Surface Weathering of Tuffs: Compositional and Microstructural Changes in the Building Stones of the Medieval Castles of Hungary
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Environmental Setting
4. Petrographic Study
5. Surface Weathering
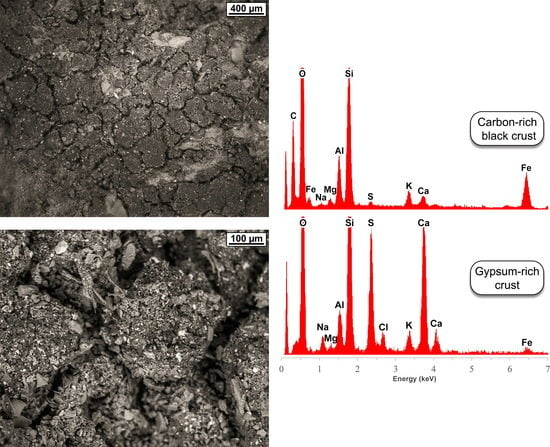
5.1. Mineralogy and Microstructure
5.2. Trace-Element Chemical Composition
5.3. Microporosity
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Török, Á. Hungarian dimensional stones: An overview. Z. Der Dtsch. Ges. Geowiss. 2007, 158, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleb, B. Eger Múltja a Jelenben–The Past in the Present Life of Eger; Eger Városi Tanács VB Műszaki Osztálya: Közdok, Budapest, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Kleb, B. Engineering-geological test on settlements with cellar difficulties. Period. Polytech. Civ. Eng. 1988, 32, 99–129. [Google Scholar]
- Baráz, C.; Kiss, G. Marked Stones and Places of Fable in the Mátra Forest (NE-Hungary); Bükk National Park Directorate: Eger, Hungry, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Harangi, S. Volcanic heritage of the Carpathian-Pannonian Region in eastern-central Europe. In Volcanic Tourist Destinations; Erfurt-Cooper, P., Ed.; Geoheritage, Geoparks and Geotourism; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 103–123. [Google Scholar]
- Forgó, L.Z.; Török, Á. Influence of petrophysical and petrographical properties on the behaviour of rhyolite tuff, example from Eger, Hungary. In International PhD Symposium in Civil Engineering, 5th ed.; Walraven, J., Blaauwendraad, J., Scarpas, T., Snijder, B., Eds.; Special Publications 271; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2004; pp. 589–597. [Google Scholar]
- Török, Á.; Forgó, L.Z.; Vogt, T.; Löbens, S.; Siegesmund, S.; Weiss, T. The influence of lithology and pore-size distribution on the durability of acid volcanic tuffs, Hungary. In Building Stone Decay: From Diagnosis to Conservation; Přikryl, R., Smith, B.J., Eds.; The Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2007; pp. 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Stück, H.; Forgó, L.Z.; Rüdrich, J.; Siegesmund, S.; Török, Á. The behaviour of consolidated volcanic tuffs: Weathering mechanisms under simulated laboratory conditions. Environ. Geol. 2008, 56, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Németh, G.; Mlinárik, L.; Török, Á. Adsorption and chemical precipitation of lead and zinc from contaminated solutions in porous rocks: Possible application in environmental protection. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 122, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Török, Á.; Barsi, Á.; Bögöly, G.; Lovas, T.; Somogyi, Á.; Görög, P. Slope stability and rockfall assessment of volcanic tuffs using RPAS with 2-D FEM slope modelling. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Germinario, L.; Török, Á. Variability of technical properties and durability in volcanic tuffs from the same quarry region–examples from Northern Hungary. Eng. Geol. 2019, 262, 105319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchetti, P.L.; Lombardi, G.; Marini, S.; Meucci, C. The volcanic rocks of the monuments of the Forum and Palatine (Rome): Characterization, alterations, and results of chemical treatments. In Lavas and Volcanic Tuffs; Charola, A.E., Koestler, R.J., Lombardi, G., Eds.; ICCROM: Rome, Italy, 1994; pp. 83–105. [Google Scholar]
- De Casa, G.; Giglio, G.; Lombardi, G.; Mariottini, M. Characterization and state of decay of the volcanic tuff of the Tabularium in the Roman Forum, Italy. In Lavas and Volcanic Tuffs; Charola, A.E., Koestler, R.J., Lombardi, G., Eds.; ICCROM: Rome, Italy, 1994; pp. 107–127. [Google Scholar]
- Paterno, M.C.P. A Study of the Weathering of Volcanic tuffs In a Tropical Environment, Including the Evaluation of a Consolidant. Master’s Thesis, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ostroumov, M.; Garduño-Monroy, V.H.; Carreón-Nieto, H.; Lozano-Santa Cruz, R. Mineralogía y geoquímica de los procesos de degradación en monumentos históricos: Primer acercamiento a un caso mexicano (Morelia, Michoacán). Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geológicas 2003, 20, 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- Topal, T.; Sözmen, B. Deterioration mechanisms of tuffs in Midas monument. Eng. Geol. 2003, 68, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijland, T.G.; Brendle, S.; van Hees, R.P.J.; de Haas, G.J.L.M. Decay of Rhenish tuff in Dutch monuments. Part 1: Use, composition and weathering. Heron 2004, 48, 149–166. [Google Scholar]
