Application of a 72 h National Early Warning Score and Incorporation with Sequential Organ Failure Assessment for Predicting Sepsis Outcomes and Risk Stratification in an Intensive Care Unit: A Derivation and Validation Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Scoring Indices
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Enrolled Background
3.2. Verification and Comparison of Scoring Indices at Admission and on Day 3 for Predicting Mortality
3.3. NEWS2 at Different Time Points for Mortality Prediction
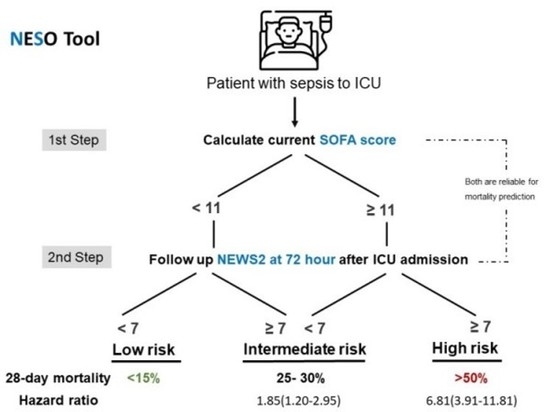
3.4. Contribution of the NESO Tool for Risk Stratification: Clinical Features, Laboratory Data, Severity, and Mortality
3.5. Validation of the NESO Tool and Potential for Other Predictions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murphy, S.L.; Kochanek, K.D.; Xu, J. Deaths: Final data for 2011. Natl. Vital Stat. Rep. 2015, 63, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Chen, F.-L.; Chen, J.-H.; Wu, M.-T.M.; Chen, Y.-L.; Chien, D.-S.; Ko, Y.J.M. Epidemiology of sepsis in Taiwan. Medicine 2019, 98, e15725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouncey, P.R.; Osborn, T.M.; Power, G.S.; Harrison, D.A.; Sadique, M.Z.; Grieve, R.D.; Jahan, R.; Harvey, S.E.; Bell, D.; Bion, J.F.; et al. Trial of early, goal-directed resuscitation for septic shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakr, Y.; Jaschinski, U.; Wittebole, X.; Szakmany, T.; Lipman, J.; Ñamendys-Silva, S.A.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Leone, M.; Lupu, M.-N.; Vincent, J.-L. Sepsis in intensive care unit patients: Worldwide data from the intensive care over nations audit. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, C.W.; Liu, V.X.; Iwashyna, T.J.; Brunkhorst, F.M.; Rea, T.D.; Scherag, A.; Rubenfeld, G.; Kahn, J.M.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Singer, M.J.J. Assessment of clinical criteria for sepsis: For the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). Jama 2016, 315, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karakike, E.; Kyriazopoulou, E.; Tsangaris, I.; Routsi, C.; Vincent, J.-L.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J. The early change of SOFA score as a prognostic marker of 28-day sepsis mortality: Analysis through a derivation and a validation cohort. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keep, J.W.; Messmer, A.S.; Sladden, R.; Burrell, N.; Pinate, R.; Tunnicliff, M.; Glucksman, E. National early warning score at Emergency Department triage may allow earlier identification of patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: A retrospective observational study. Emerg. Med. J. EMJ 2016, 33, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, C.; Hung, K.; Leung, L.; Lo, R.; Yeung, C.; Chan, S. QSOFA, SIRS and NEWS2 to Predict 60-Day Mortality in the Emergency Department: Prospective Study. In Proceedings of the D104, Critical Care: A Fine Balance—Sepsis Definitions, Outcomes and Epidemiology, Dallas, TX, USA, 17–22 May 2019; p. A7157. [Google Scholar]
- Mellhammar, L.; Linder, A.; Tverring, J.; Christensson, B.; Boyd, J.H.; Sendi, P.; Åkesson, P.; Kahn, F. NEWS2 is superior to qSOFA in detecting sepsis with organ dysfunction in the emergency department. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inada-Kim, M.; Knight, T.; Sullivan, M.; Ainsworth-Smith, M.; Pike, N.; Richardson, M.; Hayward, G.; Lasserson, D. The prognostic value of national early warning scores (NEWS) during transfer of care from community settings to hospital: A retrospective service evaluation. BJGP Open 2020, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnikin, S.; Hayward, G.; Wilson, F.; Lasserson, D. Are referrals to hospital from out-of-hours primary care associated with National Early Warning Scores? Emerg. Med. J. 2020, 37, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silcock, D.J.; Corfield, A.R.; Staines, H.; Rooney, K.D. Superior performance of National Early Warning Score compared with quick Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment Score in predicting adverse outcomes: A retrospective observational study of patients in the prehospital setting. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Emerg. Med. 2019, 26, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khwannimit, B.; Bhurayanontachai, R.; Vattanavanit, V. Comparison of the accuracy of three early warning scores with SOFA score for predicting mortality in adult sepsis and septic shock patients admitted to intensive care unit. Heart Lung 2019, 48, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannan Panday, R.S.; Minderhoud, T.C.; Alam, N.; Nanayakkara, P.W.B. Prognostic value of early warning scores in the emergency department (ED) and acute medical unit (AMU): A narrative review. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 45, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Huang, K.-T.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, C.-C.; Wang, Y.-H.; Tseng, C.-C.; Lin, M.-C.; Fang, W.-F. Ventilator dependence risk score for the prediction of prolonged mechanical ventilation in patients who survive sepsis/septic shock with respiratory failure. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.-F.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, Y.-H.; Huang, C.-H.; Hung, K.-Y.; Fang, Y.-T.; Chang, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chen, H.-C. Incorporation of dynamic segmented neutrophil-to-monocyte ratio with leukocyte count for sepsis risk stratification. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.-F.; Douglas, I.S.; Chen, Y.-M.; Lin, C.-Y.; Kao, H.-C.; Fang, Y.-T.; Huang, C.-H.; Chang, Y.-T.; Huang, K.-T.; Wang, Y.-H. Development and validation of immune dysfunction score to predict 28-day mortality of sepsis patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapik, P.; Krzych, Ł.J.; Weigl, W.; Adamski, J.; Hultstöm, M. Mortality rate in Polish intensive care units is lower than predicted according to the APACHE II scoring system. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 1745–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serafim, R.; Gomes, J.A.; Salluh, J.; Póvoa, P.A. comparison of the quick-SOFA and systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria for the diagnosis of sepsis and prediction of mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chest 2018, 153, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, A.; Alsma, J.; Verdonschot, R.J.C.G.; Rood, P.P.M.; Zietse, R.; Lingsma, H.F.; Schuit, S.C.E. Predicting mortality in patients with suspected sepsis at the Emergency Department; A retrospective cohort study comparing qSOFA, SIRS and National Early Warning Score. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Q.; Jay, M.; Hoffman, J.L.; Calvert, J.; Barton, C.; Shimabukuro, D.; Shieh, L.; Chettipally, U.; Fletcher, G.; Kerem, Y. Multicentre validation of a sepsis prediction algorithm using only vital sign data in the emergency department, general ward and ICU. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e017833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goulden, R.; Hoyle, M.-C.; Monis, J.; Railton, D.; Riley, V.; Martin, P.; Martina, R.; Nsutebu, E. qSOFA, SIRS and NEWS for predicting inhospital mortality and ICU admission in emergency admissions treated as sepsis. Emerg. Med. J. 2018, 35, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.M.; Tran, A.; Taljaard, M.; Cheng, W.; Rochwerg, B.; Seely, A.J.; Perry, J.J. Prognostic accuracy of the quick sequential organ failure assessment for mortality in patients with suspected infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 168, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raith, E.P.; Udy, A.A.; Bailey, M.; McGloughlin, S.; MacIsaac, C.; Bellomo, R.; Pilcher, D.V. Prognostic accuracy of the SOFA score, SIRS criteria, and qSOFA score for in-hospital mortality among adults with suspected infection admitted to the intensive care unit. Jama 2017, 317, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Rodríguez, F.; López-Izquierdo, R.; del Pozo Vegas, C.; Delgado-Benito, J.F.; del Pozo Pérez, C.; Carbajosa Rodríguez, V.; Mayo Iscar, A.; Martín-Conty, J.L.; Escudero Cuadrillero, C.; Castro-Villamor, M.A. A multicenter observational prospective cohort study of association of the prehospital national early warning score 2 and hospital triage with early mortality. Emerg. Med. Int. 2019, 2019, 5147808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, A.E.; Trzeciak, S.; Kline, J.A. The Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score for predicting outcome in patients with severe sepsis and evidence of hypoperfusion at the time of emergency department presentation. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, F.L.; Bota, D.P.; Bross, A.; Mélot, C.; Vincent, J.-L. Serial evaluation of the SOFA score to predict outcome in critically ill patients. Jama 2001, 286, 1754–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vosylius, S.; Sipylaite, J.; Ivaskevicius, J. Determinants of outcome in elderly patients admitted to the intensive care unit. Age Ageing 2005, 34, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baradari, A.G.; Firouzian, A.; Davanlou, A.; Aarabi, M.; Daneshiyan, M.; Kiakolaye, Y.T. Comparison of Patients’ Admission, Mean and Highest Sofa Scores in Prediction of Icu Mortality: A Prospective Observational Study. Mater. Socio-Med. 2016, 28, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, K.S.; Hsann, Y.M.; Lim, V.; Ong, B.C. The effect of comorbidity and age on hospital mortality and length of stay in patients with sepsis. J. Crit. Care 2010, 25, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knaus, W.A.; Draper, E.A.; Wagner, D.P.; Zimmerman, J.E. APACHE II: A severity of disease classification system. Crit. Care Med. 1985, 13, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Póvoa, P. C-reactive protein: A valuable marker of sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2002, 28, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Guo, S.B.; Mei, X.; Yang, P. Predictive performance of quick Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment for mortality and ICU admission in patients with infection at the ED. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 34, 1788–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-M.; Hung, K.-Y.; Chang, Y.-C.; Fang, Y.-T.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chen, H.-C.; Huang, K.-T.; Chang, H.-C.; et al. Dynamic monitoring of kidney injury status over 3 days in the intensive care unit as a sepsis phenotype associated with hospitalmortality and hyperinflammation. Biomed. J. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Vincent, J.-L.; Adhikari, N.K.; Machado, F.R.; Angus, D.C.; Calandra, T.; Jaton, K.; Giulieri, S.; Delaloye, J.; Opal, S. Sepsis: A roadmap for future research. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 581–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Prediction Rules | Cut-Off Values | AUC (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Admission NEWS2 | ||
| 7-day mortality | >8 | 0.566 * |
| 14-day mortality | >8 | 0.568 * |
| 21-day mortality | >11 | 0.511 * |
| 28-day mortality | >11 | 0.569 * |
| Day 3 SOFA | ||
| 7-day mortality | >11 | 0.740 * |
| 14-day mortality | >10 | 0.680 * |
| 21-day mortality | >8 | 0.684 * |
| 28-day mortality | >8 | 0.677 * |
| Day 3 NEWS2 | ||
| 7-day mortality | >8 | 0.741 * |
| 14-day mortality | >6 | 0.657 * |
| 21-day mortality | >6 | 0.669 * |
| 28-day mortality | >6 | 0.649 * |
| Modified Day 3 NEWS2 | ||
