A CNN-MPSK Demodulation Architecture with Ultra-Light Weight and Low-Complexity for Communications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
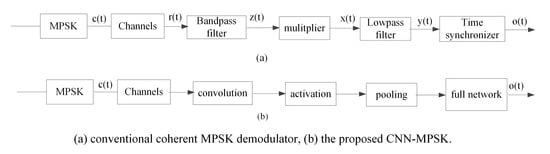
2. Conventional Modulation and Demodulation of MPSK
3. The Proposed CNN-MPSK Architecture
3.1. Architecture Presentation
3.2. Parameter Distribution of CNN-MPSK
4. Comparison between CNN-MPSK and Coherent Demodulation in Terms of Performance and Computational Complexity
4.1. The Accuracy and Loss Curves
4.2. BER Comparison of CNN-MPSK and Coherent Demodulation
4.3. Comparison of Multiplications and Additions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koh, K.; Mortazavi, S.Y.; Afroz, S. Time Interleaved RF Carrier Modulations and Demodulations. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2014, 61, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, A.D.; Reed, J.T.; Odom, J.L.; Lanterman, A.D.; Ma, X. Performance of a Linear-Detector Joint Radar-Communication System in Doubly Selective Channels. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Rahman, A.I.; Cartledge, J.C. Evaluating the Impact of QAM Constellation Subset Selection on the Achievable Information Rates of Multidimensional Formats in Fully Loaded Systems. J. Lightw. Technol. 2018, 36, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Yang, J.; Gui, G. Data-driven deep learning for automatic modulation recognition in cognitive radios. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 4074–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, J.N.; Morocho-Cayamcela, M.E.; Lim, W. CGDNet: Efficient hybrid deep learning model for robust automatic modulation recognition. IEEE Netw. Lett. 2021, 3, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Z. Deep learning based modulation recognition with multi-cue fusion. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 1757–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, T.J.; Roy, T.; Clancy, T.C. Over-the-air deep learning based radio signal classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2018, 12, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, F.; Chen, P.; Wu, L.; Wang, X. Automatic modulation classification: A deep learning enabled approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 10760–10772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.H.; Dang, X. Low-complexity deep learning and RBFN architectures for modulation classification of space-time block-code (STBC)-MIMO systems. Digit. Signal Process. 2020, 99, 102656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Fan, Y. Unsupervised feature learning and automatic modulation classification using deep learning model. Phys. Commun. 2017, 25, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, P.; Banerjee, S.; Hempel, M.; Sharif, H. A novel deep learning and polar transformation framework for an adaptive automatic modulation classification. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 13243–13258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Fu, M.; Cui, Y.; Chen, X. Modulation format recognition and OSNR estimation using CNN-based deep learning. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2017, 29, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, H.; Wang, C.; Gan, C.; Xiang, Y. Automatic modulation classification using CNN-LSTM based dual-stream structure. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 13521–13531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Modulation recognition with pre-denoising convolutional neural network. Electron. Lett. 2020, 56, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.A.; Fang, Y.; Huang, H.; Bao, C.; Pan, Z.; et al. Eye diagram measurement-based joint modulation format, OSNR, ROF, and skew monitoring of coherent channel using deep learning. J. Light. Technol. 2019, 37, 5907–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Meng, J. Convolutional neural network and multi-feature fusion for automatic modulation classification. Electron. Lett. 2019, 55, 895–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, M.; Guan, Y.L.; Li, S.; Xiang, W. Adaptive spatial modulation MIMO based on machine learning. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2019, 37, 2117–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikha, H.B.; Almadhor, A.; Khalid, W. Machine Learning for 5G MIMO Modulation Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Cheng, K.; Kang, G. A machine-learning-based blind detection on interference modulation order in NOMA systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 2463–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.N.; Zhong, K.; Al-Arashi, W.H.; Yu, C.; Lu, C.; Lau, A.P.T. Modulation format identification in coherent receivers using deep machine learning. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2016, 28, 1886–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, P.; Lin, Z. Artificial intelligence in education: A review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 5264–5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.N.; Lu, C.; Lau, A.P.T. Joint modulation format/bit-rate classification and signal-to-noise ratio estimation in multipath fading channels using deep machine learning. Electron. Lett. 2016, 52, 1272–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lu, S.; El-Hajjar, M.; Yang, L.L. Machine learning assisted adaptive index modulation for mmWave communications. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2020, 1, 1425–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Li, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, A.; Liu, W.; Hou, X. Deep Learning Aided Grant-Free NOMA Toward Reliable Low-Latency Access in Tactile Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 2995–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.A.; Shirmohammadi, S.; Altamimi, S. A Multimodal Deep Learning-Based Distributed Network Latency Measurement System. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 2487–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Bu, Y.; Chen, P.; Lau, F.C.; Al Otaibi, S. Irregular-Mapped Protograph LDPC-Coded Modulation: A Bandwidth-Efficient Solution for 6G-Enabled Mobile Networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, Y.S.; Hou, X.; Jap, D.; Breier, J.; Bhasin, S. Back to the basics: Seamless integration of side-channel pre-processing in deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 3215–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesiya, M.F. Digital Information Transmission Using Carrier Modulation. In Contemporary Communication Systems; Lange, M., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 600–610. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Chen, P.; Cai, G.; Lau, F.C.; Liew, S.C.; Han, G. Outage-Limit-Approaching Channel Coding for Future Wireless Communications: Root-Protograph Low-Density Parity-Check Codes. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2019, 14, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safak, M. Optimum Receiver in AWGN Channel. In Digital Communications; Wiley, John Wiley and Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2017; pp. 298–319. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Xie, Z.; Fang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Mumtaz, S.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. Physical-Layer Network Coding: An Efficient Technique for Wireless Communications. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haykin, S. Signaling over AWGN Channels. In Digital Communication Systems; Knecht, J., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 323–410. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin, S.; Moher, M. Digital band-pass transmission techniques. In Communication Systems; Hong, S., Melhom, A., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 313–350. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, L.; Jiang, J. Finite impulse response filter design. In Digital Signal Processing: Fundamentals and Applications; Merken, S., Ed.; Academic Press: Stanford, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 229–236, 550–558. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Wang, L.; Lau, F.C.M. One Analog STBC-DCSK Transmission Scheme not Requiring Channel State Information. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2013, 360, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.D.; Swamy, M.N.S. FIR Digital Filter Design. In Digital Signal Processing: Theory and Practice; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 325–338. [Google Scholar]







| Type of Operation | Input Shape | Output Shape | Size of Kernel | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| convolution | 1 × n × 1 | 1 × n × 1 | 1 × 3 | 4 |
| activation | 1 × n × 1 | 1 × n × 1 | 0 | 0 |
| pooling | 1 × n × 1 | 1 × × 1 | 0 | 0 |
| full connection | 1 × × 1 | 1 × M | M × | M × + M |
| Type of Demodulation | Multiplications | Additions | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| coherent | |||
| CNN-BPSK |
| Type of Algorithms | Parameters | Multiplications | Additions | −5 dB | 0 dB | 10 dB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| our CNN BPSK | 10 | 10 | 10 | 78.6% | 92% | 99.9% |
| our CNN 4PSK | 10 | 10 | 10 | 50.9% | 70.8% | 99.8% |
| our CNN 8PSK | 10 | 10 | 10 | 24% | 40.9% | 99% |
| our CNN 16PSK | 10 | 10 | 10 | 12% | 21.8% | 61.6% |
| ResNet BPSK [7] | 50% | 97% | 99% | |||
| ResNet 4PSK [7] | 7% | 70% | 99% | |||
| ResNet 8PSK [7] | 7% | 25% | 99% | |||
| ResNet 16PSK [7] | 6% | 40% | 85% | |||
| DBN BPSK [11] | 75% | 97% | 99% | |||
| DBN 4PSK [11] | 60% | 80% | 99% | |||
| CNN based BPSK [11] | 61% | 90% | 99% | |||
| CNN based 4PSK [11] | 50% | 75% | 99% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, X. A CNN-MPSK Demodulation Architecture with Ultra-Light Weight and Low-Complexity for Communications. Symmetry 2022, 14, 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14050873
Wang B, Lin Z, Zhang X. A CNN-MPSK Demodulation Architecture with Ultra-Light Weight and Low-Complexity for Communications. Symmetry. 2022; 14(5):873. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14050873
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Bingrui, Zhijian Lin, and Xingang Zhang. 2022. "A CNN-MPSK Demodulation Architecture with Ultra-Light Weight and Low-Complexity for Communications" Symmetry 14, no. 5: 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14050873
APA StyleWang, B., Lin, Z., & Zhang, X. (2022). A CNN-MPSK Demodulation Architecture with Ultra-Light Weight and Low-Complexity for Communications. Symmetry, 14(5), 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14050873