Social Risk Dissociates Social Network Structure across Lateralized Behaviors in Spider Monkeys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Social Network Construction from Live Coded Behavior
2.2. Social Network Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
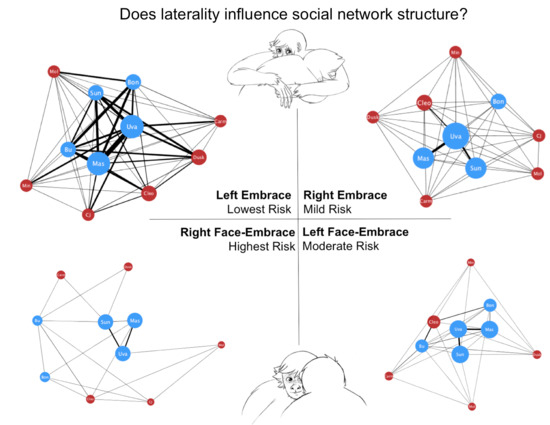
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Monkey | Sex | Embrace | Face-Embrace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bon Jovi (Bon) | M | 92 | 16 |
| Butch (Bu) | M | 107 | 39 |
| Carmelita (Carm) | F | 36 | 17 |
| Cleo | F | 126 | 63 |
| CJ | F | 78 | 14 |
| Dusky (Dusk) | F | 92 | 27 |
| Mason (Mas) | M | 181 | 61 |
| Mints (Min) | F | 47 | 2 |
| Molly (Mol) | F | 81 | 11 |
| Sunday (Sun) | M | 151 | 22 |
| Uva | M | 198 | 80 |


References
- Rogers, L.J.; Vallortigara, G. When and why did brains break symmetry? Symmetry 2015, 7, 2181–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNeilage, P.F.; Rogers, L.J.; Vallortigara, G. Origins of the left & right brain. Sci. Am. 2009, 301, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rogers, L.J.; Vallortigara, G.; Andrew, R.J. Divided Brains: The Biology and Behaviour of Brain Asymmetries; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vallortigara, G.; Rogers, L.J. Survival with an asymmetrical brain: Advantages and disadvantages of cerebral lateralization. Behav. Brain Sci. 2005, 28, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeving, E.R.; Belnap, S.C.; Nelson, E.L. Embraces are lateralized in spider monkeys (Ateles fusciceps rufiventris). Am. J. Primatol. 2017, 79, e22654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Melo, A.R.; Calmé, S.; Smith-Aguilar, S.E.; Ramos-Fernandez, G. Fission-fusion dynamics as a temporally and spatially flexible behavioral strategy in spider monkeys. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2018, 72, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffner, C.M.; Aureli, F. Embraces and grooming in captive spider monkeys. Int. J. Primatol. 2005, 26, 1093–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, J.F. Communication mechanisms and social integration in the black spider monkey, ateles fusciceps robustus, and related species. Smithson. Contrib. Zool. 1976, 213, 1–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aureli, F.; Schaffner, C.M.; Boesch, C.; Bearder, S.K.; Call, J.; Chapman, C.A.; Connor, R.; Di Fiore, A.; Dunbar, R.I.; Henzi, S.P. Fission-fusion dynamics. Curr. Anthropol. 2008, 49, 627–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos-Fernandez, G.; King, A.J.; Beehner, J.C.; Bergman, T.J.; Crofoot, M.C.; Di Fiore, A.; Lehmann, J.; Schaffner, C.M.; Snyder-Mackler, N.; Zuberbühler, K. Quantifying uncertainty due to fission–fusion dynamics as a component of social complexity. Proc. R. Soc. B 2018, 285, 20180532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sueur, C.; Jacobs, A.; Amblard, F.; Petit, O.; King, A.J. How can social network analysis improve the study of primate behavior? Am. J. Primatol. 2011, 73, 703–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brent, L.J.; Lehmann, J.; Ramos-Fernández, G. Social network analysis in the study of nonhuman primates: A historical perspective. A. J. Primatol. 2011, 73, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wey, T.; Blumstein, D.T.; Shen, W.; Jordán, F. Social network analysis of animal behaviour: A promising tool for the study of sociality. Anim. Behav. 2008, 75, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, O. The human connectome: A complex network. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1224, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton-Fisher, N.E. Animal Behaviour Pro: V1; Apple: Canterbury, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, P.; Bateson, P.P.G.; Bateson, P. Measuring Behaviour: An Introductory Guide; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Altmann, J. Observational study of behavior: Sampling methods. Behaviour 1974, 49, 227–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamada, T.; Kawai, S. An algorithm for drawing general undirected graphs. Inf. Process. Lett. 1989, 31, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerth, G.; Perony, N.; Schweitzer, F. Bats are able to maintain long-term social relationships despite the high fission–fusion dynamics of their groups. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2011, 278, 2761–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voelkl, B.; Kasper, C.; Schwab, C. Network measures for dyadic interactions: Stability and reliability. Am. J. Primatol. 