Skin Lesion Extraction Using Multiscale Morphological Local Variance Reconstruction Based Watershed Transform and Fast Fuzzy C-Means Clustering
Abstract
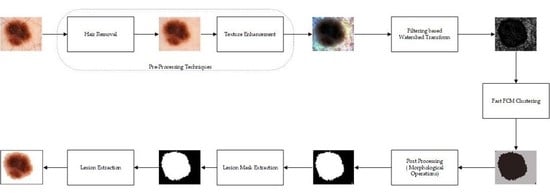
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Preprocessing techniques comprise hair removal and texture enhancement. To remove the hairs from the dermoscopic images, one of the popular hair removal approaches, DullRazor [2] is used. It removes the hairs from the input images and helps in further processing of the images.
- (2)
- Due to the large intensity variations in dermoscopic images, it is very difficult to segregate the lesion regions from healthy skin regions. Therefore, to enhance the lesion regions, the hair-removed images are processed through a contrast enhancement technique known as dominant orientation-based texture histogram equalization (DOTHE), and it enhances the lesion regions of the dermoscopic images based on histogram equalization.
- (3)
- Further, the preprocessed images come across the MMLVR-WT for generation of superpixels of images and compute the histogram of superpixel images to achieve fast fuzzy c-means (FCM). The proposed method uses the local variance method for accurate detection of boundary regions and helps to separate the lesions from healthy skin regions effectively.
- (4)
- Later, the postprocessing technique is used to remove the undesired pixel regions from the lesion regions.
2. Related Work
3. Datasets
4. Proposed Method
4.1. Input Image
4.2. Preprocessing Techniques
4.2.1. Hair Removal
4.2.2. Texture Enhancement
- (i)
- Initially the entire image that is to be enhanced is divided into a number of blocks.
- (ii)
- To differentiate each image block into smooth and rough blocks, a variance threshold is applied to each one.
- (iii)
- The rough blocks are further divided into dominant and non-dominant orientation blocks, based on singular value decomposition (SVD) of the gradient vectors of the block.
- (iv)
- The intensity distribution or histogram is computed from dominant orientation blocks (textures blocks) of the image.
- (v)
- Depending on the cumulative density function (CDF) of the input image, the texture histogram of the input image is mapped into a new dynamic range of the image.
- (vi)
- Finally, the texture-enhanced image is obtained using the mapped histogram.
4.3. Filtering-Based Watershed Transform
4.3.1. Gaussian Filter
4.3.2. Local Variance for Boundary Region Extraction
4.3.3. Multiscale Morphological Local Variance Reconstruction (MMLVR) Based on Watershed Transform
4.4. Fast Fuzzy C-Means Clustering
4.5. Postprocessing
4.5.1. Morphological Operation
4.5.2. Extraction of the Biggest Blob
5. Performance Analysis
6. Results and Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zortea, M.; Flores, E.; Scharcanski, J. A simple weighted thresholding method for the segmentation of pigmented skin lesions in macroscopic images. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 64, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Ng, V.; Gallagher, R.; Coldman, A.; McLean, D. Dullrazor®: A software approach to hair removal from images. Comput. Biol. Med. 1997, 27, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, F.; Sharma, A.; Khalaf, O.I.; Alotaibi, Y.; Alsufyani, A.; Alghamdi, S. Research on the Natural Language Recognition Method Based on Cluster Analysis Using Neural Network. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, S.; Khalaf, O.I. Prediction of Occupation Stress by Implementing Convolutional Neural Network Techniques. J. Cases Inf. Technol. 2021, 23, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavera Romero, C.A.; Ortiz, J.H.; Khalaf, O.I.; Ríos Prado, A. Business Intelligence: Business Evolution after Industry 4.0. