Crosstalk among Indoleamines, Neuropeptides and JH/20E in Regulation of Reproduction in the American Cockroach, Periplaneta americana
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Insects
2.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.3. Preparation and Injection of dsRNA
2.4. mRNA Quantification
2.5. Competitive ELISA
2.6. CCAP and sNPF Injection into the Hemolymph
2.7. Immunocytochemistry
2.8. Measurements of Ecdysteroid (20E) Titer
2.9. Ecdysteroid (20E) Injection
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. RESULTS
3.1. aaNAT Acts in Vitellogenesis
3.2. Effect of Indoleamines on Vitellogenin Synthesis
3.3. CCAP and sNPF Concentration in the Hemolymph after Injection of dsRNAaaNAT
3.4. Effect of CCAP and sNPF Injections on Ecdysteroid (20E) Titer in the Hemolymph and Ovary
3.5. Effect of Neuropeptides (CCAP and sNPF) on JH Synthesis Pathway during Vitellogenesis
3.6. Ovarian Cellular Distribution of PaVgR Protein
3.7. Dose Responses by Injection of 20E on Vitellogenesis
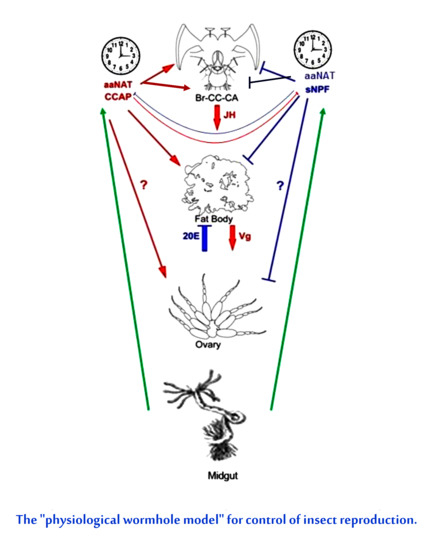
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tufail, M.; Takeda, M. Insect vitellogenin/lipophorin receptors: Molecular structures, role in oogenesis, and regulatory mechanisms. J. Insect Physiol. 2009, 55, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufail, M.; Nagaba, Y.; Elgendy, A.M.; Takeda, M. Regulation of vitellogenin genes in insects. Entomol. Sci. 2014, 17, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmogy, M.; Mohamed, A.A.; Tufail, M.; Uno, T.; Takeda, M. Molecular and functional characterization of the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana, Rab5: The first exopterygotan low molecular weight ovarian GTPase during oogenesis. Insect Sci. 2018, 25, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonet, G.; Poels, J.; Claeys, I.; Van Loy, T.; Franssens, V.; De Loof, A.; Vanden Broek, J. Neuroendrocrinological and molecular aspects of insect reproduction. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2004, 16, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raikhel, A.S.; Browon, M.R.; Belles, X. Hormonal control of reproductive processes. In Comprehensive Molecular Insect Science; Gilbert, L.I., Iatrou, K., Gill, S.S., Eds.; Elsevier Pergamon: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 3, pp. 433–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swevers, L. An update on ecdysone signaling during insect oogenesis. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2019, 31, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotaki, T. Oosorption in the stink bug, Plautia crossota stali: Induction and vitellogenin dynamics. J. Insect Physiol. 2003, 49, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Koopmanschap, A.B.; Privee, H.; de Kort, C.A.D. The mode of regulation of the corpus allatum activity during starvation in adult females of the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Say). J. Insect Physiol. 1982, 28, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoofs, L.; De Loof, A.; Van Hiel, M.B. Neuropeptides as regulators of behavior in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2017, 62, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Dong, S.; Li, M.-T.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Stanley, D.; Chen, X.-X. The endoparasitoid, Cotesia vestalis, regulates host physiology by reprogramming the neuropeptide transcriptional network. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sevala, V.L.; Sevala, V.M.; Loughton, B.G. FMRFamide-like activity in the female locust during vitellogenesis. J. Comp. Neurol. 1993, 337, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerstiaens, A.; Benfekih, L.; Zouiten, H.; Verhaert, P.; Loof, A.D.; Schoofs, L. Led-NFP 1 stimulates ovarian development in locusts. Peptides 1999, 20, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardie, J.; Richard, O.; Girardie, A. Detection of vitellogenin in the hemolymph of larval female locusts (Locusta migratoria) treated with neurohormone, Lom-OMP. J. Insect Physiol. 1996, 42, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardie, J.; Huet, J.C.; Atay-Kadiri, Z.; Ettaouil, S.; Delbecque, J.P.; Fournier, B.; Pernollet, J.C.; Girardie, A. Isolation, sequence determination, physical, and physiological characterization of the neuroparsins and ovary maturing proteins of Schistocerca gregaria. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 28, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayali, A. The role of the arthropod stomatogastric nervous system in moulting behaviour and ecdysis. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakai, T.; Satake, H.; Minakata, H.; Takeda, M. Characterization of crustacean cardioactive peptide as a novel insect midgut factor: Isolation, localization, and stimulation of α-amylase activity and gut contraction. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 5671–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mikani, A.; Watari, Y.; Takeda, M. Brain-midgut cross-talk and autocrine metabolastat via the sNPF/CCAP negative feed-back loop in the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res. 2015, 362, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammie, S.C.; Truman, J.W. Neuropeptide hierarchies and the activation of sequential motor behaviors in the hawkmoth, Manduca sexta. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 4389–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mesce, K.A.; Fahrbach, S.E. Integration of endocrine signals that regulate insect ecdysis. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2002, 23, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veelaert, D.; Passier, P.; Devreese, B.; Vanden Broeck, J.; Van Beeumen, J.; Vullings, H.G.B.; Diederen, J.H.B.; Schoofs, L.; De Loof, A. Isolation and characterization of an adipokinetic hormone release-inducing factor in locusts: The crustacean cardioactive peptide. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donini, A.; Agricola, H.J.; Lange, A.B. Crustacean cardioactive peptide is a modulator of oviduct contractions in Locusta migratoria. J. Insect Physiol. 2001, 47, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wielendaele, P.; Badisco, L.; Vanden Broeck, J. Neuropeptidergic regulation of reproduction in insects. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 188, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendy, A.M.; Tufail, M.; Mohamed, A.A.; Takeda, M. A putative direct repeat element plays a dual role in the induction and repression of insect vitellogenin-1 gene expression. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 234, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufail, M.; Lee, J.; Hatakeyama, M.; Oishi, K.; Takeda, M. Cloning of vitellogenin cDNA of the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana (Dictyoptera), and its structural and expression analyses. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2000, 45, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, H.; Bembenek, J.; Takeda, M. Multiple forms of arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase (NAT) from cockroach female colleterial glands and activity changes along oocyte maturation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2003, 134, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamruzzaman, A.S.M.; Asano, H.; Hiragaki, S.; Takeda, M. Indoleamines regulate vitellogenesis via cross-talks with allatotrophe in the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 4, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tordjman, S.; Chokron, S.; Delorme, R.; Charrier, A.; Bellissant, E.; Jafari, N.; Fougerou, C. Melatonin: Pharmacology, functions and therapeutic benefits. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiragaki, S.; Suzuki, T.; Mohamed, A.A.; Takeda, M. Structures and functions of insect arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase (iaaNAT); a key enzyme for physiological and behavioral switch in arthropods. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ichihara, N.; Okada, M.; Takeda, M. Characterization and purification of polymorphic arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase from the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2001, 32, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, M.; Escriva, L.; Collantes-Alegre, J.M.; Meca, G.; Rosato, E.; Martinez-Torres, D. Melatonin in the seasonal response of the aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richter, K.; Peschke, E.; Peschke, D. Effect of melatonin on the release of prothoracicotrophic hormone from the brain of Periplaneta americana (Blattodea: Blattidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 1999, 96, 341–345. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.A.M.; Wang, Q.; Bembenek, J.; Ichihara, N.; Hiragaki, S.; Suzuki, T.; Takeda, M. N-acetyltransferase (nat) is a critical conjunct of photoperiodism between the circadian system and endocrine axis in Antheraea pernyi. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jarosch, A.; Moritz, R.F.A. RNA interference in honeybees: Off-target effects caused by dsRNA. Apidologie 2012, 43, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunes, F.M.; Aleixo, A.C.; Barchuk, A.R.; Bomtorin, A.D.; Grozinger, C.M.; Simões, Z.L. Non-target effects of green fluorescent protein (GFP)-derived double-stranded RNA (dsRNA-GFP) used in honey bee RNA interference (RNAi) assays. Insects 2013, 4, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Oi, F.M.; Scharf, M.E. Social exploitation of hexamerin: RNAi reveals a major caste-regulatory factor in termites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 4499–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alshukri, B.; Astarita, F.; Al-Esawy, M.; Abd El Halim, H.M.E.; Pennacchio, F.; Gatehouse, A.M.R.; Edwards, M.G. Targeting the potassium ion channel genes SK and SH as a novel approach for control of insect pests: Efficacy and biosafety. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2505–2516. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schimittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, T.; Satake, H.; Takeda, M. Nutrient-induced α-amylase and protease activity is regulated by crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP) in the cockroach midgut. Peptides 2006, 27, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcheron, P.; Moriniere, M.; Grassi, J.; Pradelles, P. Development of an enzyme immunoassay for ecdysteroids using acetylcholinesterase as label. Insect Biochem. 1989, 19, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slinger, A.; Isaac, R. Ecdysteroid titres during embryogenesis of the cockroach, Periplaneta americana. J. Insect Physiol. 1988, 34, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, R.J.; Strambi, A.; Strambi, C. The significance of free ecdysteroids in the haemolymph of adult cockroaches. J. Insect Physiol. 1984, 30, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruntenko, N.E.; Rauschenbach, I.Y. Interplay of JH, 20E and biogenic amines under normal and stress conditions and its effect on reproduction. J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bembenek, J.; Sehadova, H.; Ichihara, N.; Takeda, M. Day/night fluctuations in melatonin content, arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase activity and nat mRNA expression in the CNS, peripheral tissues and hemolymph of the cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 140, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granger, N.A.; Sturgis, S.L.; Ebersohl, R.; Geng, C.; Sparks, T.C. Dopaminergic control of corpora allata in the larval tobacco horn worm, Manduca sexta. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1996, 32, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Saha, T.T.; Zou, Z.; Raikhel, A.S. Regulatory pathways controlling female insect reproduction. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 489–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannini, L.; Ciolfi, S.; Dallai, R.; Frati, F.; Hoffmann, K.H.; Meyering-Vos, M. Putative-farnesoic acid O-methyltransferase (FAMeT) in medfly reproduction. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 75, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Marchal, E.; Hult, E.F.; Tobe, S.S. Characterization of the juvenile hormone pathway in the viviparous cockroach, Diploptera punctata. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shinoda, T.; Itoyama, K. Juvenile hormone acid methyltransferase: A key regulatory enzyme for insect metamorphosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11986–11991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieira, C.U.; Bonetti, A.M.; Simões, Z.L.; Maranhão, A.Q.; Costa, C.S.; Costa, M.C.; Siquieroli, A.C.; Nunes, F.M. Farnesoic acid O-methyl transferase (FAMeT) isoforms: Conserved traits and gene expression patterns related to caste differentiation in the stingless bee, Melipona scutellaris. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2008, 67, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtenshaw, S.M.; Su, P.P.; Zhang, J.R.; Tobe, S.S.; Dayton, L.; Bendena, W.G. A putative farnesoic acid O-methyltransferase (FAMeT) orthologue in Drosophila melanogaster (CG10527): Relationship to juvenile hormone biosynthesis? Peptides 2008, 29, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tian, L.; Tobe, S.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, X.; Liu, Y.; Bendena, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.Q. Drosophila CG10527 mutants are resistant to juvenile hormone and its analog methoprene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 401, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, C.; Yang, B.; Gu, J.; Liu, Z. Cloning and characterization of a putative farnesoic acid O-methyltransferase gene from the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchal, E.; Zhang, J.; Badisco, L.; Verlinden, H.; Hult, E.F.; Van Wielendaele, P.; Yagi, K.J.; Tobe, S.S.; Vanden Broeck, J. Final steps in juvenile hormone biosynthesis in the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomtorin, A.D.; Mackert, A.; Rosa, G.C.; Moda, L.M.; Martins, J.R.; Bitondi, M.M.; Hartfelder, K.; Simões, Z.L. Juvenile hormone biosynthesis gene expression in the corpora allata of honeybee (Apis mellifera L.) female castes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tufail, M.; Hatakeyama, M.; Takeda, M. Molecular evidence for two vitellogenin genes and processing of vitellogenins in the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2001, 48, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verlinden, H.; Gijbels, M.; Lismont, E.; Lenaerts, C.; Vanden Broeck, J.; Marchal, E. The pleiotropic allatoregulatory neuropeptides and their receptors: A mini-review. J. Insect Physiol. 2015, 80, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gäde, G.; Hoffmann, K.H. Neuropeptides regulating development and reproduction in insects. Physiol. Entomol. 