- Doehne, E.; Simon, S.; Mueller, U.; Carson, D.; Ormsbee, A. Characterization of carved rhyolite tuff–The Hieroglyphic Stairway of Copán, Honduras. Restor. Build. Monum. 2005, 11, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedef, V.; Kocak, K.; Doyen, A.; Ozsen, H.; Kekec, B. Effect of salt crystallization on stones of historical buildings and monuments, Konya, Central Turkey. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedel, H. Salt-induced alveolar weathering of rhyolite tuff on a building: Causes and processes. In Proceedings of the International Conference “Salt Weathering on Buildings and Stone Sculptures”, Copenhagen, Denmark, 22–24 October 2008; pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Erguler, Z.A. Field-based experimental determination of the weathering rates of the Cappadocian tuffs. Eng. Geol. 2009, 105, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccioli, P.; Cattuto, C.; Plescia, P.; Valentini, V.; Negrotti, R. Geochemical and engineering geological properties of the volcanic tuffs used in the Etruscan tombs of Norchia (northern Latium, Italy) and a study of the factors responsible for their rapid surface and structural decay. Archaeometry 2010, 52, 229–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguchi, C.; Takaya, Y.; Yamazaki, M.; Ohnishi, R.; Thidar, A.; Hatta, T. High acidic sulphate salt production on the cave wall in the Yoshimi Hyaku-Ana historic site, central Japan. In Proceedings of the XIX CBGA Congress, Thessaloniki, Greece, 23–26 September 2010; pp. 413–419. [Google Scholar]
- Oguchi, C.T.; Yuasa, H. Simultaneous wetting/drying, freeze/thaw and salt crystallization experiments of three types of Oya tuff. In Natural Stone Resources for Historical Monuments; Přikryl, R., Török, Á., Eds.; Special Publications 333; The Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2010; pp. 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes-Zamudio, V.; Angeles-Chávez, C.; Cervantes, J. Clay minerals in historic buildings. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 104, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, A.B. Durability assessment of the Alaçatı tuff (Izmir) in western Turkey. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 1909–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosonyi, E.; Cobârzan, N. Weathering, conservation state and compatibility studies on the construction materials used for renovation of the historical Dej reformed church fortifying walls. Rom. J. Mater. 2016, 46, 542–551. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.H.; Araki, N. Evaluation of nondestructive diagnosis and material characteristics of stone lantern at Damyang Gaeseonsaji temple site in Korea. J. Conserv. Sci. 2019, 35, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harangi, S. Neogene to Quaternary volcanism of the Carpathian-Pannonian Region–A review. Acta Geol. Hung. 2001, 44, 223–258. [Google Scholar]
- Harangi, S.; Lenkey, L. Genesis of the Neogene to Quaternary volcanism in the Carpathian-Pannonian region: Role of subduction, extension, and mantle plume. In Cenozoic Volcanism in the Mediterranean Area; Beccaluva, L., Bianchini, G., Wilson, M., Eds.; Special Paper 418; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2007; pp. 67–92. [Google Scholar]
- Seghedi, I.; Downes, H. Geochemistry and tectonic development of Cenozoic magmatism in the Carpathian-Pannonian region. Gondwana Researh 2011, 20, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horváth, F.; Musitz, B.; Balázs, A.; Végh, A.; Uhrin, A.; Nádor, A.; Koroknai, B.; Pap, N.; Tóth, T.; Wórum, G. Evolution of the Pannonian basin and its geothermal resources. Geothermics 2015, 53, 328–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukács, R.; Harangi, S.; Guillong, M.; Bachmann, O.; Fodor, L.; Buret, Y.; Dunkl, I.; Sliwinski, J.; von Quadt, A.; Peytcheva, I.; et al. Early to Mid-Miocene syn-extensional massive silicic volcanism in the Pannonian Basin (East-Central Europe): Eruption chronology, correlation potential and geodynamic implications. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 179, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Péczely, G. Éghajlattan; Nemzeti Tankönyvkiadó: Budapest, Hungry, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Climate-Data.org Hungary Climate. 2018. Available online: https://en.climate-data.org/europe/hungary-20 (accessed on 7 June 2018).
