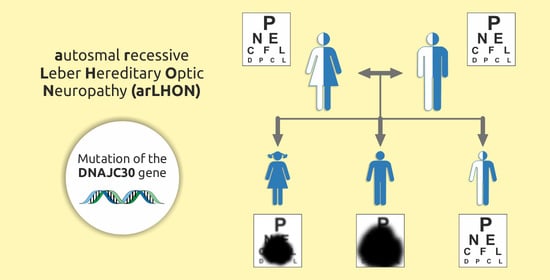
Phenotypic Variation of Autosomal Recessive Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (arLHON) in One Family
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case Study
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu-Wai-Man, P.; Chinnery, P.F. Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy. In GeneReviews®; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Amore, G.; Romagnoli, M.; Carbonelli, M.; Barboni, P.; Carelli, V.; La Morgia, C. Therapeutic Options in Hereditary Optic Neuropathies. Drugs 2021, 81, 57–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieninger, S.; Xiao, T.; Weisschuh, N.; Kohl, S.; Rüther, K.; Kroisel, P.M.; Brockmann, T.; Knappe, S.; Kellner, U.; Lagrcze, W.; et al. DNAJC30 disease-causing gene variants in a large Central European cohort of patients with suspected Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy and optic atrophy. J. Med. Genet. 2022, 59, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odom, J.V.; Bach, M.; Brigell, M.; Holder, G.E.; McCulloch, D.L.; Mizota, A.; Tormene, A.P. International Society for Clinical Electrophysiology of Vision: ISCEV standard for clinical visual evoked potentials—(2016 update). Doc. Ophthalmol. 2016, 133, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, A.G.; Frishman, L.J.; Grigg, J.; Hamilton, R.; Jeffrey, B.G.; Kondo, M.; Li, S.; McCulloch, D.L. ISCEV Standard for full-field clinical electroretinography (2022 update). Doc. Ophthalmol. 2022, 144, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortlock, K.E.; Binns, A.; Aldebasi, Y.H.; North, R.V. Inter-subject, inter-ocular and inter-session repeatability of the photopic negative response of the electroretinogram recorded using DTL and skin electrodes. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2010, 121, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueven, N. Idebenone for Leber’s hereditaty optic neuropathy. Drugs Today 2016, 52, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catarino, B.C.; von Livonius, B.; Priglinger, C.; Banik, R.; Matloob, S.; Tamhankar, M.A.; Castillo, L.; Friedburg, C.; Halfpenny, C.A.; Lincoln, J.A.; et al. Real-World Clinical Experience with Idebenone in the treatment of Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy. Neuro-Ophthalmology 2020, 40, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suno, M.; Nagaoka, A. Inhibition of lipid peroxidation by idebenone in brain mitochondria in the presence of succinate. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 1989, 8, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.S.; Mahroo, O.A.; Mollon, J.D.; Yu-Wai-Man, P. Retinal Ganglion Cells—Diversity of Cell Types and Clinical Relevance. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 661938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkman, M.A.; You-Wai-Man, P.; Korsten, A.; Lonhardt, M.; Dimitriadis, K.; De Coo, I.F.; Klopstock, T.; Chinnery, P.F. Gene-enviroment interaction in Leber hereditary optic neuropaty. Brain 2009, 132, 2317–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emperador, S.; Lopez-Gallardo, E.; Hernandez-Ainsa, C.; Habbane, M.; Montoya, J.; Bayona-Bafaluy, M.P.; Ruiz-Pesini, E. Ketogenic treatment reduces the percentage of a LHON heteroplasmic mutation and increases mtDNA amount of a LHON homoplasmic mutation. