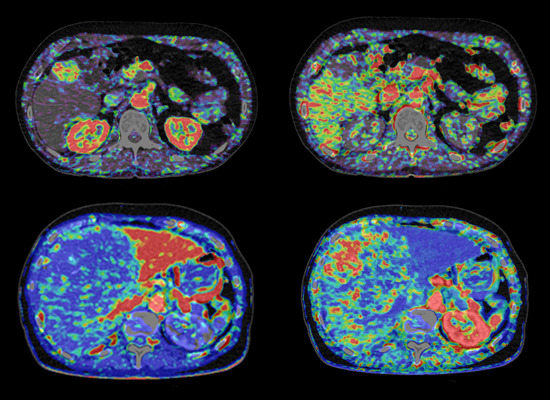
Computed Tomography (CT) Perfusion in Abdominal Cancer: Technical Aspects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. What is CT Perfusion?
3. Technical Aspects, Contrast Administration, Radiation Dose and Kinetic Models
4. Patient Preparation
5. Motion Correction and Data Processing

6. Clinical Examples with CT Perfusion



7. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Kim, J.W.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Chang, N.K.; Heo, S.H.; Shin, S.S.; Lee, J.H.; Hur, Y.H.; Kang, H.K. Perfusion CT in colorectal cancer: Comparison of perfusion parameters with tumor grade and microvessel density. Korean J. Radiol. 2012, 13, S89–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, V.; Halligan, S.; Daley, F.; Wellsted, D.M.; Guenther, T.; Bartram, C.I. Colorectal tumor vascularity: Quantitative assessment with multidetector CT—Do tumor perfusion measurements reflect angiogenesis? Radiology 2008, 249, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petralia, G.; Bonello, L.; Viotti, S.; Preda, L.; D’ Andrea, G.; Bellomi, M. CT perfusion in oncology: How to do it. Cancer Imag. 2010, 10, 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wintermark, M.; Flanders, A.E.; Velthuis, B.; Meuli, R.; van Leeuwen, M.; Goldsher, D.; Pineda, C.; Serena, J.; van der Schaaf, I.; Waaijer, A.; et al. Perfusion-CT assessment of infarct core and penumbra: Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis in 130 patients suspected of acute hemispheric stroke. Stroke 2006, 37, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambadakone, A.R.; Sahani, D.V. Body perfusion CT: Technique, clinical applications, and advances. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 47, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, V.; Liaw, J.; Bartram, C.I.; Halligan, S. Effect of temporal interval between scan acquisitions on quantitative vascular parameters in colorectal cancer: Implications for helical volumetric perfusion CT techniques. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 191, W288–W292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, V.; Dattani, M.; Farwell, J.; Shekhdar, J.; Tam, E.; Patel, S.; Juttla, J.; Simcock, I.; Stirling, J.; Mandeville, H.; et al. Radiation dose from volumetric helical perfusion CT of the thorax, abdomen or pelvis. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 21, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervaise, A.; Osemont, B.; Lecocq, S.; Noel, A.; Micard, E.; Felblinger, J.; Blum, A. CT image quality improvement using adaptive iterative dose reduction with wide-volume acquisition on 320-detector CT. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, A.K.; Paden, R.G.; Silva, A.C.; Kujak, J.L.; Lawder, H.J.; Pavlicek, W. Iterative reconstruction technique for reducing body radiation dose at CT: Feasibility study. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 193, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, N.; Yoshikawa, T.; Ohno, Y.; Somiya, Y.; Sekitani, T.; Sugihara, N.; Koyama, H.; Kanda, T.; Kanata, N.; Murakami, T.; et al. Hepatic CT perfusion measurements: A feasibility study for radiation dose reduction using new image reconstruction method. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 3048–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, K.A. Tumour angiogenesis and its relation to contrast enhancement on computed tomography: A review. Eur. J. Radiol. 1999, 30, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Tsutomu, C. Pancreatic perfusion CT in early stage of severe acute pancreatitis. Int. J. Inflamm. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, K.A. Perfusion CT for the assessment of tumour vascularity: Which protocol? Br. J. Radiol. 2003, 76, S36–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, E.E.; Chen, X.; Hadway, J.; Lee, T.-Y. Hepatic perfusion in a tumor model using DCE-CT: An accuracy and precision study. Phys. Med. Biol. 2008, 53, 4249–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, K.A.; Hayball, M.P.; Dixon, A.K. Functional images of hepatic perfusion obtained with dynamic CT. Radiology 1993, 188, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenic, A.; Nabavi, D.G.; Craen, R.A.; Gelb, A.W.; Lee, T.