2011, 73, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrangham, R.; Crofoot, M.; Lundy, R.; Gilby, I. Use of overlap zones among group-living primates: A test of the risk hypothesis. Behaviour 2007, 144, 1599–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.; Lee, P. Predation risk as an influence on group size in cercopithecoid primates: Implications for social structure. J. Zool. 1998, 245, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernvall, J.; Wright, P.C. Diversity components of impending primate extinctions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11279–11283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rebecchini, L.; Schaffner, C.M.; Aureli, F. Risk is a component of social relationships in spider monkeys. Ethology 2011, 117, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedigan, L.M.; Baxter, M.J. Sex differences and social organization in free-ranging spider monkeys (Ateles geoffroyi). Primates 1984, 25, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, A.; Milich, K.; Di Fiore, A. Demography and life history of a group of white-bellied spider monkeys (Ateles belzebuth) in western amazonia. Am. J. Primatol. 2018, e22899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.C.; Baty, M.; Ghandour, R.M.; Stockman, J.K.; Francisco, L.; Wagman, J. The intersection of intimate partner violence against women and hiv/aids: A review. Int. J. Inj. Control Saf. Promot. 2008, 15, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jewkes, R.K.; Levin, J.B.; Penn-Kekana, L.A. Gender inequalities, intimate partner violence and hiv preventive practices: Findings of a south african cross-sectional study. Soc. Sci. Med. 2003, 56, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güntürkün, O. Human behaviour: Adult persistence of head-turning asymmetry. Nature 2003, 421, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapelain, A.; Pimbert, P.; Aube, L.; Perrocheau, O.; Debunne, G.; Bellido, A.; Blois-Heulin, C. Can population-level laterality stem from social pressures? Evidence from cheek kissing in humans. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ocklenburg, S.; Güntürkün, O. Head-turning asymmetries during kissing and their association with lateral preference. Laterality 2009, 14, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedgewick, J.R.; Elias, L.J. Family matters: Directionality of turning bias while kissing is modulated by context. Laterality Asymmetries Body Brain Cogn. 2016, 21, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Kamp, J.; Canal-Bruland, R. Kissing right? On the consistency of the head-turning bias in kissing. Laterality 2011, 16, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Packheiser, J.; Rook, N.; Dursun, Z.; Mesenhöller, J.; Wenglorz, A.; Güntürkün, O.; Ocklenburg, S. Embracing your emotions: Affective state impacts lateralisation of human embraces. Psychol. Res. 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, O.; Stein, L.; Lucas, M. Lateral preferences in adult embracing: A test of the “hemispheric asymmetry” theory of infant cradling. J. Genet. Psychol. 1995, 156, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Monkey | Sex | Left Affiliative | Right Affiliative | Embrace | Face-Embrace |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bon Jovi (Bon) | M | 202 | 57 | 214 | 62 |
| Butch (Bu) | M | 294 | 82 | 263 | 128 |
| Carmelita (Carm) | F | 76 | 25 | 82 | 24 |
| Cleo | F | 208 | 62 | 208 | 73 |
| CJ | F | 108 | 32 | 123 | 19 |
| Dusky (Dusk) | F | 164 | 46 | 191 | 31 |
| Mason (Mas) | M | 372 | 104 | 342 | 141 |
| Mints (Min) | F | 79 | 38 | 136 | 4 |
| Molly (Mol) | F | 94 | 25 | 110 | 15 |
| Sunday (Sun) | M | 261 | 101 | 296 | 83 |
| Uva | M | 386 | 144 | 445 | 121 |
| Behavior | Laterality | Contact | Partner | Risk Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left Embrace | Low | Low | Low | Lowest |
| Right Embrace | High | Low | Low | Mild |
| Left Face-Embrace | Low | High | High | Moderate |
| Right Face-Embrace | High | High | High | Highest |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boeving, E.R.; Nelson, E.L. Social Risk Dissociates Social Network Structure across Lateralized Behaviors in Spider Monkeys. Symmetry 2018, 10, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10090390
Boeving ER, Nelson EL. Social Risk Dissociates Social Network Structure across Lateralized Behaviors in Spider Monkeys. Symmetry. 2018; 10(9):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10090390
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoeving, Emily R., and Eliza L. Nelson. 2018. "Social Risk Dissociates Social Network Structure across Lateralized Behaviors in Spider Monkeys" Symmetry 10, no. 9: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10090390
APA StyleBoeving, E. R., & Nelson, E. L. (2018). Social Risk Dissociates Social Network Structure across Lateralized Behaviors in Spider Monkeys. Symmetry, 10(9), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10090390