Can Ultrasound and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Help Differentiate between Subpleural Focal Organizing Pneumonia and Primary Lung Malignancy?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Baseline US and CEUS
2.3. Data Analysis and Collection
2.4. Reference Standards
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Conventional Ultrasonic Features
3.3. CEUS Features
3.4. Multivariate Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drakopanagiotakis, F.; Polychronopoulos, V.; Judson, M.A. Organizing pneumonia. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2008, 335, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyil, F.T.; Agca, M.; Misirlioglu, A.; Arsev, A.A.; Sevim, T. Organizing Pneumonia as a Histopathological Term. Turk. Thorac. J. 2017, 18, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.H.; Chae, E.J.; Song, J.W.; Do, K.H.; Jang, S.J. Chest CT imaging features for prediction of treatment response in cryptogenic and connective tissue disease-related organizing pneumonia. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 2722–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Jansen, H.M. American thoracic society/European respiratory society international multidisciplinary consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 277–304. [Google Scholar]
- Baque-Juston, M.; Pellegrin, A.; Leroy, S.; Marquette, C.H.; Padovani, B. Organizing pneumonia: What is it? A conceptual approach and pictorial review. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2014, 95, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Liu, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Yu, H. Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Presenting as a Solitary Mass: Clinical, Imaging, and Pathologic Features. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Pan, Y.; Song, C.; Hao, W.; Wu, S.; Wei, X.; Pan, T.; Li, J. Focal organizing pneumonia mimicking lung cancer: A surgeon’s view. Am. Surg. 2012, 78, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.J.; Yoo, E.H.; Kim, K.C.; Kim, E.J. Comparison of clinical features and prognosis in patients with cryptogenic and secondary organizing pneumonia. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, S.V.; Patel, D.; Machnicki, S.; Naidich, D.; Stover, D.; Travis, W.D.; Brown, K.K.; Naidich, J.J.; Mahajan, A.; Esposito, M.; et al. Algorithmic Approach to the Diagnosis of Organizing Pneumonia: A Correlation of Clinical, Radiologic, and Pathologic Features. Chest 2022, 162, 156–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woge, M.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Yi, E.S. Cicatricial organizing pneumonia: A clinicopathologic and radiologic study on a cohort diagnosed by surgical lung biopsy at a single institution. Hum. Pathol. 2020, 101, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, W.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J. Focal organizing pneumonia in patients: Differentiation from solitary bronchioloalveolar carcinoma using dual-energy spectral computed tomography. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 3974–3983. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.S.; Lee, K.S.; Han, J.; Kim, E.A.; Kim, T.S.; Choo, I.W. Focal organizing pneumonia: CT and pathologic findings. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2001, 16, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdogan, Y.; Ozyurek, B.A.; Ozmen, O.; Yilmaz Demirci, N.; Duyar, S.S.; Dadali, Y.; Demirag, F.; Karakaya, J. The Evaluation of FDG PET/CT Scan Findings in Patients with Organizing Pneumonia Mimicking Lung Cancer. Mol. Imaging Radionucl. Ther. 2015, 24, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baha, A.; Yildirim, F.; Kokturk, N.; Akdemir, U.O.; Demircan, S.; Turktas, H. F-18-FDG uptake in focal organising pneumonia mimicking bronchial carcinoma. Clin. Respir. J. 2016, 10, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong-Xia, Z.; Wen, H.; Ling-Gang, C.; Wen-Jia, C.; Shuo, L.; Li-Juan, D.; Hai-Man, S.; Yang, Z. A New Method for Discriminating between Bronchial and Pulmonary Arterial Phases using Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, S.; Guan, R.H.; Zhang, H.; Fu, J.J.; Wu, W.; Yan, K. Role of Arrival Time Difference Between Lesions and Lung Tissue on Contrast-Enhanced Sonography in the Differential Diagnosis of Subpleural Pulmonary Lesions. J. Ultrasound Med. 2016, 35, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, R.; Pina, C.D.; Cioni, D.; Crocetti, L. Guidelines for the use of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer Suppl. 