- EEA. Air Quality in Europe–2019 Report; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2009.
- EEA Air Pollutant Emissions Data Viewer (Gothenburg Protocol, LRTAP Convention). 2017. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/dashboards/air-pollutant-emissions-data-viewer (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- OLM. Hungarian Air Quality Network–Automatic Monitoring Network. 2020. Available online: http://www.levegominoseg.hu/automatic-monitoring-network (accessed on 21 March 2020).
- Lantai, K.; Wopera, Á.; Nagy, G. Air quality in the Northern Hungarian region. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 41, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Tiner, T. Far from the core–regions and industrial parks in economic shadow in Hungary. Part one. Hung. Geogr. Bull. 2010, 59, 89–106. [Google Scholar]
- Massey, S.W. The effects of ozone and NOx on the deterioration of calcareous stone. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 227, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Agarwal, A.K.; Bharathi, K.V.L. Characterization of exhaust particulates from diesel engine. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3023–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germinario, L.; Siegesmund, S.; Maritan, L.; Simon, K.; Mazzoli, C. Trachyte weathering in the urban built environment related to air quality. Herit. Sci. 2017, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charola, A.E.; Ware, R. Acid deposition and the deterioration of stone: A brief review of a broad topic. In Natural Stone, Weathering Phenomena, Conservation Strategies and Case Studies; Siegesmund, S., Weiss, T., Vollbrecht, A., Eds.; Special Publications 205; The Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2002; pp. 393–406. [Google Scholar]
- Graue, B.; Siegesmund, S.; Oyhantcabal, P.; Naumann, R.; Licha, T.; Simon, K. The effect of air pollution on stone decay: The decay of the Drachenfels trachyte in industrial, urban, and rural environments–a case study of the Cologne, Altenberg and Xanten cathedrals. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 1095–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colella, C.; de’ Gennaro, M.; Aiello, R. Use of zeolitic tuff in the building industry. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2001, 45, 551–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzner, B. Volcanic tuffs: The description and quantitative recording of their weathered state. In Lavas and Volcanic Tuffs; Charola, A.E., Koestler, R.J., Lombardi, G., Eds.; ICCROM: Rome, Italy, 1994; pp. 33–51. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B.J.; Török, Á.; McAlister, J.J.; Megarry, J. Observations on the factors influencing stability of building stones following contour scaling: A case study of the oolitic limestones from Budapest, Hungary. Build. Environ. 2003, 38, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, O.; Siegesmund, S.; Licha, T.; Török, Á. Geochemical and mineralogical composition of black weathering crusts on limestones from seven different European countries. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Oguchi, C.T. Role of pore size distribution in salt uptake, damage, and predicting salt susceptibility of eight types of Japanese building stones. Eng. Geol. 2010, 115, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedekind, W.; Ruedrich, J.; Siegesmund, S. Natural building stones of Mexico–Tenochtitlán: Their use, weathering and rock properties at the Templo Mayor, Palace Heras Soto and the Metropolitan Cathedral. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 1787–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Doncel, R.; Wedekind, W.; Leiser, T.; Molina-Maldonado, S.; Velasco-Sánchez, A.; Dohrmann, R.; Kral, A.; Wittenborn, A.; Aguillón-Robles, A.; Siegesmund, S. Salt bursting tests on volcanic tuff rocks from Mexico. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akın, M.; Özvan, A.; Dinçer, İ.; Topal, T. Evaluation of the physico-mechanical parameters affecting the deterioration rate of Ahlat ignimbrites (Bitlis, Turkey). Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.V.; Schmincke, H.U. Pyroclastic Rocks; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Steindlberger, E. Volcanic tuffs from Hesse (Germany) and their weathering behaviour. Environ. Geol. 2004, 46, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedekind, W.; López-Doncel, R.; Dohrmann, R.; Kocher, M.; Siegesmund, S. Weathering of volcanic tuff rocks caused by moisture expansion. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 1203–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heap, M.J.; Farquharson, J.I.; Kushnir, A.R.; Lavallée, Y.; Baud, P.; Gilg, H.A.; Reuschlé, T. The influence of water on the strength of Neapolitan Yellow Tuff, the most widely used building stone in Naples (Italy). Bull. Volcanol. 