Electrochemical Behavior of Ocean Polymetallic Nodules and Low-Grade Nickel Sulfide Ore in Acidithiobacillus Ferrooxidans-Coupled Bio-Leaching
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Bacteria Culture
2.2. Coupled Leaching Procedure
2.3. Electrode and Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. A. Ferrooxidans-Coupled Leaching Experiment
3.1.1. Effect of Leaching System on Extraction of Ni, Co, Cu, and Mn
3.1.2. Effect of Dominant Factors on Extraction of Ni and Mn
3.1.3. Effect of A. Ferrooxidans on Ni, Cu, Co, Mn Coupled Leaching
3.2. Electrochemical Aspects of Low-Grade Sulfur-Nickel Ore and Polymetallic Nodule Corrosion Cell in A. Ferrooxidans Bio-Leaching System
3.2.1. Electrode Potential
3.2.2. Chemical Reaction
3.2.3. Corrosion Kinetic
3.2.4. Effects of pH and Fe(III) on Coupled Bio-Leaching
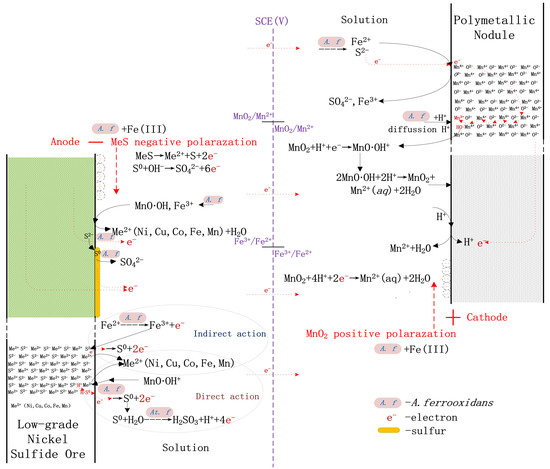
3.3. Mechanism of Multi-Metal Coupled Bioleaching
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, L.; Qu, J.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, P.; Han, L. Recovery of Ni, Co, Mn, and Mg from nickel laterite ores using alkaline oxidation and hydrochloric acid leaching. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 143, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegorzewski, A.V.; Kǒpcke, M.; Kuhn, T.; Stinikova, M.A.; Wotruba, H. Thermal pre-treatment of polymetallic nodules to create metal (Ni, Cu, Co)–rich individual particles for further processing. Minerals 2018, 8, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhan, E.; Sarangi, K.; Subbaiah, T. Recovery of manganese and nickel from polymetallic manganese nodule using commercial extractants. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2014, 126, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, G. Acid leaching of metals from deep-sea manganese nodules—A critical review of fundamentals and applications. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 1379–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhi, P.K.; Park, K.H.; Nam, C.W.; Park, J.T.; Barik, S.P. Extraction of rare earth metals from deep sea nodule using H2SO4 solution. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 119, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Luo, W.J.; Gao, Y. Effect of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans on humic-acid passivation layer on pyrite surface. Minerals 2018, 8, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.P.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.M.; Cai., Z.L.; He, J.T.; Xu, C.B. Vanadium Bioleaching Behavior by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans from a Vanadium-Bearing Shale. Minerals 2018, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- José, A.D.; Jennyfer, S.; Eduardo, L. Bioleaching of arsenic-bearing copper ores. Minerals 2018, 8, 215. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, Y.L.; Li, H.R. Enhancement of bio-oxidation of refractory arsenopyritic gold ore by adding pyrolusite in bioleaching system. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2016, 26, 2479–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Mohanty, S.; Akcil, A.; Sukla, L.B.; Das, A.P. A greener approach for resource recycling: Manganese bioleaching. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, J.; Coto, O.; Schippers, A. Anaerobic and aerobic reductive dissolutions of iron-rich nickel laterite overburden by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 168, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.; Cézac, P.; Hoadley, A.F.A.; Contamine, F.; Hugues, P.D. A review of sulfide minerals microbially assisted leaching in stirred tank reactors. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 119, 118–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, T.; White, G.E.; Edwards, M.J.; Gomez-Perez, L.; Richardson, D.J.; Butt, J.N. Mechanisms of bacterial extracellular electron exchange. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2016, 68, 87–138. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Qiu, G. Leaching kinetics of pyrolusite from manganese–silver ores in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. Hydrometallurgy 2004, 72, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Natarajan, K.A. Electrobioleaching of polymetallic ocean nodules. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 62, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, C.; Kuhn, T.; Versteegh, G.J.M.; Wegorzewski, A.V.; Kasten, S. The geochemical behavior of metals during early diagenetic alteration of buried manganese nodules. Deep-Sea Res. Part I 2018, 142, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, T.M. Regional tectonics, geology, magma chamber processes and mineralisation of the Jinchuan nickel-copper-PGE deposit, Gansu Province, China: A review. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 431–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Q.; Yu, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Sun, Y.; Khan, A. A novel method of dissolving realgar by immobilized Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 143, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijing General Research Institute of Mining & Metallurgy. Analysis of Ore and Nonferrous Metals Handbook; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1990. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, F.; Zhan, J.; Wang, Z.; Chai, L.; Zhang, C. Simultaneous leaching of low grade bismuthinite and pyrolusite ores in hydrochloric acid medium. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 166, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandraprabha, M.N.; Natarajan, K.A. Role of outer membrane exopolymers of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans in adsorption of cells onto pyrite and chalcopyrite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 123, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhuchhanda, M.; Devi, N.B.; Rao, K.S.; Rath, P.C.; Paramguru, R.K. Galvanic interaction between sulfide minerals and pyrolusite. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2000, 4, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- José, M.G.; Cantero, D.; Johnson, D.B. Comparison of the effects of temperature and pH on iron oxidation and survival of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans (type strain) and a ‘Leptospirillum ferrooxidans’-like isolate. Process Metall. 1999, 9, 689–696. [Google Scholar]
- Leahy, M.J.; Schwarz, M.P. Modelling jarosite precipitation in isothermal chalcopyrite bioleaching columns. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 98, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.Q. Decomposition mechanism of pentlandite during electrochemical bio-oxidation process. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Schaffie, M.; Petersen, J.; Schippers, A.; Ranbar, M. Conventional and electrochemical bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrates by moderately thermophilic bacteria at high pulp density. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 106, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.K.; Chan, R.C.; Nichols, W.S.; Bose, S. Hydrothermal MnO2: Synthesis, structure, morphology and discharge performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 139, 325–341. [Google Scholar]
- Walanda, D.K.; Lawrance, G.A.; Donne, S.W. Kinetics of Mn2O3 digenstion in H2SO4 solutions|NOVA. J. Solid State Chem. 2009, 182, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar]
- Kozawa, A.; Powers, R.A. The Manganese Dioxide Electrode in Alkaline Electrolyte; The Electron-Proton Mechanism for the Discharge Process from MnO2 to MnO1.5. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1966, 113, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, C.; Vargas, I.T.; Bruns, M.A.; Regan, J.M. Electrochemically active microorganisms from an acid mine drainage-affected site promote cathode oxidation in microbial fuel cells. Bioelectrochemistry 2017, 118, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, S.; Ghahreman, A.; Rashchi, F.; Moghaddam, J. The mechanism of electrochemical dissolution of sphalerite in sulfuric acid media. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 253, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.; Giannetti, B.F. The electrochemical behavior of pyrite-pyrrhotite mixtures. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2003, 553, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.; Jandová, J.; Lisá, K.; Vranka, F. Leaching of manganese deep ocean nodules in FeSO4–H2SO4–H2O solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 77, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Gonzalez, E. Theoretical studies on high–valent manganese porphyrins: Toward a deeper understanding of the energetics, electron distributions, and structural features of the reactive intermediates of enzymatic and synthetic manganese–catalyzed oxidative processes. Isr. J. Chem. 2010, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaman, A.T.; Cemek, M.; Edwards, K.J. Kinetics of pyrite, pyrrhotite and chalcopyrite dissolution by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Can. J. Microbiol. 2016, 62, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quatrini, R.; Appia-Ayme, C.; Denis, Y.; Jedilicki, E.; Holmes, D.S.; Bonnefoy, V. Extending the models for iron and sulfur oxidation in the extreme Acidophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, A.; Valenzuela, L.; Beard, S.; Mackey, A.J.; Shabanowitz, J.; Hunt, D.F.; Jerez, C.A. Periplasmic Proteins of the extremophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans a high throughput proteomics analysis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2007, 6, 2239–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugio, T.; Tsujita, Y.; Hirayama, K.; Inagaki, K.; Tano, T. Mechanism of Tetravalent Manganese Reduction with Elemental Sulfur by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1988, 52, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbehti, A.; Brasseur, G.; Lemeslemeunier, D. First evidence for existence of an uphill electron transfer through the bc(1) and NADH-Q oxidoreductase complexes of the acidophilic obligate chemolithotrophic ferrous ion-oxidizing bacterium Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 3602–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Polymetallic Nodule | Low-Grade Nickel Sulfide Ore | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Cu | Co | Ni | Cu | Co |
| 1.65 | 1.40 | 0.204 | 0.86 | 0.57 | 0.01 |
| Mn | TFe | S | Mn | TFe | S |
| 21.84 | 10.46 | 0.42 | 0.27 | 9.67 | 7.18 |
| SiO2 | Na2O | K2O | SiO2 | MgO | K2O |
| 21.43 | 0.18 | 3.20 | 39.23 | 32.43 | 0.42 |
| Al2O3 | CaO | TiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | TiO2 |
| 6.42 | 3.20 | 1.05 | 6.12 | 4.34 | 0.42 |
| Solution | Rsol1 | Ract1 | ηCPE | Rsol1 | Ract2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-grade nickel sulfide ore | Polymetallic nodule | ||||
| A. ferrooxidans + Fe(III) | 22.4 | 2268 | 0.814 | 24.6 | 2532 |
| Fe(III) | 21.8 | 2291 | 0.799 | 25.2 | 2671 |
| A. ferrooxidans | 24.3 | 2586 | 0.825 | 26.5 | 2763 |
| control | 27.4 | 2978 | 0.795 | 30.1 | 3512 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, J.-X.; Feng, Y.-L.; Li, H.-R.; Du, Z.-W.; Deng, X.-Y.; Wang, H.-J. Electrochemical Behavior of Ocean Polymetallic Nodules and Low-Grade Nickel Sulfide Ore in Acidithiobacillus Ferrooxidans-Coupled Bio-Leaching. Minerals 2019, 9, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9020070
Kang J-X, Feng Y-L, Li H-R, Du Z-W, Deng X-Y, Wang H-J. Electrochemical Behavior of Ocean Polymetallic Nodules and Low-Grade Nickel Sulfide Ore in Acidithiobacillus Ferrooxidans-Coupled Bio-Leaching. Minerals. 2019; 9(2):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9020070
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Jin-Xing, Ya-Li Feng, Hao-Ran Li, Zhu-Wei Du, Xiang-Yi Deng, and Hong-Jun Wang. 2019. "Electrochemical Behavior of Ocean Polymetallic Nodules and Low-Grade Nickel Sulfide Ore in Acidithiobacillus Ferrooxidans-Coupled Bio-Leaching" Minerals 9, no. 2: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9020070
APA StyleKang, J. -X., Feng, Y. -L., Li, H. -R., Du, Z. -W., Deng, X. -Y., & Wang, H. -J. (2019). Electrochemical Behavior of Ocean Polymetallic Nodules and Low-Grade Nickel Sulfide Ore in Acidithiobacillus Ferrooxidans-Coupled Bio-Leaching. Minerals, 9(2), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9020070