Enhanced Systemic Response of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Regulators in Campylobacter and Salmonella Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Serum Samples
2.2. Measurement of Serum MMPs and TIMP-1 Concentrations
2.3. Statistical Analyses
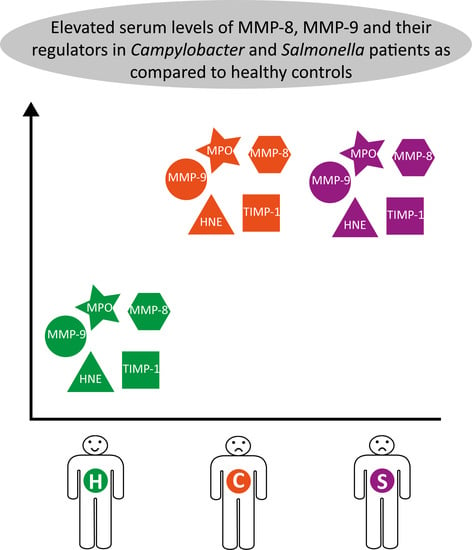
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2013. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Food Safety Authority. Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of Campylobacter in broiler batches and of Campylobacter and Salmonella on broiler carcasses, in the EU, 2008; Part B: Analysis of factors associated with Campylobacter colonisation of broiler batches and with Campylobacter contamination of broiler carcasses; and investigation of the culture method diagnostic characteristics used to analyse broiler carcass samples. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, M.J. Epidemiologic and clinical features of Campylobacter jejuni infections. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 176, S103–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, H.; Hansen, K.K.; Gradel, K.O.; Kristensen, B.; Ejlertsen, T.; Østergaard, C.; Schønheyder, H.C. Bacteraemia as a result of Campylobacter species: A population-based study of epidemiology and clinical risk factors. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feodoroff, B.; Lauhio, A.; Ellström, P.; Rautelin, H. A nationwide study of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli bacteremia in Finland over a 10-year period, 1998-2007, with special reference to clinical characteristics and antimicrobial susceptibility. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, e99–e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachamkin, I.; Allos, B.M.; Ho, T. Campylobacter Species and Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannu, T.; Mattila, L.; Rautelin, H.; Pelkonen, P.; Lahdenne, P.; Siitonen, A.; Leirisalo-Repo, M. Campylobacter-triggered reactive arthritis: A population-based study. Rheumatol. Oxf. Engl. 2002, 41, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiller, R.C. Role of infection in irritable bowel syndrome. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 42, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorsa, T.; Tjäderhane, L.; Konttinen, Y.T.; Lauhio, A.; Salo, T.; Lee, H.-M.; Golub, L.M.; Brown, D.L.; Mäntylä, P. Matrix metalloproteinases: Contribution to pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of periodontal inflammation. Ann. Med. 2006, 38, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfakry, H.; Malle, E.; Koyani, C.N.; Pussinen, P.J.; Sorsa, T. Neutrophil proteolytic activation cascades: A possible mechanistic link between chronic periodontitis and coronary heart disease. Innate Immun. 2016, 22, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, E.; Dassé, E.; Haye, B.; Petitfrère, E. TIMPs as multifacial proteins. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2004, 49, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Rosen, H.; Madtes, D.K.; Shao, B.; Martin, T.R.; Heinecke, J.W.; Fu, X. Myeloperoxidase Inactivates TIMP-1 by Oxidizing Its N-terminal Cysteine Residue. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 31826–31834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Medina, C.; Radomski, M.W. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Intestinal Inflammation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 318, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Von Lampe, B.; Barthel, B.; Coupland, S.; Riecken, E.; Rosewicz, S. Differential expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in colon mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2000, 47, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baugh, M.D.; Perry, M.J.; Hollander, A.P.; Davies, D.R.; Cross, S.S.; Lobo, A.J.; Taylor, C.J.; Evans, G.S. Matrix metalloproteinase levels are elevated in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautelin, H.I.; Oksanen, A.M.; Veijola, L.I.; Sipponen, P.I.; Tervahartiala, T.I.; Sorsa, T.A.; Lauhio, A. Enhanced systemic matrix metalloproteinase response in Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Ann. Med. 2009, 41, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautelin, H.; Tervahartiala, T.; Lauhio, A.; Sorsa, T.; Kolho, K.-L. Assessment of systemic matrix metalloproteinase and their regulator response in children with Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 2010, 70, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanlaere, I.; Libert, C. Matrix Metalloproteinases as Drug Targets in Infections Caused by Gram-Negative Bacteria and in Septic Shock. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Handley, S.A.; Miller, V.L. General and specific host responses to bacterial infection in Peyer’s patches: A role for stromelysin-1 (matrix metalloproteinase-3) during Salmonella enterica infection. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 64, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, A.; Hagström, J.; Mustonen, H.; Kokkola, A.; Tervahartiala, T.; Sorsa, T.; Böckelman, C.; Haglund, C. Serum MMP-8 and TIMP-1 as prognostic biomarkers in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2018, 40, 1010428318799266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visse, R.; Nagase, H. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: Structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ. Res. 2003, 92, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alutis, M.E.; Grundmann, U.; Fischer, A.; Hagen, U.; Kühl, A.A.; Göbel, U.B.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. The Role of Gelatinases in Campylobacter Jejuni Infection of Gnotobiotic Mice. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 5, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alutis, M.E.; Grundmann, U.; Hagen, U.; Fischer, A.; Kühl, A.A.; Göbel, U.B.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Mediates Intestinal Immunopathogenesis in Campylobacter Jejuni-Infected Infant Mice. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 5, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, Y.; Gotoh, K.; Takeuchi, N.; Miura, H.; Nishimura, N.; Ozaki, T.; Yoshikawa, T. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in the pathogenesis of childhood gastroenteritis. J. Med. Virol. 2016, 88, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyati, K.K.; Prasad, K.N.; Agrawal, V.; Husain, N. Matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9 in Campylobacter jejuni-induced paralytic neuropathy resembling Guillain-Barré syndrome in chickens. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauhio, A.; Konttinen, Y.T.; Tschesche, H.; Nordström, D.; Salo, T.; Lähdevirta, J.; Golub, L.M.; Sorsa, T. Reduction of matrix metalloproteinase 8-neutrophil collagenase levels during long-term doxycycline treatment of reactive arthritis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristic | Campylobacter Patients | Salmonella Patients |
|---|---|---|
| Total number of patients (n) | 80 | 25 |
| Gender (Males/Females) | 42/38 | 6/19 |
| Age, median (range), years | 48 (18–77) | 53 (18–81) |
| * Treated with antimicrobials (n) | 21 | 10 |
| Hospitalized (n) | 22 a | 9 b |
| Group | MMP-8 (IQR), (ng/mL) | MMP-9 (IQR), (ng/mL) | MPO (IQR), (ng/mL) | HNE (IQR), (ng/mL) | TIMP-1 (IQR), (ng/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Campylobacter | acute phase n = 80 | 43.2 (28.7–61.5) | 291.5 (234.1–427.9) | 570.0 (480.0–736.4) | 171.6 (112.2–265.7) | 245.2 (197.5–282.3) |
| follow-up n = 73 | 20.8 (12.0–37.6) | 259.6 (209.7–323.9) | 487.7 (370.4–656.8) | 130.7 (93.6-232.6) | 203.7 (178.2–245.0) | |
| Salmonella | acute phase n = 25 | 42.4 (19.6–54.4) | 291.2 (215.4–436.6) | 600.1 (437.5–881.8) | 163.0 (113.3–212.1) | 236.9 (193.4–279.7) |
| follow-up n = 23 | 21.6 (14.2–29.2) | 254.3 (177.8–310.1) | 500.0 (391.6–700.5) | 148.5 (81.8–209.7) | 211.3 (166.1–253.4) | |
| Control | - n = 27 | 16.7 (14.8–22.5) | 151.4 (131.2–185.6) | 224.7 (145.7–299.5) | 82.0 (26.3–181.0) | 180.4 (163.9–212.0) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nilsson, A.; Tervahartiala, T.; Lennebratt, D.; Lannergård, A.; Sorsa, T.; Rautelin, H. Enhanced Systemic Response of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Regulators in Campylobacter and Salmonella Patients. Diagnostics 2018, 8, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics8040082
Nilsson A, Tervahartiala T, Lennebratt D, Lannergård A, Sorsa T, Rautelin H. Enhanced Systemic Response of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Regulators in Campylobacter and Salmonella Patients. Diagnostics. 2018; 8(4):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics8040082
Chicago/Turabian StyleNilsson, Anna, Taina Tervahartiala, David Lennebratt, Anders Lannergård, Timo Sorsa, and Hilpi Rautelin. 2018. "Enhanced Systemic Response of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Regulators in Campylobacter and Salmonella Patients" Diagnostics 8, no. 4: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics8040082
APA StyleNilsson, A., Tervahartiala, T., Lennebratt, D., Lannergård, A., Sorsa, T., & Rautelin, H. (2018). Enhanced Systemic Response of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Regulators in Campylobacter and Salmonella Patients. Diagnostics, 8(4), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics8040082