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, O.I.; Romero, C.A.T.; Azhagu Jaisudhan Pazhani, A.; Vinuja, G. VLSI Implementation of a High-Performance Nonlinear Image Scaling Algorithm. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed Awan, M.; Shafry Mohd Rahim, M.; Nobanee, H.; Yasin, A.; Ibrahim Khalaf, O.; Ishfaq, U. A Big Data Approach to Black Friday Sales. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2021, 27, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Ping, F.; Pu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Montenegro-Marin, C.E.; Khalaf, O.I. Recognize and regulate the importance of work-place emotions based on organizational adaptive emotion control. Aggress. Violent Behav. 2021, 101557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, L.; Fu, C.W.; Heng, P.A. Deeply supervised rotation equivariant network for lesion segmentation in dermoscopy images. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; Volume 11041, pp. 235–243. ISBN 9783030012007. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, F.; Tarokh, M.J.; Ziaratban, M. Skin lesion segmentation from dermoscopic images by using Mask R-CNN, Retina-Deeplab, and graph-based methods. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 67, 102533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, G.; Ye, X. Automatic skin lesion segmentation by coupling deep fully convolutional networks and shallow network with textons. J. Med. Imaging 2019, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ünver, H.M.; Ayan, E. Skin Lesion Segmentation in Dermoscopic Images with Combination of YOLO and GrabCut Algorithm. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nida, N.; Irtaza, A.; Javed, A.; Yousaf, M.H.; Mahmood, M.T. Melanoma lesion detection and segmentation using deep region based convolutional neural network and fuzzy C-means clustering. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2019, 124, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Singh, S.K.; Chakraborty, A.; Das, A.; Bag, R. Melanoma Diagnosis Using Deep Learning and Fuzzy Logic. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.M.; Jiang, S.Y.; Yin, M.L. A region-based image segmentation method with mean-shift clustering algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2008 Fifth International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery FSKD, Jinan, China , 18–20 October 2008; Volume 2, pp. 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fa, F.; Peixoto, S.A.; Rebouc, P.P. Automatic skin lesions segmentation based on a new morphological approach via geodesic active contour. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2019, 55, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.M.M.; Fonseca-Pinto, R.; Paiva, R.P.; Assuncao, P.A.A.; Tavora, L.M.N.; Thomaz, L.A.; Faria, S.M.M. Dermoscopic skin lesion image segmentation based on Local Binary Pattern Clustering: Comparative study. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 59, 101924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Alshehri, M.; AlGhamdi, R.; Sharma, P.; Deep, V. A DE-ANN Inspired Skin Cancer Detection Approach Using Fuzzy C-Means Clustering. Mob. Networks Appl. 2020, 25, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Chen, Y.-P.P. Skin cancer extraction with optimum fuzzy thresholding technique. Appl. Intell. 2014, 40, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, D. Fast and robust fuzzy c-means clustering algorithms incorporating local information for image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2007, 40, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, A. Incorporating Adaptive Local Information Into Fuzzy Clustering for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 3990–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Ashour, A.; Smarandache, F. A Novel Skin Lesion Detection Approach Using Neutrosophic Clustering and Adaptive Region Growing in Dermoscopy Images. Symmetry 2018, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, T.