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pfeffer, G.; Majamaa, K.; Turnbull, D.M.; Thorburn, D.; Chinnery, P.F. Treatment for mitochondrial disorders. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 4, CD004426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellouze, S.; Augustin, S.; Bouaita, A.; Bonnet, C.; Simonutti, C.; Forster, V.; Picaud, S.; Sahel, J.-A.; Corral-Debrinski, M. Optimized allotropic expression of the human mitochondrial ND4 prevents blindness in a rat model of mitochondrial dysfunction. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 83, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feuer, W.J.; Schiffman, J.C.; Davis, J.L.; Porciatti, V.; Gonzalez, P.; Koilkonda, R.D.; Yuan, H.; Lalwani, A.; Lam, B.L.; Guy, J. Gene Therapy for Leber Herediatry Optic Neuropathy. Opthalmology 2016, 123, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guy, J.; Feuer, W.J.; Davis, J.L.; Porciatti, V.; Gonzalez, P.J.; Koilkonda, R.D.; Yuan, H.; Hauswirth, W.W.; Lam, B.L. Gene therapy for Leber hereditary optic neuropathy: Low- and medium-dose visual results. Ophthalomology 2017, 124, 1621–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadun, A.A.; Chicani, C.F.; Ross-Cisneros, F.N.; Barboni, P.; Thoolen, M.; Shrader, W.D.; Kubis, K.; Carelli, V.; Miller, G. Effect of EPI-743 on the clinical course of the mitochondrial disease Leber hereditary optic neuropathy. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poincenot, L.; Pearson, A.L.; Karanjia, R. Demographics of a Large International Population of Patients Affected by Leber’s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy. Ophthalmol. AAO J. 2020, 127, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| PATIENT | Examination Date | EYE | Pattern VEP P100 | Flash VEP P2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1° | 15′ | 1.4 Hz | ||||||
| L [ms] | A [µV] | L [ms] | A [µV] | L [ms] | A [µV] | |||
| middle child 12-year-old | January | R | 125 | 14.4 | 121 | 17.2 | 104 | 19.8 |
| L | 164 | 5.2 | NM | NM | 115 | 18.2 | ||
| May | R | 120 | 8.2 | 129 | 4.9 | 110 | 19.1 | |
| L | 145 | 4.9 | NM | NM | 107 | 14.2 | ||
| August | R | 149 | 5.12 | 129 | 1.95 | 109 | 13.7 | |
| L | 145 | 4.09 | 102 | 1.95 | 106 | 10.3 | ||
| eldest child | 10-year-old | R | 105 | 7.4 | 129 | 5.1 | NP | NP |
| L | 109 | 7.4 | 128 | 8.9 | NP | NP | ||
| 17-year-old | R | 98 | 6.2 | 118 | 2.6 | 151 | 10.3 | |
| L | 103 | 6.3 | 115 | 2.9 | 149 | 11.5 | ||
| youngest child | 10-year-old | R | 104 | 25.7 | 108 | 19.0 | 102 | 18.1 |
| L | 113 | 28.5 | 118 | 20.8 | 107 | 31.0 | ||
| PATIENT | EYE | LA 3 ERG | LA 30 Hz ERG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a-Wave | b-Wave | Peak | |||||
| IT [ms] | A [µV] | IT [ms] | A [µV] | IT [ms] | A [µV] | ||
| Reference ranges children | 9.8↔14.0 | −2.9↔−16.8 | 25.3↔30.5 | 21.0↔68.6 | 23.2↔28.1 | 20.0↔57.1 | |
| middle child | R | 12.9 (82%) | −9.0 (66%) | 27.7 (47%) | 39.3 (54%) | 24.3 (40%) | 36.7 (65%) |
| L | 13.1 (91%) | −5.2 (12%) | 28.0 (63%) | 30.2 (20%) | 24.8 (62%) | 25.1 (18%) | |
| eldest child | R | 13.0 (83%) | −3.3 (3%) | 30.0 (95%) | 25.3 (10%) | 27.2 (96%) | 26.9 (25%) |
| L | 10.9 (15%) | −3.5 (4%) | 28.6 (74%) | 23.8 (9%) | 26.8 (95%) | 23.7 (16%) | |
| youngest child | R | 11.8 (51%) | −9.6 (73%) | 29.0 (87%) | 43.4 (70%) | 25.4 (86%) | 48.1 (92%) |
