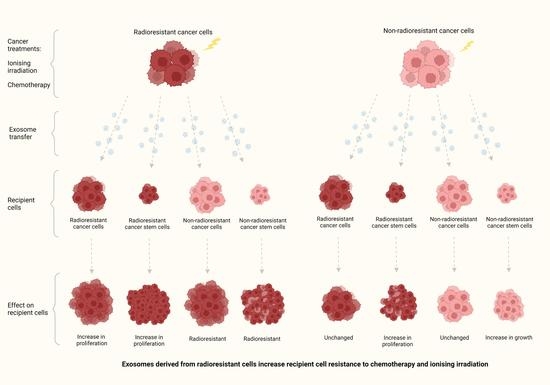
Exosomes Derived from Radioresistant Breast Cancer Cells Promote Therapeutic Resistance in Naïve Recipient Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Radiation Treatment
2.3. Exosome Isolation
2.4. Exosome Quantification
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.6. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
2.7. Exosome Treatment
2.8. Cell Viability Assay
2.9. Colony Fromation Assay
2.10. Chemosensitivity Assays
2.11. Tumoursphere-Forming Assay
2.12. Migration Assay
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation of Exosomes from Canine and Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines and Their Derived RR Counterparts
3.2. Exosomes Isolated from RR Cells Increased the Survival of Recipient Cells Compared to Exosomes Isolated from Non-RR Cells
3.3. Exosomes Isolated from RR Cells Enhanced the Migration Potential of Recipent Cells
3.4. Recipient Cells of Exosomes Isolated from Estalished RR Cells Were More Resistant to Chemotherapy and Irradiation Compared to Those Treated with Exosomes from Non-RR Cells
3.5. Exosomes Isolated from RR Cells Can Alter the Phenotype of CSCs
3.6. Exosomes Derived from RR Cells Increased the Size of the CSC Pool
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, H.L.; Fenger, J.M.; London, C.A. Dogs as a model for cancer. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2016, 4, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sharma, A.; Tiwari, R.K. Application of microarray in breast cancer: An overview. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2012, 4, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizarro, F.; Hernandez, A. Optimization of radiotherapy fractionation schedules based on radiobiological functions. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20170400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.Y.; Argyle, D.J. The evolving cancer stem cell paradigm: Implications in veterinary oncology. Vet. J. 2015, 205, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phi, L.T.H.; Sari, I.N.; Yang, Y.G.; Lee, S.H.; Jun, N.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Kwon, H.Y. Cancer stem cells (cscs) in drug resistance and their therapeutic implications in cancer treatment. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 5416923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.X.; Liu, X.M.; Lv, M.M.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J.H.; Zhong, S.L.; Ji, M.H.; Hu, Q.; Luo, Z.; Wu, J.Z.; et al. Exosomes from drug-resistant breast cancer cells transmit chemoresistance by a horizontal transfer of micrornas. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarana, C.; St Clair, D.K. Chemotherapy-induced tissue injury: An insight into the role of extracellular vesicles-mediated oxidative stress responses. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Bucci, J.; Malouf, D.; Knox, M.; Graham, P.; Li, Y. Exosomes in cancer radioresistance. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, K. Roles of exosomes in cancer chemotherapy resistance, progression, metastasis and immunity, and their clinical applications (review). Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 59, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, S.; Perocheau, D.; Touramanidou, L.; Baruteau, J. The exosome journey: From biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Chen, Q.; Lin, L.; Sha, C.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Yin, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; Gao, W.; et al. Regulation of exosome production and cargo sorting. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, L.; Muller-Haegele, S.; Mitsuhashi, M.; Gooding, W.; Okada, H.; Whiteside, T.L. Exosomes isolated from plasma of glioma patients enrolled in a vaccination trial reflect antitumor immune activity and might predict survival. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e1008347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, C.S.; Muller, L.; Whiteside, T.L.; Boyiadzis, M. Plasma exosomes as markers of therapeutic response in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Yang, L.; Baddour, J.; Achreja, A.; Bernard, V.; Moss, T.; Marini, J.C.; Tudawe, T.; Seviour, E.G.; San Lucas, F.A.; et al. Tumor microenvironment derived exosomes pleiotropically modulate cancer cell metabolism. eLife 2016, 5, e10250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Achreja, A.; Yeung, T.L.; Mangala, L.S.; Jiang, D.; Han, C.; Baddour, J.; Marini, J.C.; Ni, J.; Nakahara, R.; et al. Targeting stromal glutamine synthetase in tumors disrupts tumor microenvironment-regulated cancer cell growth. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sousa, C.M.; Biancur, D.E.; Wang, X.; Halbrook, C.J.; Sherman, M.H.; Zhang, L.; Kremer, D.; Hwang, R.F.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Ying, H.; et al. Pancreatic stellate cells support tumour metabolism through autophagic alanine secretion. Nature 2016, 536, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xing, F.