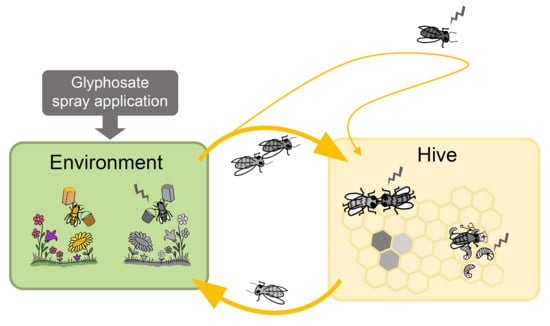
Effects of the Herbicide Glyphosate on Honey Bee Sensory and Cognitive Abilities: Individual Impairments with Implications for the Hive
Abstract
:1. Background: The Presence of the Herbicide Glyphosate in the Surroundings of Honey Bee Hives
2. Searching for Food in Disturbed Environments: Changes in Cognitive Abilities Represented by Elemental and Non-elemental Olfactory Learning
3. Homeward Flights after Feeding from Resources Containing GLY Traces
4. How Cognitive Abilities of Young Hive Bees Are Affected by GLY Traces
5. Chronic Exposure of GLY and Its Effects on the Youngest Hive Mates: How Brood Development Is Affected by an Herbicide
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Potts, S.G.; Biesmeijer, J.C.; Kremen, C.; Neumann, P.; Schweiger, O.; Kunin, W.E. Global pollinator declines: Trends, impacts and drivers. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanengelsdorp, D.; Meixner, M.D. A historical review of managed honey bee populations in Europe and the United States and the factors that may affect them. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 103, S80–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meehan, T.D.; Werling, B.P.; Landis, D.A.; Gratton, C. Agricultural landscape simplification and insecticide use in the Midwestern United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11500–11505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tscharntke, T.; Klein, A.M.; Kruess, A.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Thies, C.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Steffan-Dewenter, I. Landscape perspectives on agricultural intensification and biodiversity—Ecosystem service management. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 857–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbrook, C.M. Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohan, D.A.; Boffey, C.W.; Brooks, D.R.; Clark, S.J.; Dewar, A.M.; Firbank, L.G.; Haughton, A.J.; Hawes, C.; Heard, M.S.; May, M.J.; et al. Effects on weed and invertebrate abundance and diversity of herbicide management in genetically modified herbicide-tolerant winter-sown oilseed rape. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2005, 272, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IPBES. The Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services on Pollinators, Pollination and Food Production; Potts, S.G., Imperatriz-Fonseca, V.L., Ngo, H.T., Eds.; Secretariat of the IPBES: Bonn, Germany, 2016; 552p. [Google Scholar]
- Ollerton, J.; Winfree, R.; Tarrant, S. How many flowering plants are pollinated by animals? Oikos 2011, 120, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.-L.J.; Kingston, J.M.; Lee, A.; Holway, D.A.; Kohn, J.R. Non-native honey bees disproportionately dominate the most abundant floral resources in a biodiversity hotspot. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2019, 286, 20182901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honey Bees: Estimating the Environmental Impact of Chemicals; Devillers, J.; Pham-Delègue, M.H. (Eds.) CRC Press: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Seeley, T.D. The Wisdom of the Hive: The Social Physiology of Honey Bee Colonies; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Giesy, J.P.; Dobson, S.; Solomon, K.R. Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment for Roundup® Herbicide. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 167, 35–120. [Google Scholar]
- Frasier, W.D.; Jenkins, G. The Acute Contact and Oral Toxicities of CP67573 and MON2139 to Worker Honey Bees. Unpublished Report no. 4G1444, 1972, Submitted to U.S. Environmental Protection Agency by Monsanto Company, Prepared by Huntingdon Research Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) Glyphosate; EPA-738-F-93-011; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Prevention, Pesticides, and Toxic Substances, Office of Pesticide Programs, U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1993.
- Motta, E.V.S.; Raymann, K.; Moran, N.A. Glyphosate perturbs the gut microbiota of honey bees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 10305–10310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, P.; Yan, Z.; Ma, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Hou, C.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Diao, Q. The Herbicide Glyphosate Negatively Affects Midgut Bacterial Communities and Survival of Honey Bee during Larvae Reared in Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7786–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blot, N.; Veillat, L.; Rouzé, R.; Delatte, H. Glyphosate, but not its metabolite AMPA, alters the honeybee gut microbiota. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupke, C.H.; Hunt, G.J.; Eitzer, B.D.; Andino, G.; Given, K. Multiple Routes of Pesticide Exposure for Honey Bees Living Near Agricultural Fields. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peruzzo, P.J.; Porta, A.A.; Ronco, A.E. Levels of glyphosate in surface waters, sediments and soils associated with direct sowing soybean cultivation in north pampasic region of Argentina. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, A.M.; Gervais, J.A.; Luukinen, B.; Buhl, K.; Stone, D.; Strid, A.; Cross, A.; Jenkins, J. Glyphosate Technical Fact Sheet; National Pesticide Information Center, Oregon State University Extension Services. 2010. Available online: http://npic.orst.edu/factsheets/archive/glyphotech.html (accessed on 10 October 2012).
