceans; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1986; p. 408. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, K.H. Ecology of Coastal Waters, with Implications for Management, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Science: Malden, MA, USA, 2000; p. 406. [Google Scholar]
- Wuebbles, D.; Meehl, G.; Hayhoe, K.; Karl, T.R.; Kunkel, K.; Santer, B.; Wehner, M.; Colle, B.; Fischer, E.M.; Fu, R.; et al. CMIP5 climate model analyses: Climate extremes in the United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, B.; Tian, H.; Ren, W.; Yang, J.; Yang, Q.; He, R.; Cai, W.; Lohrenz, S. Increasing Mississippi river discharge throughout the 21st century influenced by changes in climate, land use, and atmospheric CO2. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 4978–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F. Climate change hot-spots. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.A.; Whyte, F.S.; Stephenson, T.S.; Campbell, J.D. Why dry? Investigating the future evolution of the Caribbean low level jet to explain projected Caribbean drying. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Franco, R.; Coppola, E.; Giorgi, F.; Pavia, E.G.; Tefera Diro, G.; Graef, F. Inter-annual variability of precipitation over Southern Mexico and Central America and its relationship to sea surface temperature from a set of future projections from CMIP5 GCMs and RegCM4 CORDEX simulations. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbach, P.; Molina, L.; Locatelli, B.; Roupsard, O.; Mahe, G.; Neilson, R.; Corrales, L.; Scholze, M.; Ciasis, P. Modeling potential equilibrium states of vegetation and terrestrial water cycle of Mesoamerica under climate change scenarios. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority of Louisiana. Louisiana’s Comprehensive Master Plan for a Sustainable Coast; Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority of Louisiana: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2012; p. 188. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Silveira, J.A.; Comin, F.A.; Filograsso, L.C. Landscape, land use, and management in the coastal zone of Yucatan Peninsula. In Gulf of Mexico Origin, Waters and Biota: Ecosystem-Based Management; Day, J.W., Yáñez-Arancibia, A., Eds.; Texas A & M University Press: College Station, TX, USA, 2013; Volume 4, pp. 225–242. [Google Scholar]
- Lara-Dominguez, A.L.; Reyes, E.; Ortiz-Perez, M.A.; Mendez-Linares, P.; Sanchez-Gil, P.; Lomeli, D.Z.; Day, J.W.; Yáñez-Arancibia, A.; Hernandez, E.S. Ecosystem approach based on environmental units for management of the Centla Wetlands Biosphere Reserve: A critical review for its future protection. In Gulf of Mexico Origin, Waters and Biota: Ecosystem-Based Management; Day, J.W., Yáñez-Arancibia, A., Eds.; Texas A & M University Press: College Station, TX, USA, 2013; Volume 4, pp. 213–223. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, J.M.; Roberts, H.H.; Stone, G.W. Mississippi River delta: An overview. J. Coast. Res. 1998, 14, 698–716. [Google Scholar]
- Dahl, T.E. Status and Trends of Wetlands in the Conterminous United States 2004 to 2009: Report to Congress; U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; p. 108.
- Yáñez-Arancibia, A.; Day, J.W. Systems approach for coastal ecosystem-based management in the Gulf of Mexico: Ecological pulsing, the basis for sustainable management. In Gulf of Mexico Origin, Waters and Biota: Ecosystem-Based Management; Day, J.W., Yáñez-Arancibia, A., Eds.; Texas A & M University Press: College Station, TX, USA, 2013; Volume 4, pp. 371–392. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, D.W. Crevasses on the lower course of the Mississippi River. In Coastal Zone’93: Eighth Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management; Magoon, O.T., Wilson, W.S., Converse, H., Eds.; American Society of Civil Engineers: New Orleans, LA, USA, 1993; pp. 360–378. [Google Scholar]
- Saucier, R.T. Recent Geographic History of the Pontchartrain Basin, Louisiana; Louisiana State University Press: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, H.H. Dynamic changes of the Holocene Mississippi River delta plain: The delta cycle. J. Coast. Res. 1997, 13, 605–627. [Google Scholar]
- Törnqvist, T.E.; Wallace, D.J.; Storms, J.E.; Wallinga, J.; Van Dam, R.L.; Blaauw, M.; Derksen, M.S.; Klerks, C.J.; Meijneken, C.; Snijders, E.M. Mississippi Delta subsidence primarily caused by compaction of Holocene strata. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokka, R.K. The role of deep processes in late 20th century subsidence of New Orleans and coastal areas of southern Louisiana and Mississippi. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karegar, M.A.; Dixon, T.H.; Malservisi, R. A three-dimensional surface velocity field for the Mississippi Delta: Implications for coastal restoration and flood potential. Geology 2015, 43, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psuty, N.P. Beach-ridge development in Tabasco, Mexico. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1965, 55, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjerfve, B. Comparative oceanography of coastal lagoons. In Estuarine Variability; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 63–81. [Google Scholar]
- Yáñez-Arancibia, A.; Day, J.W. Hydrology, water budget and residence time in the Terminos Lagoon estuarine system, southern Gulf of Mexico. In Coastal Hydrology and Processes; Singh, V.P., Xu, Y.J., Eds.; Water Resources Publications LLC: Highlands Ranch, CO, USA, 2006; pp. 423–435. [Google Scholar]
- Salas-de-León, D.A.; Monreal-Gómez, M.A.; Díaz-Flores, M.A.; Salas-Monreal, D.; Velasco-Mendoza, H.; Riverón-Enzástiga, M.L.; Ortiz-Zamora, G. Role of near-bottom currents in the distribution of sediments within the Southern Bay of Campeche, Gulf of Mexico. J. Coast. Res. 2008, 24, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Chen, G.; Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; Sun, G.; Lu, C.; Xu, X.; Ren, W.; Pan, S.; Chappelka, A. Model estimates of net primary productivity, evapotranspiration and water use efficiency in the terrestrial ecosystems of the southern United States during 1895–2007. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 1311–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.D.; Pilley, C.T.; Raghunathan, V.V.; D’Sa, E.J.; Leben, R.R.; Hoffmann, N.G.; Brickley, P.J.; Coholan, P.D.; Sharma, N.; Graber, H.C.; et al. Impacts of Loop Current frontal cyclonic eddies and wind forcing on the 2010 Gulf of Mexico oil spill. In Monitoring and Modeling the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill: A Record-Breaking Enterprise; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Naval Research Laboratory. 1/25° GOM HYCOM. Available online: http://www7320.nrlssc.navy.mil/hycomGOM/glfmex.html (accessed on 1 November 2015).