| 7-day mortality | >8 | 0.754 * |
| 14-day mortality | >6 | 0.664 * |
| 21-day mortality | >6 | 0.678 * |
| 28-day mortality | >6 | 0.668 * |
| 24 h NEWS2 | ||
| 7-day mortality | >6 | 0.645 * |
| 14-day mortality | >5 | 0.627 * |
| 21-day mortality | >6 | 0.631 * |
| 28-day mortality | >6 | 0.617 * |
| 72 h NEWS2 | ||
| 7-day mortality | >9 | 0.780 * |
| 14-day mortality | >6 | 0.724 * |
| 21-day mortality | >6 | 0.700 * |
| 28-day mortality | >6 | 0.667 * |
| 168 h NEWS2 | ||
| 7-day mortality | >12 | 0.919 * |
| 14-day mortality | >10 | 0.749 * |
| 21-day mortality | >9 | 0.695 * |
| 28-day mortality | >10 | 0.647 * |
| Worst Day 3 NEWS2 | ||
| 7-day mortality | >11 | 0.718 * |
| 14-day mortality | >11 | 0.704 * |
| 21-day mortality | >11 | 0.690 * |
| 28-day mortality | >11 | 0.672 * |
| Admission NEWS2 | Day 3 SOFA | Day 3 NEWS2 | Modified Day 3 NEWS2 | 24 h NEWS2 | 72 h NEWS2 | 168 h NEWS2 | Worst Day 3 NEWS2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Admission NEWS2 | 0.001 | 0.0004 | 0.0001 | 0.032 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0007 | |
| Day 3 SOFA | 0.003 | 0.985 | 0.773 | 0.061 | 0.1832 | 0.0002 | 0.666 | |
| Day 3 NEWS2 | 0.008 | 0.556 | 0.275 | 0.068 | 0.018 | 0.0001 | 0.520 | |
| Modified Day 3 NEWS2 | 0.004 | 0.671 | 0.528 | 0.038 | 0.406 | 0.0003 | 0.293 | |
| 24 h NEWS2 | 0.031 | 0.345 | 0.346 | 0.241 | 0.011 | 0.0001 | 0.096 | |
| 72 h NEWS2 | 0.0001 | 0.230 | 0.006 | 0.018 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.660 | |
| 168 h NEWS2 | 0.0001 | 0.084 | 0.005 | 0.011 | 0.001 | 0.448 | 0.0001 | |
| Worst Day 3 NEWS2 | 0.0001 | 0.075 | 0.075 | 0.108 | 0.007 | 0.433 | 0.205 |
| Admission NEWS2 | Day 3 SOFA | Day 3 NEWS2 | Modified Day 3 NEWS2 | 24 h NEWS2 | 72 h NEWS2 | 168 h NEWS2 | Worst Day 3 NEWS2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Admission NEWS2 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.034 | 0.0001 | 0.537 | 0.0001 | |
| Day 3 SOFA | 0.0006 | 0.678 | 0.857 | 0.088 | 0.622 | 0.369 | 0.843 | |
| Day 3 NEWS2 | 0.009 | 0.375 | 0.358 | 0.199 | 0.146 | 0.225 | 0.402 | |
| Modified Day 3 NEWS2 | 0.0009 | 0.773 | 0.03 | 0.111 | 0.303 | 0.0003 | 0.599 | |
| 24 h NEWS2 | 0.030 | 0.042 | 0.254 | 0.065 | 0.017 | 0.859 | 0.024 | |
| 72 h NEWS2 | 0.0009 | 0.748 | 0.367 | 0.096 | 0.064 | 0.861 | 0.660 | |
| 168 h NEWS2 | 0.0251 | 0.378 | 0.952 | 0.493 | 0.346 | 0.492 | 0.880 | |
| WorstDay 3 NEWS2 | 0.0002 | 0.879 | 0.299 | 0.842 | 0.026 | 0.804 | 0.410 |
| Total | Low-Risk | Intermediate-Risk | High-Risk | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 699 | 320 | 292 | 87 | |
| Age | 67.37 ± 14.94 | 68.22 ± 14.93 | 66.50 ± 15.11 | 67.21 ± 14.40 | >0.05 |
| Sex (Male) | 411 | 57.2% | 60.3% | 59.8% | 0.762 |
| BMI | 22.68 ± 4.86 | 22.67 ± 4.68 | 22.43 ± 5.26 | 23.54 ± 3.95 | >0.05 |
| DNR | 257 | 84 (26.3%) | 119 (40.8%) | 54 (62.1%) | <0.001 a |
| Number of comorbidities | 1.70 ± 1.18 | 1.70 ± 1.18 | 1.69 ± 1.17 | 1.74 ± 1.25 | >0.05 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | 2.56 ± 1.96 | 2.51 ± 1.95 | 2.57 ± 1.97 | 2.71 ± 1.96 | >0.05 |
| CAD | 182 (26.0%) | 93 (29.1%) | 70 (24.0%) | 19 (21.8%) | 0.227 |
| Hypertension | 395 (56.6%) | 191 (59.7%) | 160 (54.8%) | 44 (51.2%) | 0.264 |
| COPD | 105 (15%) | 58 (18.1%) | 35 (12.0%) | 13 (13.8) | 0.099 |
| Asthma | 26 (3.7%) | 10 (3.1%) | 13 (4.5%) | 3 (3.4) | 0.515 |
| Pulmonary TB | 54 (7.7%) | 24 (7.5%) | 23 (7.9%) | 7 (8.0%) | 0.978 |
| Malignancy | 158 (22.7%) | 69 (21.6%) | 67 (23.2%) | 22 (25.3%) | 0.749 |
| HBV | 25 (3.6%) | 10 (3.1%) | 10 (3.4%) | 5 (5.7%) | 0.497 |
| HCV | 34 (4.9%) | 12 (3.8%) | 16 (5.5%) | 6 (6.9%) | 0.675 |
| Cirrhosis | 56 (8%) | 18 (5.6%) | 27 (9.2%) | 11 (12.6%) | 0.060 |
| DM | 315 (45.1%) | 146 (45.6%) | 134 (45.9%) | 35 (40.2%) | 0.624 |
| CVA | 130 (18.6%) | 55 (17.2%) | 61 (20.9%) | 14 (16.1%) | 0.408 |