- Couture, G.; Legris, J.; Langevin, R. Évaluation des Impacts du Glyphosate Utilisé Dans le Milieu Forestier; Ministere des Ressources Naturelles, Direction de Penvironment forestier, Service du Suivi Environmental, Charles-Bourg: Quebec, QC, Canada, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, K.; Thompson, D. Ecological Risk Assessment for Aquatic Organisms from Over-Water Uses of Glyphosate. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2003, 6, 289–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.; Reichenbecher, W.; Teichmann, H.; Tappeser, B.; Lötters, S. Questions concerning the potential impact of glyphosate-based herbicides on amphibians. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 1688–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, F.; Hidalgo, C.; Sancho, J.V. Determination of glyphosate residues in plants by precolumn derivatization and coupled-column liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. AOAC Int. 2000, 83, 728–734. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, H.M.; Levine, S.L.; Doering, J.; Norman, S.; Manson, P.; Sutton, P.; Von Mérey, G. Evaluating exposure and potential effects on honeybee brood (Apis mellifera) development using glyphosate as an example. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2014, 10, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molan, P.C. The antibacterial activity of honey: 1. The nature of the antibacterial activity. Bee World 1992, 73, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, F.; Guo, E.; Kamp, L. Survey of glyphosate residues in honey, corn and soy products. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2014, 5, 249. [Google Scholar]
- Chamkasem, N.; Vargo, J.D. Development and independent laboratory validation of an analytical method for the direct determination of glyphosate, glufosinate, and aminomethylphosphonic acid in honey by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J. Regul. Sci. 2017, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, C.J.; King, H.P.; Delenstarr, G.; Kumar, R.; Rubio, F.; Glaze, T. Glyphosate residue concentrations in honey attributed through geospatial analysis to proximity of large-scale agriculture and transfer off-site by bees. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US EPA White Paper in Support of the Proposed Risk Assessment Process for Bees; Chemical Safety and Pollution Prevention, Office of Pesticides Programs, Environmental Fate and Effects Division: Ottawa, Canada, 2012.
- Raina-Fulton, R. A review of methods for the analysis of orphan and difficult pesticides: Glyphosate, glufosinate, quaternary ammonium and phenoxy acid herbicides, and dithiocarbamate and phthalimide fungicides. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, E.A.D.; Mulhauser, B.; Mulot, M.; Mutabazi, A.; Glauser, G.; Aebi, A. A worldwide survey of neonicotinoids in honey. Science 2017, 358, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herbert, L.T.; Vazquez, D.E.; Arenas, A.; Farina, W.M. Effects of field-realistic doses of glyphosate on honeybee appetitive behaviour. J. Exp. Boil. 2014, 217, 3457–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbuena, M.S.; Tison, L.; Hahn, M.-L.; Greggers, U.; Menzel, R.; Farina, W.M. Effects of sublethal doses of glyphosate on honeybee navigation. J. Exp. Boil. 2015, 218, 2799–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mengoni Goñalons, C.M.; Farina, W.M. Impaired associative learning after chronic exposure to pesticides in young adult honey bees. J. Exp. Boil. 2018, 221, jeb176644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vázquez, D.E.; Ilina, N.; Pagano, E.A.; Zavala, J.A.; Farina, W.M. Glyphosate affects the larval development of honey bees depending on the susceptibility of colonies. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Frisch, K. The Dance Language and Orientation of Bees; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Chittka, L.; Thomson, J.D. (Eds.) Cognitive Ecology of Pollination; Animal Behavior and Floral Evolution Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999; pp. 83–105. [Google Scholar]
- Lindauer, M. Communication among Social Bees; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Dukas, R. Life History of Learning: Performance Curves of Honeybees in the Wild. Ethology 2008, 114, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galizia, G.C.; Eisenhardt, D.; Giurfa, M. Honeybee Neurobiolgy and Behavior: A Tribute to Randolf Menzel; Springer: Heildelberg, Germany, 2012; 509p. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoz, J.-C.; Giurfa, M. Invertebrate learning and memory: Fifty years of olfactory conditioning of the proboscis extension response in honeybees. Learn. Mem. 2012, 19, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Menzel, R. The honeybee as a model for understanding the basis of cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, L.-H.; Wu, W.-Y.; Berenbaum, M.R. Behavioral responses of honey bees (Apis mellifera) to natural and synthetic xenobiotics in food. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giurfa, M. Behavioral and neural analysis of associative learning in the honeybee: A taste from the magic well. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2007, 193, 801–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurfa, M. Cognitive neuroethology: Dissecting non-elemental learning in a honeybee brain. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2003, 13, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deisig, N. Configural Olfactory Learning in Honeybees: Negative and Positive Patterning Discrimination. Learn. Mem. 2001, 8, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knudsen, J.T.; Eriksson, R.; Gershenzon, J.; Ståhl, B. Diversity and Distribution of Floral Scent. Bot. Rev. 2006, 72, 1–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, R.; Greggers, U.; Smith, A.; Berger, S.; Brandt, R.; Brunke, S.; Bundrock, G.; Hülse, S.; Plümpe, T.; Schaupp, F.; et al. Honey bees navigate according to a map-like spatial memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3040–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menzel, R.; Fuchs, J.; Kirbach, A.; Lehmann, K.; Greggers, U. Navigation and communication in honeybees, Chap. 2.5. In Honeybee Neurobiology and Behavior: A Tribute to Randolf Menzel; Galizia, C.G., Eisenhardt, D., Giurfa, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 103–116. [Google Scholar]
- Menzel, R.; Geiger, K.; Joerges, J.; Müller, U.; Chittka, L. Bees travel novel homeward routes by integrating separately acquired vector memories. Anim. Behav. 1998, 55, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeGrandi-Hoffman, G.; Martin, J.H. The size and distribution of the honey bee (Apis mellifera L.) cross-pollinating population on male-sterile sunflowers (Helianthus annuus L.). J. Apic. Res. 1993, 32, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüter, C.; Farina, W.M. Nectar distribution and its relation to food quality in honeybee (Apis mellifera) colonies. Insectes Sociaux 2007, 54, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, J.A. The relationship between sugar flowand foraging and recruiting behaviour of honey bees (Apis mellifera L.). Anim. Behav. 1970, 18, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amdam, G.V.; Norberg, K.; Fondrk, M.K.; Page, R.E. Reproductive ground plan may mediate colony-level selection effects on individual foraging behavior in honey bees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11350–11355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masson, C.; Arnold, G. Organization and Plasticity of the Olfactory System of the Honeybee, Apis mellifera. In Neurobiology and Behavior of Honeybees; Menzel, R., Mercer, A., Eds.; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin, Germany, 1987; pp. 280–295. [Google Scholar]
- Arenas, A.; Ramírez, G.P.; Balbuena, M.S.; Farina, W.M. Behavioral and neural plasticity caused by early social experiences: The case of the honeybee. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, W.M.; Grüter, C.; Acosta, L.; Mc Cabe, S. Honeybees learn floral odors while receiving nectar from foragers within the hive. Naturwissenschaften 2007, 94, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, A.; Fernández, V.M.; Farina, W.M. Floral odor learning within the hive affects honeybees’ foraging decisions. Naturwissenschaften 2007, 94, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frings, H. The loci of olfactory end-organs in the honey-bee, Apis mellifera Linn. J. Exp. Zool. 1944, 97, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, R.E., Jr.; Erber, J.; Fondrk, M. The effect of genotype on response thresholds to sucrose and foraging behavior of honey bees (Apis mellifera L.). J. Comp. Physiol. A 1998, 182, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankiw, T.; Nelson, M.; Page, R.E.; Fondrk, M.K. The communal crop: Modulation of sucrose response thresholds of pre-foraging honey bees with incoming nectar quality. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2004, 55, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.; Farina, W.M. Honeybees modify gustatory responsiveness after receiving nectar from foragers within the hive. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2008, 62, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, G.P.; Martinez, A.S.; Fernández, V.M.; Bielsa, G.C.; Farina, W.M. The Influence of Gustatory and Olfactory Experiences on Responsiveness to Reward in the Honeybee. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmer, S.H.; Kerbaol, A.; Aras, P.; Jumarie, C.; Boily, M. Effects of realistic doses of atrazine, metolachlor, and glyphosate on lipid peroxidation and diet-derived antioxidants in caged honey bees (Apis mellifera). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 8010–8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boily, M.; Sarrasin, B.; Deblois, C.; Aras, P.; Chagnon, M. Acetylcholinesterase in honey bees (Apis mellifera) exposed to neonicotinoids, atrazine and glyphosate: Laboratory and field experiments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5603–5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Yao, J.; Adamczyk, J.; Luttrell, R. Feeding toxicity and impact of imidacloprid formulation and mixtures with six representative pesticides at residue concentrations on honey bee physiology (Apis mellifera). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 0178421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, H.L.; Ribbands, C.R. Food transmission within the honeybee community. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Boil. Sci. 1952, 140, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Crailsheim, K. Trophallactic interactions in the adult honeybee (Apis mellifera L.). Apidologie 1998, 29, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faita, M.R.; de Medeiros Oliveira, E.; Júnior, V.V.A.; Orth, A.I.; Nodari, R.O. Changes in hypopharyngeal glands of nurse bees (Apis mellifera) induced by pollen-containing sublethal doses of the herbicide Roundup. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertholf, L.M. The moults of the honeybee. J. Econ. Entomol. 1925, 18, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Michelette, E.R.; Soares, A.E.E. Characterization of preimaginal developmental stages in Africanized honeybee workers. Apidologie 1993, 24, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rembold, H.; Kremer, J.P.; Ulrich, G.M. Characterization of postembryonic developmental stages. Apidologie 1980, 11, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodschneider, R.; Crailsheim, K. Nutrition and health in honey bees. Apidologie 2010, 41, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorc, A.; Ellis, J.D. Cell death localization in situ in laboratory reared honeybee (Apis mellifera L.) larvae treated with pesticides. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2011, 99, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorc, A.; Evans, J.D.; Scharf, M.; Ellis, J.D. Gene expression in honey bee (Apis mellifera) larvae exposed to pesticides and Varroa mites (Varroa destructor). J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seide, V.E.; Bernardes, R.C.; Pereira, E.J.G.; Lima, M.A.P. Glyphosate is lethal and Cry toxins alter the development of the stingless bee Melipona quadrifasciata. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1854–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Anelli, C.M.; Sheppard, W.S. Sublethal effects of pesticide residues in brood comb on worker honeybee (Apis mellifera) development and longevity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14720. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.Y.; Otis, G.W. Inspection and feeding of larvae by worker honeybees (Hymenoptera: Apidae): Effect of starvation and food quantity. J. Insect Behav. 1991, 4, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Conte, Y.; Sreng, L.; Poitout, S.H. Brood Pheromone Can Modulate the Feeding Behavior of Apis mellifera Workers (Hymenoptera: Apidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 1995, 88, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmency, H. Pleiotropic effects of herbicide-resistance genes on crop yield: A review. Pest Manag. Sci. 2013, 69, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütte, G.; Eckerstorfer, M.; Rastelli, V.; Reichenbecher, W.; Restrepo-Vassalli, S.; Ruohonen-Lehto, M.; Saucy, A.-G.W.; Mertens, M. Herbicide resistance and biodiversity: Agronomic and environmental aspects of genetically modified herbicide-resistant plants. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2017, 29, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.M. Current state of herbicides in herbicide-resistant crops. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromenshenk, J.J.; Preston, E.M. Public participation in environmental monitoring: A means of attaining network capability. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1986, 6, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromenshenk, J.; Gudatis, J.; Carlson, S.; Thomas, J.; Simmons, M. Population dynamics of honey bee nucleus colonies exposed to industrial pollutants. Apidologie 1991, 22, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farina, W.M.; Balbuena, M.S.; Herbert, L.T.; Mengoni Goñalons, C.; Vázquez, D.E. Effects of the Herbicide Glyphosate on Honey Bee Sensory and Cognitive Abilities: Individual Impairments with Implications for the Hive. Insects 2019, 10, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10100354
Farina WM, Balbuena MS, Herbert LT, Mengoni Goñalons C, Vázquez DE. Effects of the Herbicide Glyphosate on Honey Bee Sensory and Cognitive Abilities: Individual Impairments with Implications for the Hive. Insects. 2019; 10(10):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10100354
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarina, Walter M., M. Sol Balbuena, Lucila T. Herbert, Carolina Mengoni Goñalons, and Diego E. Vázquez. 2019. "Effects of the Herbicide Glyphosate on Honey Bee Sensory and Cognitive Abilities: Individual Impairments with Implications for the Hive" Insects 10, no. 10: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10100354
APA StyleFarina, W. M., Balbuena, M. S., Herbert, L. T., Mengoni Goñalons, C., & Vázquez, D. E. (2019). Effects of the Herbicide Glyphosate on Honey Bee Sensory and Cognitive Abilities: Individual Impairments with Implications for the Hive. Insects, 10(10), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10100354