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Meng, H.; Nandi, A.K. Superpixel-Based Fast Fuzzy C-Means Clustering for Color Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 27, 1753–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, A.-R.; Li, J.; Yang, G.; O’Shea, S.J. A machine learning approach to automatic detection of irregularity in skin lesion border using dermoscopic images. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2020, 6, e268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afza, F.; Sharif, M.; Mittal, M.; Khan, M.A.; Jude Hemanth, D. A hierarchical three-step superpixels and deep learning framework for skin lesion classification. Methods 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tsui, Y.Y.; Mandal, M. Skin Lesion Segmentation Using Deep Learning with Auxiliary Task. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.-R.; Li, J.; O’Shea, S.J. Towards the automatic detection of skin lesion shape asymmetry, color variegation and diameter in dermoscopic images. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0234352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salih, O.; Viriri, S. Skin Lesion Segmentation Using Stochastic Region-Merging and Pixel-Based Markov Random Field. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y. Skin lesion segmentation using high-resolution convolutional neural network. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 186, 105241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- das Chagas, J.V.S.; Ivo, R.F.; Guimarães, M.T.; de Rodrigues, D.A.; de Rebouças, S.E.; Filho, P.P. Fast fully automatic skin lesions segmentation probabilistic with Parzen window. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2020, 85, 101774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Raman, B.; Nayyar, K.; Awasthi, R. Automated skin lesion segmentation using attention-based deep convolutional neural network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 65, 102358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Q.; Celebi, M.E.; García, I.F. Hair removal methods: A comparative study for dermoscopy images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2011, 6, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Kaur, L.; Singh, K. Histogram equalization techniques for enhancement of low radiance retinal images for early detection of diabetic retinopathy. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2019, 22, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Vishwakarma, D.K.; Walia, G.S.; Kapoor, R. Contrast enhancement via texture region based histogram equalization. J. Mod. Opt. 2016, 63, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, D.; Kanungo, J.; Mahajan, A. An error-efficient Gaussian filter for image processing by using the expanded operand decomposition logarithm multiplication. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2018, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, G.; Chandran, K.; Khalaf, O.I.; Alotaibi, Y.; Alsufyani, A.; Alghamdi, S.A. Accurate Magnetic Resonance Image Super-Resolution Using Deep Networks and Gaussian Filtering in the Stationary Wavelet Domain. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 71406–71417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallaperumal, K.; Krishnaveni, K.; Varghese, J.; Saudia, S.; Annam, S.; Kumar, P. An efficient Multiscale Morphological Watershed Segmentation using Gradient and Marker Extraction. In Proceedings of the 2006 Annual IEEE India Conference, New Delhi, India, 10–12 April 2006; 2006; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Arroyo, J.L.