| CKD | 218 (31.2%) | 96 (30.0%) | 87 (29.8%) | 35 (40.2%) | 0.129 |
| Intubation | 639 (91.4%) | 292 (91.3%) | 264 (90.4%) | 83 (95.4%) | 0.341 |
| NIPPV | 29 (4.1%) | 11 (3.4%) | 15 (5.1%) | 3 (3.4%) | 0.540 |
| APACHE II | - | 22.86 ± 7.83 | 24.99 ± 8.38 | 27.47 ± 7.76 | <0.05 |
| Adm NEWS2 | - | 6.81 ± 3.05 | 8.41 ± 2.95 | 9.82 ± 3.19 | <0.001 a |
| 24 h NEWS2 | - | 5.60 ± 2.22 | 7.60 ± 2.52 | 8.53 ± 2.53 | <0.001 a |
| 168 h NEWS2 | - | 7.73 ± 4.29 | 8.44 ± 3.66 | 10.13 ± 3.82 | <0.05 c |
| Adm SOFA | - | 7.83 ± 3.08 | 9.03 ± 3.59 | 12.86 ± 2.83 | <0.001 a |
| Day 3 SOFA | - | 6.20 ± 2.17 | 7.81 ± 2.97 | 13.94 ± 2.75 | <0.001 a |
| Adm WBC (K) | - | 14.24 ± 8.11 | 14.47 ± 8.03 | 13.62 ± 8.95 | >0.05 |
| Day 3 WBC (K) | - | 12.33 ± 6.97 | 13.14 ± 6.28 | 13.78 ± 7.45 | >0.05 |
| Adm SeMo ratio | - | 29.22 ± 35.72 | 30.30 ± 28.92 | 31.03 ± 26.09 | >0.05 |
| Day 3 SeMo ratio | - | 25.05 ± 21.79 | 27.00 ± 31.18 | 36.91 ± 30.13 | <0.05 c |
| Day 3 Adm SeMo ratio | - | −4.57 ± 38.82 | −3.35 ± 39.34 | 7.49 ± 34.55 | 0.027 c |
| Adm CRP | - | 126.49 ± 107.27 | 155.61 ± 119.11 | 160.60 ± 126.00 | 0.012 b |
| Day 3 CRP | - | 106.67 ± 90.79 | 136.34 ± 100.02 | 167.28 ± 113.97 | <0.05 a |
| Variable | HR | 95%CI of HR | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crude | |||
| Risk stratification † | |||
| Intermediate-risk group | 2.344 | 1.698–3.236 | <0.001 |
| High-risk group | 6.810 | 3.927–11.811 | <0.001 |
| Adjusted | |||
| Risk stratification † | |||
| Intermediate-risk group | 1.884 | 1.203–2.950 | 0.023 |
| High-risk group | 5.361 | 2.704–7.521 | 0.002 |
| Variation of SeMo ratio (day 3 Adm) | 1.004 | 1.000–1.008 | 0.027 |
| DNR | 3.382 | 2.300–4.972 | <0.001 |
| Day 3 WBC | 1.030 | 1.003–1.057 | 0.027 |
| Day 3 CRP | 0.999 | 0.997–1.001 | 0.309 |
| 168 h NEWS2 | 1.145 | 1.093–1.199 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, C.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chen, H.-C.; Chang, Y.-P.; Chen, Y.-M.; Huang, K.-T.; Wang, Y.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; et al. Application of a 72 h National Early Warning Score and Incorporation with Sequential Organ Failure Assessment for Predicting Sepsis Outcomes and Risk Stratification in an Intensive Care Unit: A Derivation and Validation Cohort Study. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11090910
Hsu C-Y, Tsai Y-H, Lin C-Y, Chang Y-C, Chen H-C, Chang Y-P, Chen Y-M, Huang K-T, Wang Y-H, Wang C-C, et al. Application of a 72 h National Early Warning Score and Incorporation with Sequential Organ Failure Assessment for Predicting Sepsis Outcomes and Risk Stratification in an Intensive Care Unit: A Derivation and Validation Cohort Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(9):910. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11090910
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Chih-Yi, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Chiung-Yu Lin, Ya-Chun Chang, Hung-Cheng Chen, Yu-Ping Chang, Yu-Mu Chen, Kuo-Tung Huang, Yi-Hsi Wang, Chin-Chou Wang, and et al. 2021. "Application of a 72 h National Early Warning Score and Incorporation with Sequential Organ Failure Assessment for Predicting Sepsis Outcomes and Risk Stratification in an Intensive Care Unit: A Derivation and Validation Cohort Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 9: 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11090910
APA StyleHsu, C.-Y., Tsai, Y.-H., Lin, C.-Y., Chang, Y.-C., Chen, H.-C., Chang, Y.-P., Chen, Y.-M., Huang, K.-T., Wang, Y.-H., Wang, C.-C., Lin, M.-C., & Fang, W.-F. (2021). Application of a 72 h National Early Warning Score and Incorporation with Sequential Organ Failure Assessment for Predicting Sepsis Outcomes and Risk Stratification in an Intensive Care Unit: A Derivation and Validation Cohort Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(9), 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11090910