-Y. Dynamic CT measurement of cerebral blood flow: A validation study. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1999, 20, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nabavi, D.G.; Cenic, A.; Dool, J.; Smith, R.M.; Espinosa, F.; Craen, R.A.; Gelb, A.W.; Lee, T.Y. Quantitative assessment of cerebral hemodynamics using CT: Stability, accuracy, and precision studies in dogs. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1999, 23, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüner, J.M.; Paamand, R.; Højgaard, L.; Law, I. Brain perfusion CT compared with 15O-H2O-PET in healthy subjects. EJNMMI Res. 2011, 1, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, K.A.; Griffiths, M.R. Perfusion CT: A worthwhile enhancement? Br. J. Radiol. 2003, 76, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, K.A. Measurement of tissue perfusion by dynamic computed tomography. Br. J. Radiol. 1991, 64, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, K.A. Tumour angiogenesis and its relation to contrast enhancement on computed tomography: A review. Eur. J. Radiol. 1999, 30, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieselmann, A.; Kowarschik, M.; Ganguly, A.; Hornegger, J.; Fahrig, R. Deconvolution-based CT and MR brain perfusion measurement: Theoretical model revisited and practical implementation details. Int. J. Biomed. Imag. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, S.; Meyer, H.; Hein, P.; Lembcke, A.; Rueckert, J.-C.; Rogalla, P. Comparison of free breathing versus breath-hold in perfusion imaging using dynamic volume CT. Insights Imag. 2012, 3, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellomi, M.; Petralia, G.; Sonzogni, A.; Zampino, M.G.; Rocca, A. CT perfusion for the monitoring of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radiation therapy in rectal carcinoma: Initial experience. Radiology 2007, 244, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petralia, G.; Bonello, L.; Viotti, S.; Preda, L.; D’ Andrea, G.; Bellomi, M. CT perfusion in oncology: How to do it. Canc. Imag. 2010, 10, 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kandel, S.; Kloeters, C.; Meyer, H.; Hein, P.; Hilbig, A.; Rogalla, P. Whole-organ perfusion of the pancreas using dynamic volume CT in patients with primary pancreas carcinoma: Acquisition technique, post-processing and initial results. Eur. Radiol. 2009, 19, 2641–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorella, D.; Heiserman, J.; Prenger, E.; Partovi, S. Assessment of the reproducibility of postprocessing dynamic CT perfusion data. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2004, 25, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanelli, P.C.; Lev, M.H.; Eastwood, J.D.; Gonzalez, R.G.; Lee, T.Y. The effect of varying user-selected input parameters on quantitative values in CT perfusion maps1. Acad. Radiol. 2004, 11, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.S.; Chandler, A.G.; Wei, W.; Herron, D.H.; Anderson, E.F.; Kurzrock, R.; Charnsangavej, C. Reproducibility of CT perfusion parameters in liver tumors and normal liver. Radiology 2011, 260, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, V.; Halligan, S.; Hugill, J.-A.; Bassett, P.; Bartram, C.I. Quantitative assessment of colorectal cancer perfusion using MDCT: Inter- and intraobserver agreement. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 185, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, V.; Halligan, S.; Gharpuray, A.; Wellsted, D.; Sundin, J.; Bartram, C.I. Quantitative assessment of colorectal cancer tumor vascular parameters by using perfusion CT: Influence of tumor region of interest1. Radiology 2008, 247, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Yang, Z.-G.; Chen, H.-J.; Chen, T.-W.; Huang, J. Gastric adenocarcinoma: Can perfusion CT help to noninvasively evaluate tumor angiogenesis? Abdom. Imag. 2011, 36, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’ Assignies, G.; Couvelard, A.; Bahrami, S.; Vullierme, M.