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. Segmentation of skin lesions in dermoscopy images using fuzzy classification of pixels and histogram thresholding. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 168, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, N.; Mahdavi-Amiri, N. Kernel sparse representation based model for skin lesions segmentation and classification. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 182, 105038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Chen, H.; Dou, Q.; Qin, J.; Heng, P.-A. Automated Melanoma Recognition in Dermoscopy Images via Very Deep Residual Networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozorgtabar, B.; Sedai, S.; Roy, P.K.; Garnavi, R. Skin lesion segmentation using deep convolution networks guided by local unsupervised learning. IBM J. Res. Dev. 2017, 61, 6:1–6:8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajeddin, N.Z.; Asl, B.M. A general algorithm for automatic lesion segmentation in dermoscopy images. In Proceedings of the 2016 23rd Iranian Conference on Biomedical Engineering and 2016 1st International Iranian Conference on Biomedical Engineering (ICBME), Tehran, Iran, 24–25 November 2016; pp. 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Soudani, A.; Barhoumi, W. An image-based segmentation recommender using crowdsourcing and transfer learning for skin lesion extraction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 118, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegun, A.A.; Viriri, S. Deep Learning-Based System for Automatic Melanoma Detection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 7160–7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Dahal, L.; Samarakoon, P.N.; Tushar, F.I.; Martí, R. DSNet: Automatic dermoscopic skin lesion segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 120, 103738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xia, Y.; Shen, C. A Mutual Bootstrapping Model for Automated Skin Lesion Segmentation and Classification. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2482–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaymak, R.; Kaymak, C.; Ucar, A. Skin lesion segmentation using fully convolutional networks: A comparative experimental study. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 161, 113742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, L. Skin Lesion Analysis towards Melanoma Detection Using Deep Learning Network. Sensors 2018, 18, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pezhman Pour, M.; Seker, H. Transform domain representation-driven convolutional neural networks for skin lesion segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 144, 113129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, Ş.; Özkaya, U. Skin Lesion Segmentation with Improved Convolutional Neural Network. J. Digit. Imaging 2020, 33, 958–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, K.; Gilani, S.O.; Waris, A.; Ahmed, A.; Jamil, M.; Khan, M.N.; Sohail Kashif, A. Skin Lesion Segmentation from Dermoscopic Images Using Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2020, 20, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azad, R.; Asadi-Aghbolaghi, M.; Fathy, M.; Escalera, S. Bi-Directional ConvLSTM U-Net with Densley Connected Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, B.; Xia, Z.; Jiang, F.; Jiang, X.; Ge, Z.; Xu, Y.; Qin, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, T.; Wang, S. Skin lesion segmentation via generative adversarial networks with dual discriminators. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 64, 101716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Hardie, R.C.; Narayanan Narayanan, B.; De Silva, S. Deep Learning Ensemble Methods for Skin Lesion Analysis towards Melanoma Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE National Aerospace and Electronics Conference (NAECON), Dayton, OH, USA, 15–19 July 2019; pp. 