2008, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, T.; Huang, L.; Deng, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, S.; Gong, X.; Liu, W. Logistic regression analysis of conventional ultrasonography, strain elastosonography, and contrast-enhanced ultrasound characteristics for the differentiation of benign and malignant thyroid nodules. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Lu, Q.; Xu, J.; Huang, J.; Gao, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Du, L.; Yan, F. Value of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound in the Differential Diagnosis of Focal Splenic Lesions. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 2947–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, D.; Partovi, S.; Imfeld, S.; Uthoff, H.; Baldi, T.; Aschwanden, M.; Jaeger, K.A. Novel applications of contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging in vascular medicine. Vasa 2013, 42, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Cui, L.G.; Tan, S.; Sun, Y. Ultrasound-Guided Biopsy of Pleural-Based Pulmonary Lesions by Injection of Contrast-Enhancing Drugs. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bi, K.; Xia, D.M.; Fan, L.; Ye, X.F.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, M.J.; Chen, H.W.; Cong, Y.; Zhu, H.M.; Tang, C.H.; et al. Development and Prospective Validation of an Ultrasound Prediction Model for the Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Subpleural Pulmonary Lesions: A Large Ambispective Cohort Study. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 656060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yang, W.; Fu, J.J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Bai, J.; Chen, M.H.; Yan, K. Microflow imaging of contrast-enhanced ultrasound for evaluation of neovascularization in peripheral lung cancer. Medicine 2016, 95, e4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado, F.; Daniels, C.E.; Hoffman, E.A.; Yi, E.S.; Ryu, J.H. Focal organizing pneumonia on surgical lung biopsy: Causes, clinicoradiologic features, and outcomes. Chest 2007, 132, 1579–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, A.; Zumla, A.; Bomanji, J. Role of fluorine 18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography in focal and generalized infectious and inflammatory disorders. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, M.F.; Latef, F.S.; El-Hennawy, E.S.; Selima, W.Z. The Diagnostic Role of Lung Ultrasound in Critically Ill Patients In Comparison With Chest X-ray. QJM Int. J. Med. 2021, 114, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görg, C.; Seifart, U.; Holzinger, I.; Wolf, M.; Zugmaier, G. Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma: Sonographic pattern of ‘pneumonia’. Eur. J. Ultrasound 2002, 15, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperandeo, M.; Rea, G.; Grimaldi, M.A.; Trovato, F.; Dimitri, L.M.; Carnevale, V. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound does not discriminate between community acquired pneumonia and lung cancer. Thorax 2017, 72, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.; Sung, S.W.; Lee, K.Y.; Sim, S.B.; Park, J.K. Pure ground-glass opacity on chest computed tomography: Predictive factors for invasive adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, H.F. Abstract IA01: Heterogeneity of the tumor vasculature: Why doesn’t anti-VEGF/VEGF receptor therapy work better? Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, IA01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrealba, J.R.; Fisher, S.; Kanne, J.P.; Butt, Y.M.; Glazer, C.; Kershaw, C.; Burguete, D.; Gokaslan, T.; Batra, K. Pathology-radiology correlation of common and uncommon computed tomographic patterns of organizing pneumonia. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 71, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rednic, N.; Orasan, O. Subpleural lung tumors ultrasonography. Med. Ultrason. 2010, 12, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]