- NOAA. ERDDAP. Available online: http://coastwatch.pfeg.noaa.gov/erddap/griddap/GOMModisAquaK490.graph (accessed on 1 November 2015).
- Perez-Brunius, P.; García-Carrillo, P.; Dubranna, J.; Sheinbaum, J.; Candela, J. Direct observations of the upper layer circulation in the southern Gulf of Mexico. Deep Sea Res. 2013, 85, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner-Devine, A.R.; Hetland, R.D.; MacDonald, D.G. Mixing and transport in coastal river plumes. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2015, 47, 569–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saramul, S.; Ezer, T. On the dynamics of low latitude, wide and shallow coastal system: Numerical simulations of the Upper Gulf of Thailand. Ocean Dyn. 2014, 64, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, W.J.; Garvine, R.W. Plumes and coastal currents near large river mouths. Estuaries 1995, 18, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hetland, R.D.; Marta-Almeida, M.; DiMarco, S.F. A numerical investigation of the Mississippi and Atchafalaya freshwater transport, filling and flushing times on the Texas-Louisiana shelf. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androulidakis, Y.S.; Kourafalou, V.H. On the processes that influence the transport and fate of Mississippi waters under flooding outflow conditions. Ocean Dyn. 2013, 63, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMego, G.J.; Bosart, L.F.; Endersen, G.W. An examination of the frequency and mean conditions surrounding frontal incursions into the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea. Mon. Weather Rev. 1976, 104, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.W.; Kemp, G.P.; Reed, D.J.; Cahoon, D.R.; Boumans, R.M.; Suhayda, J.M.; Gambrell, R. Vegetation death and rapid loss of surface elevation in two contrasting Mississippi delta salt marshes: The role of sedimentation, autocompaction and sea-level rise. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meselhe, E.A.; Georgiou, I.; Allison, M.A.; McCorquodale, J.A. Numerical modelsing of hydrodynamics and sediment transport in lower Mississippi at a proposed delta building site. J. Hydrol. 2012, 472, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, C.A. Effects of Reservoirs on Flood Discharges in the Kansas and Missouri River Basins; U.S. Geological Survey Circular 1120-E; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; p. 20.
- Yañez-Arancibia, A.; Aguirre-León, A.; Soberón-Chavez, G. Estuarine-related fisheries in Terminos lagoon and adjacent continental shelf (Southern Gulf of Mexico). In Conservation and Development: The Sustainable Use of Wetlands Resources, In Proceedings of the 3rd International Wetland Conference, Rennes, France, 19–23 September 1998; Maltby, E., Dugan, P.J., Lefervre, J.C., Eds.; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 1992; pp. 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Currie-Alder, B. The role of participation in ecosystem-based management: Insight from the Usumacinta watershed and the Terminos Lagoon, Mexico. In Gulf of Mexico Origin, Waters and Biota: Ecosystem-Based Management; Day, J.W., Yáñez-Arancibia, A., Eds.; Texas A & M University Press: College Station, TX, USA, 2013; Volume 4, pp. 201–212. [Google Scholar]
- Freudenburg, W.R.; Gramling, R.B.; Laska, S.; Erikson, K. Catastrophe in the Making: The Engineering of Katrina and the Disasters of Tomorrow; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; p. 224. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, L.; Calderon, R.; Cepeda, M.F.; Oczkowski, A.; Olsen, S.B.; Robadue, D. Managing Freshwater Inflows to Estuaries: Laguna de Terminos and its Watershed, Mexico; USAID & The Nature Conservancy: Narragansett, RI, USA, 2005; p. 28. [Google Scholar]








© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kemp, G.P.; Day, J.W.; Yáñez-Arancibia, A.; Peyronnin, N.S. Can Continental Shelf River Plumes in the Northern and Southern Gulf of Mexico Promote Ecological Resilience in a Time of Climate Change? Water 2016, 8, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8030083
Kemp GP, Day JW, Yáñez-Arancibia A, Peyronnin NS. Can Continental Shelf River Plumes in the Northern and Southern Gulf of Mexico Promote Ecological Resilience in a Time of Climate Change? Water. 2016; 8(3):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8030083
Chicago/Turabian StyleKemp, G. Paul, John W. Day, Alejandro Yáñez-Arancibia, and Natalie S. Peyronnin. 2016. "Can Continental Shelf River Plumes in the Northern and Southern Gulf of Mexico Promote Ecological Resilience in a Time of Climate Change?" Water 8, no. 3: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8030083
APA StyleKemp, G. P., Day, J. W., Yáñez-Arancibia, A., & Peyronnin, N. S. (2016). Can Continental Shelf River Plumes in the Northern and Southern Gulf of Mexico Promote Ecological Resilience in a Time of Climate Change? Water, 8(3), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8030083