2005, 30, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikani, A.; Wang, Q.S.; Takeda, M. Brain-midgut short neuropeptide F mechanism that inhibits digestive activity of the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana upon starvation. Peptides 2012, 34, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Žitňan, D.; Watanabe, K.; Kawada, T.; Satake, H.; Kaneko, Y.; Hiruma, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Shinoda, T. Neuropeptide receptor transcriptome reveals unidentified neuroendocrine pathways. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaneko, Y.; Hiruma, K. Short neuropeptide F (sNPF) is a stage-specific suppressor for juvenile hormone biosynthesis by corpora allata, and a critical factor for the initiation of insect metamorphosis. Dev. Biol. 2014, 393, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, C.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Ye, H. Neuropeptides in the cerebral ganglia of the mud crab, Scylla paramamosain: Transcriptomic analysis and expression profiles during vitellogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoofs, L.; Clynen, E.; Cerstiaens, A.; Baggerman, G.; Wei, Z.; Vercammen, T.; Nachman, R.; Loof, A.D.; Tanaka, S. Newly discovered functions for some myotropic neuropeptides in locusts. Peptides 2001, 22, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikhel, A.S. The accumulative pathway of vitellogenin in the mosquito oocyte: A high-resolution immuno-and cytochemical study. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1984, 87, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sappington, T.W.; Hays, A.R.; Raikhel, A.S. Mosquito vitellogenin receptor: Purification, developmental and biochemical characterization. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 25, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, M.; Takeda, M. Molecular cloning, characterization and regulation of the cockroach vitellogenin receptor during oogenesis. Insect. Mol. Biol. 2005, 14, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soller, M.; Bownes, M.; Kubli, E. Control of oocyte maturation in sexually mature Drosophila females. Dev. Biol. 1999, 208, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stay, B.; Friedel, T.; Tobe, S.S.; Mundall, E.C. Feedback control of juvenile hormone synthesis in cockroaches: Possible role for ecdysterone. Science 1980, 207, 898–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romana, I.; Pascual, N.; Bellés, X. The ovary is a source of circulating ecdysteroids in Blattella germanica (L.) (Dictyoptera, Blattellidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 1995, 92, 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- Friedel, T.; Feyereisen, R.; Mundall, E.C.; Tobe, S.S. The allatostatic effect of 20- hydroxyecdysone on the adult viviparous cockroach, Diploptera punctata. J. Insect Physiol. 1980, 26, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| aaNAT-FT7 | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGATAATGGCAGTATCCAGAAC |
| aaNAT-FT7 | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAGATATTATGCGCACTTCTAC |
| aaNAT qpcr F | TGTGTTTCAACCAGCTCTGC |
| aaNAT qpcr R | AACTTCCACTCGTAGTGGTTCC |
| Vg1 Forward | CCAGACATTATCAGACCTCCAGTAG |
| Vg1 Reverse | TGTAGGTTTGAAGGCCACAATAGTA |
| Vg2 Forward | CTTACACGAGGTCGCAAATCAG |
| Vg2 Reverse | CTGTCATGTGATACGTGTCTTTGAG |
| VgR Forward | TGTCTTGTGAAGATGGATTTGTGTG |
| VgR Reverse | CACTGTTGTCTCCACAATCATCAAA |
| JHAMT Forward | GAAGCTCTCATAGTATTCGTGGC |
| JHAMT Reverse | AGGATCTTCTGACTGATGGTAGG |
| FAMeT Forward | ACTGTATGTAGGACGGGCAAAG |
| FAMeT Reverse | CCAGTCAGCACCTCATATTCAG |
| Actin Forward | TGAATCCTAAGGCCAACAGG |
| Actin Reverse | ACCGGAATCCAGCACAATAC |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamruzzaman, A.S.M.; Mikani, A.; Mohamed, A.A.; Elgendy, A.M.; Takeda, M. Crosstalk among Indoleamines, Neuropeptides and JH/20E in Regulation of Reproduction in the American Cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Insects 2020, 11, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030155
Kamruzzaman ASM, Mikani A, Mohamed AA, Elgendy AM, Takeda M. Crosstalk among Indoleamines, Neuropeptides and JH/20E in Regulation of Reproduction in the American Cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Insects. 2020; 11(3):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030155
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamruzzaman, A. S. M., Azam Mikani, Amr A. Mohamed, Azza M. Elgendy, and Makio Takeda. 2020. "Crosstalk among Indoleamines, Neuropeptides and JH/20E in Regulation of Reproduction in the American Cockroach, Periplaneta americana" Insects 11, no. 3: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030155
APA StyleKamruzzaman, A. S. M., Mikani, A., Mohamed, A. A., Elgendy, A. M., & Takeda, M. (2020). Crosstalk among Indoleamines, Neuropeptides and JH/20E in Regulation of Reproduction in the American Cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Insects, 11(3), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030155