| Variable | FOP (n = 23) | PLM (n = 100) | Value | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (%) | 0.357 | 0.55 | ||
| Male | 12 (52.2%) | 59 (59.0%) | ||
| Age (years) | 64.57 ± 11.8614 | 66.29 ± 11.0543 | −0.666 * | 0.507 |
| Symptoms (%) | 1.1895 | 0.276 | ||
| Asymptomatic | 2 (8.7%) | 18 (18.0%) | ||
| Cough | 15 (65.2%) | 45 (45.0%) | ||
| Fever | 2 (8.7%) | 8 (8.0%) | ||
| Chest pain | 4 (17.4%) | 11 (11.0%) | ||
| Weight loss | 0 (0%) | 18 (18.0%) |
| Variable | FOP (n = 23) | PLM (n = 100) | Value | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lesion largest diameter | 3.92 ± 1.88 | 5.5 ± 2.91 | −3.231 * | 0.002 |
| Angle between lesion border and thoracic wall | 6.657 | 0.01 | ||
| Acute angle | 14 (60.9%) | 32 (32.0%) | ||
| Obtuse angle | 9 (39.1%) | 68 (68.0%) | ||
| Whether accompanied by pleural effusion | 1.052 | 0.305 | ||
| Yes | 1 (4.3%) | 15 (15.0%) | ||
| No | 22 (95.7%) | 85 (85.0%) | ||
| Air bronchial sign | 24.028 | <0.001 | ||
| Present | 15 (65.25) | 16 (16.0%) | ||
| Absent | 8 (34.8%) | 84 (84.0%) | ||
| Whether blood flow is displayed | 0.226 | 0.635 | ||
| Yes | 20 (87.0%) | 80 (80.0%) | ||
| No | 3 (13.0%) | 20 (20.05) | ||
| Doppler spectra features | - | 0.062 | ||
| Single-phase wave arterial spectrum | 7 (35.0%) | 49 (61.3%) | ||
| Three-phase wave arterial spectrum | 11 (55.0%) | 20 (25%) | ||
| Venous spectrum | 2 (10.0%) | 7 (8.8%) | ||
| Mixed spectrum | 0 (0%) | 4 (5.0%) |
| Variable | FOP (n = 23) | PLM (n = 100) | Value | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arrive time (s) | 8.74 ± 4.22 | 11.81 ± 5.1 | −2.525 * | 0.017 |
| Main blood supply artery | 22.882 | <0.001 | ||
| Pulmonary artery | 23 (100%) | 45 (45.0%) | ||
| Bronchial artery | 0 (0%) | 55 (55.0%) | ||
| Degree of enhancement | 0.098 | 0.754 | ||
| Iso-/hyper-enhancement | 22 (95.7%) | 91 (91.0%) | ||
| Hypo-enhancement | 1 (4.3%) | 9 (9.0%) | ||
| Distribution of contrast agent | 40.752 | <0.001 | ||
| Homogeneous | 19 (82.6%) | 16 (16.0%) | ||
| Heterogeneous | 4 (17.45) | 84 (84.0%) | ||
| Entry mode at artery phase | 14.975 | 0.005 | ||
| Punctate type | 3 (13.0%) | 6 (6.0%) | ||
| Centripetal type | 4 (17.4%) | 31 (31.0%) | ||
| Diffuse type | 11 (47.8%) | 19 (19.0%) | ||
| Dendritic type | 5 (21.7%) | 18 (18.0%) | ||
| Disordered and irregular type | 0 (0%) | 26 (26.0%) | ||
| Non-perfusion area | 8.149 | 0.004 | ||
| Present | 2 (8.7%) | 40 (40.0%) | ||
| Absent | 21 (91.3%) | 60 (60.0%) |
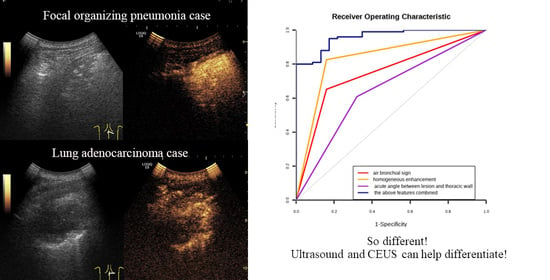
| Variables | Hazard Ratio (B) | Standard Error (Sx) | Wald Value | p | OR (95% CI) | Area | Sensitivity | Specificity | Youden Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homogeneous enhancement | 3.433 | 1.118 | 9.438 | 0.01 | 35.26 [2.38, 522.65] | 0.833 | 0.840 | 0.826 | 1.666 |
| Air bronchial sign | 1.759 | 0.825 | 4.546 | 0.025 | 6.9 [1.28, 37.18] | 0.746 | 0.840 | 0.662 | 1.502 |
| Acute angle | 1.963 | 0.851 | 5.317 | 0.033 | 6.18 [1.16, 33.09] | 0.644 | 0.680 | 0.609 | 1.289 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Cui, L.; Du, T.; Mei, F. Can Ultrasound and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Help Differentiate between Subpleural Focal Organizing Pneumonia and Primary Lung Malignancy? Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2074. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092074
Fu Y, Lei Y, Cui L, Du T, Mei F. Can Ultrasound and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Help Differentiate between Subpleural Focal Organizing Pneumonia and Primary Lung Malignancy? Diagnostics. 2022; 12(9):2074. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092074
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Ying, Yutao Lei, Ligang Cui, Tingting Du, and Fang Mei. 2022. "Can Ultrasound and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Help Differentiate between Subpleural Focal Organizing Pneumonia and Primary Lung Malignancy?" Diagnostics 12, no. 9: 2074. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092074
APA StyleFu, Y., Lei, Y., Cui, L., Du, T., & Mei, F. (2022). Can Ultrasound and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Help Differentiate between Subpleural Focal Organizing Pneumonia and Primary Lung Malignancy? Diagnostics, 12(9), 2074. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12092074