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Q.; Cui, H.; Sun, C.; Meng, Z.; Su, R. Cascade knowledge diffusion network for skin lesion diagnosis and segmentation. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 99, 106881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Gaussian Filter Kernel Size | Sigma | Acc | DC | JI | SN | SP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 × 3 | 1 | 96.41 | 95.61 | 91.95 | 99.63 | 94.76 |
| 2 | 95.96 | 95.08 | 90.62 | 99.12 | 93.91 | |
| 3 | 96.10 | 95.24 | 90.91 | 99.11 | 94.15 | |
| 4 | 96.12 | 95.26 | 90.85 | 99.11 | 94.18 | |
| 5 | 96.02 | 95.15 | 90.75 | 99.09 | 94.03 | |
| 6 | 96.03 | 95.15 | 90.76 | 99.09 | 94.04 | |
| 7 | 96.03 | 95.15 | 90.76 | 99.09 | 94.05 | |
| 8 | 96.03 | 95.15 | 90.76 | 99.09 | 94.04 | |
| 9 | 96.03 | 95.15 | 90.76 | 99.09 | 94.04 | |
| 5 × 5 | 1 | 96.02 | 95.16 | 90.77 | 99.30 | 93.90 |
| 2 | 96.11 | 95.26 | 90.75 | 99.22 | 94.10 | |
| 3 | 96.02 | 95.21 | 91.11 | 99.03 | 94.16 | |
| 4 | 95.99 | 95.11 | 90.68 | 99.28 | 93.85 | |
| 5 | 96.16 | 95.21 | 91.05 | 99.27 | 94.14 | |
| 6 | 96.10 | 95.24 | 90.91 | 99.16 | 94.11 | |
| 7 | 96.16 | 95.21 | 91.05 | 99.15 | 94.02 | |
| 8 | 96.12 | 95.26 | 90.95 | 99.20 | 94.12 | |
| 9 | 96.09 | 95.23 | 90.89 | 99.20 | 94.07 | |
| 7 × 7 | 1 | 95.98 | 95.11 | 90.67 | 99.28 | 93.14 |
| 2 | 93.15 | 95.29 | 91.00 | 98.90 | 94.04 | |
| 3 | 96.09 | 95.22 | 90.89 | 99.07 | 94.02 | |
| 4 | 96.17 | 95.20 | 91.03 | 98.76 | 94.39 | |
| 5 | 96.16 | 95.29 | 91.01 | 98.77 | 94.17 | |
| 6 | 96.02 | 95.06 | 91.13 | 98.93 | 94.05 | |
| 7 | 96.17 | 95.12 | 91.06 | 98.97 | 94.06 | |
| 8 | 96.13 | 95.10 | 91.11 | 98.97 | 94.18 | |
| 9 | 96.12 | 95.03 | 91.26 | 98.95 | 94.13 | |
| 9 × 9 | 1 | 95.98 | 95.11 | 90.67 | 99.28 | 93.84 |
| 2 | 96.02 | 95.22 | 91.24 | 99.15 | 94.07 | |
| 3 | 96.15 | 95.29 | 91.01 | 98.96 | 94.13 | |
| 4 | 96.16 | 95.29 | 91.01 | 98.84 | 94.11 | |
| 5 | 96.02 | 95.07 | 91.16 | 98.91 | 94.08 | |
| 6 | 96.15 | 95.36 | 91.33 | 98.83 | 94.04 | |
| 7 | 96.17 | 95.02 | 91.25 | 98.90 | 94.16 | |
| 8 | 96.11 | 95.40 | 91.21 | 98.88 | 94.05 | |
| 9 | 96.02 | 95.40 | 91.21 | 98.88 | 94.14 |
| Gaussian Filter Kernel Size | Sigma | Acc | DC | JI | SN | SP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 × 3 | 1 | 96.18 | 95.33 | 91.07 | 99.17 | 94.23 |
| 2 | 96.21 | 95.37 | 91.15 | 99.31 | 94.19 | |
| 3 | 96.18 | 95.34 | 91.10 | 99.31 | 94.15 | |
| 4 | 96.16 | 95.32 | 91.05 | 99.31 | 94.12 | |
| 5 | 96.16 | 95.32 | 91.05 | 99.31 | 94.12 | |
| 6 | 96.16 | 95.31 | 91.05 | 99.31 | 94.11 | |
| 7 | 96.18 | 95.34 | 91.10 | 99.31 | 94.15 | |
| 8 | 96.18 | 95.34 | 91.09 | 99.31 | 94.15 | |
| 9 | 96.18 | 95.34 | 91.09 | 99.31 | 94.15 | |
| 5 × 5 | 1 | 96.21 | 95.49 | 91.37 | 99.27 | 94.39 |
| 2 | 96.24 | 95.41 | 91.21 | 99.19 | 94.33 | |
| 3 | 96.24 | 95.41 | 91.21 | 99.21 | 94.32 | |
| 4 | 96.29 | 95.46 | 91.32 | 99.16 | 94.43 | |
| 5 | 96.22 | 95.37 | 91.16 | 99.18 | 94.29 | |
| 6 | 96.26 | 95.43 | 91.26 | 99.19 | 94.36 | |
| 7 | 96.25 | 95.42 | 91.24 | 99.19 | 94.35 | |
| 8 | 96.28 | 95.45 | 91.29 | 99.19 | 94.39 | |
| 9 | 96.25 | 95.41 | 91.22 | 99.09 | 94.40 | |
| 7 × 7 | 1 | 96.30 | 95.48 | 91.35 | 99.22 | 94.41 |
| 2 | 96.26 | 95.42 | 91.25 | 99.15 | 94.38 | |
| 3 | 96.34 | 95.53 | 91.43 | 99.19 | 94.50 | |
| 4 | 96.34 | 95.52 | 91.42 | 99.22 | 94.47 | |
| 5 | 96.24 | 95.41 | 91.22 | 99.20 | 94.33 | |
| 6 | 96.21 | 95.37 | 91.15 | 99.15 | 94.31 | |
| 7 | 96.23 | 95.39 | 91.19 | 99.15 | 94.34 | |
| 8 | 96.23 | 95.40 | 91.20 | 99.16 | 94.34 | |
| 9 | 96.20 | 95.36 | 91.13 | 99.19 | 94.26 | |
| 9 × 9 | 1 | 96.04 | 95.37 | 90.21 | 99.18 | 93.94 |
| 2 | 96.19 | 95.13 | 91.12 | 99.05 | 93.07 | |