2018, 80, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pötzl, C.; Siegesmund, S.; Dohrmann, R.; Koning, J.M.; Wedekind, W. Deterioration of volcanic tuff rocks from Armenia: Constraints on salt crystallization and hydric expansion. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmens, H.; Norris, D. Spatial and Temporal Trends in Heavy Metal Accumulation in Mosses in Europe (1990–2005); Centre for Ecology and Hydrology: Bangor, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Winther, M.; Slentø, E. Heavy Metal Emissions for Danish Road Transport; NERI Technical Report No. 780; National Environmental Research Institute: Aarhus, Danmark, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Comite, V.; Álvarez de Buergo, M.; Barca, D.; Belfiore, C.M.; Bonazza, A.; La Russa, M.F.; Pezzino, A.; Randazzo, L.; Ruffolo, S.A. Damage monitoring on carbonate stones: Field exposure tests contributing to pollution impact evaluation in two Italian sites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 152, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.H.; Chu, C.J.; Li, J.; Song, B. Heavy metal pollution in soils on railroad side of Zhengzhou-Putian section of Longxi-Haizhou Railroad, China. Pedosphere 2009, 19, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salma, I.; Pósfai, M.; Kovács, K.; Kuzmann, E.; Homonnay, Z.; Posta, J. Properties and sources of individual particles and some chemical species in the aerosol of a metropolitan underground railway station. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 3460–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiłkomirski, B.; Sudnik-Wójcikowska, B.; Galera, H.; Wierzbicka, M.; Malawska, M. Railway transportation as a serious source of organic and inorganic pollution. WaterAir Soil Pollut. 2011, 218, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dzierżanowski, K.; Gawroński, S.W. Heavy metal concentration in plants growing on the vicinity of railroad tracks: A pilot study. Chall. Mod. Technol. 2012, 3, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, K.; Ai, Y.W.; Li, W.; Gao, H.; Fang, C. The effects of railway transportation on the enrichment of heavy metals in the artificial soil on railway cut slopes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, C.M.; Murray, M. Characteristics of carbonate building stones that influence the dry deposition of acidic gases. Constr. Build. Mater. 1999, 13, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, M.; Charola, A.E.; Sterflinger, K. Weathering and deterioration. In Stone in Architecture. Properties, Durability, 5th ed.; Siegesmund, S., Snethlage, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 225–316. [Google Scholar]
- Germinario, L.; Andriani, G.F.; Laviano, R. Decay of calcareous building stone under the combined action of thermoclastism and cryoclastism: A laboratory simulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 75, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germinario, L.; Siegesmund, S.; Maritan, L.; Mazzoli, C. Petrophysical and mechanical properties of Euganean trachyte and implications for dimension stone decay and durability performance. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Location | SO2 | NO2 | CO | O3 | NOX | NO | C6H6 | PM10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eger | 7.1 | 18.6 | 486.6 | 45.3 | 27.8 | 6.0 | 1.2 | 24.7 |
| Budapest (3 stations avg.) | 5.7 | 41.0 | 621.2 | 31.5 | 80.1 | 25.8 | 0.9 | 32.2 |
| Location | Ab | Bt | Qz | Mnt | mHal | Act | Crs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eger Castle (historical walls) | 60% | 10% | 15% | 15% | - | - | - |
| Eger Castle (restored walls) | 40% | 15% | - | 5% | 20% | - | 20% |
| Sirok Castle | 60% | 25% | 5% | - | - | 10% | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Germinario, L.; Török, Á. Surface Weathering of Tuffs: Compositional and Microstructural Changes in the Building Stones of the Medieval Castles of Hungary. Minerals 2020, 10, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10040376
Germinario L, Török Á. Surface Weathering of Tuffs: Compositional and Microstructural Changes in the Building Stones of the Medieval Castles of Hungary. Minerals. 2020; 10(4):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10040376
Chicago/Turabian StyleGerminario, Luigi, and Ákos Török. 2020. "Surface Weathering of Tuffs: Compositional and Microstructural Changes in the Building Stones of the Medieval Castles of Hungary" Minerals 10, no. 4: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10040376
APA StyleGerminario, L., & Török, Á. (2020). Surface Weathering of Tuffs: Compositional and Microstructural Changes in the Building Stones of the Medieval Castles of Hungary. Minerals, 10(4), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10040376