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.Y.; Wu, K.; Sharma, S.; Mo, Y.Y.; Feng, J.; Sanders, S.; Jin, G.; Singh, R.; et al. Loss of xist in breast cancer activates msn-c-met and reprograms microglia via exosomal mirna to promote brain metastasis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4316–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Tesic Mark, M.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thery, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006, 3, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, F.; Sabattini, S.; Vascellari, M.; Marconato, L. The impact of toceranib, piroxicam and thalidomide with or without hypofractionated radiation therapy on clinical outcome in dogs with inflammatory mammary carcinoma. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2018, 16, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Estrada, X.; Landaverde-Quiroz, B.; Duenas-Bocanegra, A.A.; De Paz-Campos, M.A.; Hernandez-Alberto, G.; Solorio-Perusquia, B.; Trejo-Mandujano, M.; Perez-Guerrero, L.; Delgado-Gonzalez, E.; Anguiano, B.; et al. Molecular iodine/doxorubicin neoadjuvant treatment impair invasive capacity and attenuate side effect in canine mammary cancer. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Alakhova, D.Y.; Zhao, X.S.; Band, V.; Batrakova, E.V.; Kabanov, A.V. Eradication of cancer stem cells in triple negative breast cancer using doxorubicin/pluronic polymeric micelles. Nanomed-Nanotechnology 2020, 24, 102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Else, R.W.; Norval, M.; Neill, W.A. The characteristics of a canine mammary-carcinoma cell-line, rem-134. Brit. J. Cancer 1982, 46, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, M.; Turnbull, A.K.; Ward, C.; Meehan, J.; Martinez-Perez, C.; Bonello, M.; Pang, L.Y.; Langdon, S.P.; Kunkler, I.H.; Murray, A.; et al. Development and characterisation of acquired radioresistant breast cancer cell lines. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.F.; Yang, M.; Luo, J.J.; Zhou, H.M. Radiotherapy targeting cancer stem cells “awakens” them to induce tumour relapse and metastasis in oral cancer. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augimeri, G.; La Camera, G.; Gelsomino, L.; Giordano, C.; Panza, S.; Sisci, D.; Morelli, C.; Gyorffy, B.; Bonofiglio, D.; Ando, S.; et al. Evidence for enhanced exosome production in aromatase inhibitor-resistant breast cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazawa, M.; Tomiyama, K.; Saotome-Nakamura, A.; Obara, C.; Yasuda, T.; Gotoh, T.; Tanaka, I.; Yakumaru, H.; Ishihara, H.; Tajima, K. Radiation increases the cellular uptake of exosomes through cd29/cd81 complex formation. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Commun. 2014, 446, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramowicz, A.; Wojakowska, A.; Marczak, L.; Lysek-Gladysinska, M.; Smolarz, M.; Story, M.D.; Polanska, J.; Widlak, P.; Pietrowska, M. Ionizing radiation affects the composition of the proteome of extracellular vesicles released by head-and-neck cancer cells in vitro. J. Radiat. Res. 2019, 60, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutschelknaus, L.; Azimzadeh, O.; Heider, T.; Winkler, K.; Vetter, M.; Kell, R.; Tapio, S.; Merl-Pham, J.; Huber, S.M.; Edalat, L.; et al. Radiation alters the cargo of exosomes released from squamous head and neck cancer cells to promote migration of recipient cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Du, S.F.; Liu, L.; Gan, F.H.; Jiang, X.G.; Wangrao, K.J.; Lyu, P.; Gong, P.; Yao, Y. Radiation-induced bystander effect can be transmitted through exosomes using mirnas as effector molecules. Radiat. Res. 2020, 194, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagatay, S.T.; Mayah, A.; Mancuso, M.; Giardullo, P.; Pazzaglia, S.; Saran, A.; Daniel, A.; Traynor, D.; Meade, A.D.; Lyng, F.; et al. Phenotypic and functional characteristics of exosomes derived from irradiated mouse organs and their role in the mechanisms driving non-targeted effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widlak, P.; Pietrowska, M.; Polanska, J.; Rutkowski, T.; Jelonek, K.; Kalinowska-Herok, M.; Gdowicz-Klosok, A.; Wygoda, A.; Tarnawski, R.; Skladowski, K. Radiotherapy-related changes in serum proteome patterns of head and neck cancer patients; the effect of low and medium doses of radiation delivered to large volumes of normal tissue. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jelonek, K.; Wojakowska, A.; Marczak, L.; Muer, A.; Tinhofer-Keilholz, I.; Lysek-Gladysinska, M.; Widlak, P.; Pietrowska, M. Ionizing radiation affects protein composition of exosomes secreted in vitro from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2015, 62, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gray, M.; Turnbull, A.K.; Meehan, J.; Martinez-Perez, C.; Kay, C.; Pang, L.Y.; Argyle, D.J. Comparative analysis of the development of acquired radioresistance in canine and human mammary cancer cell lines. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutschelknaus, L.; Peters, C.; Winkler, K.; Yentrapalli, R.; Heider, T.; Atkinson, M.J.; Moertl, S. Exosomes derived from squamous head and neck cancer promote cell survival after ionizing radiation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arscott, W.T.; Tandle, A.T.; Zhao, S.; Shabason, J.E.; Gordon, I.K.; Schlaff, C.D.; Zhang, G.; Tofilon, P.J.; Camphausen, K.A. Ionizing radiation and glioblastoma exosomes: Implications in tumor biology and cell migration. Transl. Oncol. 2013, 6, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebrahimkhani, S.; Vafaee, F.; Hallal, S.; Wei, H.; Lee, M.Y.T.; Young, P.E.; Satgunaseelan, L.; Beadnall, H.; Barnett, M.H.; Shivalingam, B.; et al. Deep sequencing of circulating exosomal microrna allows non-invasive glioblastoma diagnosis. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lan, F.M.; Qing, Q.; Pan, Q.; Hu, M.; Yu, H.M.; Yue, X. Serum exosomal mir-301a as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. Cell Oncol. 2018, 41, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, A.; Imbruce, P.; Gardenghi, B.; Belli, L.; Agushi, R.; Tamanini, A.; Munari, S.; Bossi, A.M.; Scambi, I.; Benati, D.; et al. A microrna signature from serum exosomes of patients with glioma as complementary diagnostic biomarker. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2018, 136, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Liu, X.; Pan, B.; Hu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Su, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, G.; Xu, M.; Xu, X.; et al. Serum exosomal mir-122 as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of colorectal cancer with liver metastasis. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Xu, H.F.; Liu, M.Y.; Xu, Y.J.; He, J.C.; Zhou, Y.; Cang, S.D. Mechanism of exosomal microrna-224 in development of hepatocellular carcinoma and its diagnostic and prognostic value. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1890–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Zou, X.; Liu, C.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, S.; Geng, X.; Zhu, W. Microrna expression profile in serum reveals novel diagnostic biomarkers for endometrial cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.T.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhu, X.J.; Chen, L.; Ma, Y.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Yang, X.Z.; Liu, Z. Exosomal mir-1246 in serum as a potential biomarker for early diagnosis of gastric cancer. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.L.; Cheng, J.N.; Yao, Y.F.; Lou, C.J.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q. Combination of four serum exosomal mirnas as novel diagnostic biomarkers for early-stage gastric cancer. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Li, L.X.; Diao, Y.J.; Wang, J.; Ye, Y.; Hao, X.K. Identification of urinary exosomal mirnas for the non-invasive diagnosis of prostate cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.; Park, Y.H.; Jung, S.H.; Jang, S.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Chung, Y.J. Urinary exosome microrna signatures as a noninvasive prognostic biomarker for prostate cancer. Npj Genom. Med. 2021, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidenfeld, K.; Schif-Zuck, S.; Abu-Tayeh, H.; Kang, K.; Kessler, O.; Weissmann, M.; Neufeld, G.; Barkan, D. Dormant tumor cells expressing loxl2 acquire a stem-like phenotype mediating their transition to proliferative growth. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 71362–71377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salas, Y.; Marquez, A.; Diaz, D.; Romero, L. Epidemiological study of mammary tumors in female dogs diagnosed during the period 2002-2012: A growing animal health problem. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]












Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Payton, C.; Pang, L.Y.; Gray, M.; Argyle, D.J. Exosomes Derived from Radioresistant Breast Cancer Cells Promote Therapeutic Resistance in Naïve Recipient Cells. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121310
Payton C, Pang LY, Gray M, Argyle DJ. Exosomes Derived from Radioresistant Breast Cancer Cells Promote Therapeutic Resistance in Naïve Recipient Cells. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(12):1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121310
Chicago/Turabian StylePayton, Chantell, Lisa Y. Pang, Mark Gray, and David J. Argyle. 2021. "Exosomes Derived from Radioresistant Breast Cancer Cells Promote Therapeutic Resistance in Naïve Recipient Cells" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 12: 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121310
APA StylePayton, C., Pang, L. Y., Gray, M., & Argyle, D. J. (2021). Exosomes Derived from Radioresistant Breast Cancer Cells Promote Therapeutic Resistance in Naïve Recipient Cells. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(12), 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121310