| 3 | 96.22 | 95.42 | 91.06 | 98.96 | 94.03 | |
| 4 | 96.16 | 95.25 | 90.26 | 98.94 | 94.11 | |
| 5 | 96.04 | 95.41 | 91.04 | 98.91 | 93.08 | |
| 6 | 96.29 | 95.26 | 91.30 | 98.73 | 94.04 | |
| 7 | 96.07 | 95.02 | 91.21 | 98.93 | 94.16 | |
| 8 | 96.11 | 95.30 | 91.07 | 98.38 | 94.25 | |
| 9 | 96.12 | 95.40 | 91.21 | 98.88 | 94.24 |
| Method | Acc | DC | JI | SN | SP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nida et al. [15] | 94.2 | 94.0 | 93.0 | 95.0 | 94.0 |
| Garcia-Arroyo and Garcia-Zapirain [40] | 93.4 | 86.9 | 79.1 | 87.0 | 97.8 |
| Moradi and Mahdavi-Amiri [41] | 93.0 | 91.2 | 83.6 | 92.1 | 91.5 |
| Yu et al. [42] | 94.9 | 89.7 | 82.9 | 91.1 | 95.7 |
| Bozorgtabar et al. [43] | 92.3 | 89.2 | 80.6 | --- | --- |
| Tajeddin and Asl [44] | 94.6 | 88.8 | 81.0 | 83.2 | 98.7 |
| Xie et al. [31] | 93.8 | 91.8 | 85.8 | 87.0 | 96.4 |
| Proposed method | 95.4 | 94.5 | 93.2 | 94.7 | 98.5 |
| Method | Acc | DC | JI | SN | SP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ünver and Ayan [14] | 93.3 | 84.2 | 74.8 | 90.8 | 92.6 |
| Soudani and Barhoumi [45] | 94.9 | 88.1 | 78.9 | 85.8 | 95.6 |
| Adegun and Viriri [46] | 95.0 | 92.0 | -- | 97.0 | 96.0 |
| Banerjee et al. [16] | 97.3 | 93.0 | 86.9 | 91.4 | 98.7 |
| Hasan et al. [47] | 95.3 | -- | -- | 87.5 | 95.5 |
| Xie et al. [48] | 94.7 | 87.8 | 80.4 | 87.4 | 96.8 |
| Kaymak et al. [49] | 93.9 | 84.1 | 72.5 | -- | -- |
| Guo et al. [24] | 95.3 | 90.4 | 83.2 | 97.5 | 88.8 |
| Li and Shen [50] | 95.0 | 83.9 | 75.3 | 85.5 | 97.4 |
| Pezhman Pour and Seker [51] | 94.5 | 87.1 | 78.2 | 88.3 | 98.1 |
| Öztürk and Özkaya [52] | 95.3 | 88.6 | 78.3 | 85.4 | 98.0 |
| Bagheri et al. [12] | 94.1 | 87.4 | 80.0 | 88.3 | 96.5 |
| Liu et al. [28] | 94.32 | -- | 79.46 | 88.76 | -- |
| Zafar et al. [53] | -- | 85.8 | 77.2 | -- | -- |
| Zhang et al. [13] | 92.7 | 81.8 | 72.9 | 83.7 | 96.4 |
| Chagas et al. [32] | 95.7 | 89.3 | 82.5 | 84.7 | 99.3 |
| Proposed method | 97.8 | 93.2 | 87.1 | 96.8 | 99.8 |
| Method | Acc | DC | JI | SN | SP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Azad et al. [54] | 93.7 | -- | -- | 78.5 | 98.2 |
| Lei et al. [55] | 92.9 | 88.5 | 82.4 | 95.3 | 91.1 |
| Ali et al. [56] | 93.6 | 88.7 | 81.5 | --- | --- |
| Arora et al. [33] | 95.0 | 91.0 | 83.0 | 94.0 | 95.0 |
| Ali et al. [26] | 93.6 | -- | -- | 100 | 92.5 |
| Li and Shen [50] | 95.0 | 83.9 | 75.3 | 85.5 | 97.4 |
| Jin et al. [57] | 93.4 | 87.7 | 79.4 | 96.7 | 90.4 |
| Salih and Viriri [30] | 89.47 | 80.67 | 72.45 | 79.45 | 95.09 |
| Proposed method | 96.9 | 93.0 | 87.0 | 95.8 | 98.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rout, R.; Parida, P.; Alotaibi, Y.; Alghamdi, S.; Khalaf, O.I. Skin Lesion Extraction Using Multiscale Morphological Local Variance Reconstruction Based Watershed Transform and Fast Fuzzy C-Means Clustering. Symmetry 2021, 13, 2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13112085
Rout R, Parida P, Alotaibi Y, Alghamdi S, Khalaf OI. Skin Lesion Extraction Using Multiscale Morphological Local Variance Reconstruction Based Watershed Transform and Fast Fuzzy C-Means Clustering. Symmetry. 2021; 13(11):2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13112085
Chicago/Turabian StyleRout, Ranjita, Priyadarsan Parida, Youseef Alotaibi, Saleh Alghamdi, and Osamah Ibrahim Khalaf. 2021. "Skin Lesion Extraction Using Multiscale Morphological Local Variance Reconstruction Based Watershed Transform and Fast Fuzzy C-Means Clustering" Symmetry 13, no. 11: 2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13112085
APA StyleRout, R., Parida, P., Alotaibi, Y., Alghamdi, S., & Khalaf, O. I. (2021). Skin Lesion Extraction Using Multiscale Morphological Local Variance Reconstruction Based Watershed Transform and Fast Fuzzy C-Means Clustering. Symmetry, 13(11), 2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13112085