| L | 11.9 (56%) | −8.8 (60%) | 28.8 (83%) | 38.9 (53%) | 25.4 (87%) | 43.6 (82%) | |
| Reference ranges adults | 6.6↔13.6 | −1.2↔−18.5 | 24.0↔32.1 | 11.1↔72.6 | 23.4↔28.6 | 13.9↔67.4 | |
| mother | R | 12.7 (76%) | −1.8 (4%) | 27.9 (14%) | 5.6 (1%) | 24.7 (17%) | 6.8 (0%) |
| L | 11.3 (34%) | −3.1 (8%) | 28.3 (24%) | 10.8 (2%) | 25.2 (35%) | 11.9 (1%) | |
| father | R | 11.1 (24%) | −4.3 (18%) | 28.8 (36%) | 27.7 (46%) | 26.1 (70%) | 28.4 (54%) |
| L | 10.9 (18%) | −2.8 (7%) | 30.5 (83%) | 23.0 (28%) | 26.2 (74%) | 21.8 (25%) | |
| PATIENT | DATE | EYE | IT [ms] | A [µV] | W-Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| middle child | January | R | 64 (29%) | 15.1 (0%) | 0.79 (0%) |
| L | 78 (69%) | 2.5 (1%) | 1.00 (4%) | ||
| February | R | 60 (21%) | −3.5 (27%) | 1.08 (48%) | |
| L | 61 (21%) | −4.7 (44%) | 1.16 (69%) | ||
| March | R | 42 (14%) | −4.0 (35%) | 0.90 (34%) | |
| L | 46 (16%) | −3.5 (21%) | 0.97 (74%) | ||
| May | R | 40 (13%) | −5.6 (80%) | 0.96 (71%) | |
| L | 43 (14%) | −4.1 (37%) | 0.95 (65%) | ||
| August | R | 39 (21%) | −6.6 (87%) | 1.11 (99%) | |
| L | 39 (22%) | −5.3 (67%) | 1.12 (100%) | ||
| eldest child | March | R | 73 (92%) | −3.9 (34%) | 0.83 (10%) |
| L | 75 (94%) | −3.0 (10%) | 0.82 (8%) | ||
| August | R | 46 (33%) | −3.4 (18%) | 0.93 (48%) | |
| L | 44 (33%) | −2.8 (6%) | 0.88 (20%) | ||
| youngest child | August | R | 61 (74%) | −4.9 (59%) | 0.98 (70%) |
| L | 59 (70%) | −4.8 (58%) | 0.94 (48%) | ||
| mother | August | R | 77 (95%) | −1.8 (1%) | 0.77 (3%) |
| L | 58 (40%) | −2.1 (3%) | 0.82 (14%) | ||
| father | August | R | 57 (29%) | −5.5 (81%) | 0.99 (87%) |
| L | 56 (21%) | −5.0 (71%) | 1.06 (96%) |
| PATIENT | EYE | MACULA | DISC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ILM-RPE Thickness [µm] | Mean GCL + IPL Thickness [µm] | Mean RNFL Thickness [µm] | ||
| middle child | R | 251 | 54 | 80 |
| L | 247 | 52 | 75 | |
| eldest child | R | 233 | 52 | 66 |
| L | 233 | 53 | 67 | |
| youngest child | R | 253 | 66 | 89 |
| L | 254 | 64 | 81 | |
| mother | R | 284 | 70 | 65 |
| L | 287 | 67 | 65 | |
| father | R | 270 | 82 | 91 |
| L | 270 | 81 | 92 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pojda-Wilczek, D.; Wójcik, J.; Kmak, B.; Krawczyński, M.R. Phenotypic Variation of Autosomal Recessive Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (arLHON) in One Family. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112701
Pojda-Wilczek D, Wójcik J, Kmak B, Krawczyński MR. Phenotypic Variation of Autosomal Recessive Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (arLHON) in One Family. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(11):2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112701
Chicago/Turabian StylePojda-Wilczek, Dorota, Justyna Wójcik, Bożena Kmak, and Maciej Robert Krawczyński. 2022. "Phenotypic Variation of Autosomal Recessive Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (arLHON) in One Family" Diagnostics 12, no. 11: 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112701
APA StylePojda-Wilczek, D., Wójcik, J., Kmak, B., & Krawczyński, M. R. (2022). Phenotypic Variation of Autosomal Recessive Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (arLHON) in One Family. Diagnostics, 12(11), 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112701