-P.; Hammel, P.; Hentic, O.; Sauvanet, A.; Bedossa, P.; Ruszniewski, P.; Vilgrain, V. Pancreatic endocrine tumors: Tumor blood flow assessed with perfusion CT reflects angiogenesis and correlates with prognostic factors. Radiology 2009, 250, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, A.; Shuto, K.; Okazumi, S.; Ohira, G.; Natsume, T.; Hayano, K.; Narushima, K.; Saito, H.; Ohta, T.; Nabeya, Y.; et al. Role of Perfusion CT in assessing tumor blood flow and malignancy level of gastric cancer. Dig. Surg. 2010, 27, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-P.; Meng, Q.-F.; Sun, C.-H.; Xu, D.-S.; Fan, M.; Yang, X.-F.; Chen, D.-Y. Tumor angiogenesis and dynamic CT in colorectal carcinoma: Radiologic-pathologic correlation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, V.; Halligan, S.; Wellsted, D.M.; Bartram, C.I. Can perfusion CT assessment of primary colorectal adenocarcinoma blood flow at staging predict for subsequent metastatic disease? A pilot study. Eur. Radiol. 2009, 19, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y. The promise of dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging in radiation therapy. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 21, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Ohno, Y.; Kanata, N.; Koyama, H.; Takenaka, D.; Sugimura, K. CT hepatic perfusion measurement: Comparison of three analytic methods. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 2075–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, K.A.; Hayball, M.P.; Dixon, A.K. Functional images of hepatic perfusion obtained with dynamic CT. Radiology 1993, 188, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomley, M.J.; Coulden, R.; Dawson, P.; Kormano, M.; Donlan, P.; Bufkin, C.; Lipton, M.J. Liver perfusion studied with ultrafast CT. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1995, 19, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, D.; Bonaffini, P.A.; Ratti, L.; Antolini, L.; Corso, R.; Fazio, F.; Sironi, S. Hepatocellular carcinoma treated with transarterial chemoembolization: Dynamic perfusion-CT in the assessment of residual tumor. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 5993–6000. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Delrue, L.; Blanckaert, P.; Mertens, D.; Cesmeli, E.; Ceelen, W.P.; Duyck, P. Assessment of tumor vascularization in pancreatic adenocarcinoma using 128-slice perfusion computed tomography imaging. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2011, 35, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liang, Z.; Hao, S.; Zhu, L.; Ashish, M.; Jin, C.; Fu, D.; Ni, Q. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Dynamic 64-slice helical CT with perfusion imaging. Abdom. Imag. 2009, 34, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hansen, M.L.; Norling, R.; Lauridsen, C.; Fallentin, E.; Bæksgaard, L.; Kofoed, K.F.; Svendsen, L.B.; Nielsen, M.B. Computed Tomography (CT) Perfusion in Abdominal Cancer: Technical Aspects. Diagnostics 2013, 3, 261-270. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics3020261
Hansen ML, Norling R, Lauridsen C, Fallentin E, Bæksgaard L, Kofoed KF, Svendsen LB, Nielsen MB. Computed Tomography (CT) Perfusion in Abdominal Cancer: Technical Aspects. Diagnostics. 2013; 3(2):261-270. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics3020261
Chicago/Turabian StyleHansen, Martin Lundsgaard, Rikke Norling, Carsten Lauridsen, Eva Fallentin, Lene Bæksgaard, Klaus Fuglsang Kofoed, Lars Bo Svendsen, and Michael Bachmann Nielsen. 2013. "Computed Tomography (CT) Perfusion in Abdominal Cancer: Technical Aspects" Diagnostics 3, no. 2: 261-270. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics3020261
APA StyleHansen, M. L., Norling, R., Lauridsen, C., Fallentin, E., Bæksgaard, L., Kofoed, K. F., Svendsen, L. B., & Nielsen, M. B. (2013). Computed Tomography (CT) Perfusion in Abdominal Cancer: Technical Aspects. Diagnostics, 3(2), 261-270. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics3020261