Plant-Derived Insecticides Under Meta-Analyses: Status, Biases, and Knowledge Gaps
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Literature Identification
2.3. Literature Screening and Elimination
2.4. Literature Eligibility and Inclusion for Meta-Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
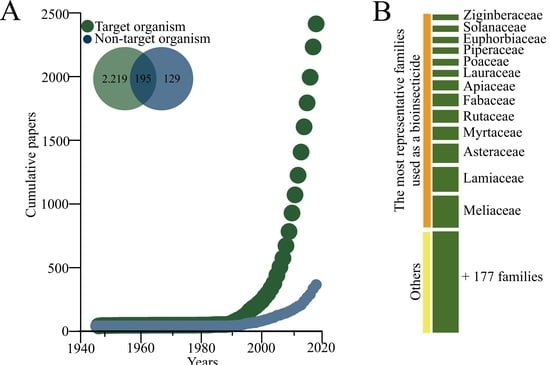
3.1. Literature Survey Summary
3.2. Qualitative Overview and Temporal Trends
3.3. Meta-Analyses: Quantitative Overall Trends
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guedes, R.N.C. Insecticide resistance, control failure likelihood and the First Law of Geography. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steffen, W.; Grinevald, J.; Crutzen, P.; McNeill, J. The Anthropocene: Conceptual and historical. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2011, 369, 842–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Gols, R.; Benrey, B. Crop domestication and naturally selected species interactions. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gibbs, K.E.; MacKey, R.L.; Currie, D.J. Human land use, agriculture, pesticides and losses of imperiled species. Divers. Distrib. 2009, 15, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktar, M.W.; Sengupta, D.; Chowdhury, A. Impact of pesticides use in agriculture: Their benefits and hazards. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2009, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guedes, R.N.C.; Smagghe, G.; Stark, J.D.; Desneux, N. Pesticide-induced stress in arthropod pests for optimized integrated pest management programs. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, J.; Dobson, H. The benefits of pesticides to mankind and the environment. Crop. Prot. 2007, 26, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddi, K.; Turchen, L.M.; Viteri-Jumbo, L.O.; Guedes, R.N.C.; Pereira, E.J.G.; Aguiar, R.W.S.; Oliveira, E.E. Rethinking biorational insecticides for pest management: Unintended effects and consequences. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, N.; Woodward, R.T. Under- and over-use of pesticides: An international analysis. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 89, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, G.A. Attitudes and behaviours regarding use of crop protection products—A survey of more than 8500 smallholders in 26 countries. Crop. Prot. 2008, 27, 834–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, R.N.C.; Walse, S.S.; Throne, J.E. Sublethal exposure, insecticide resistance, and community stress. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2017, 21, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Copping, L.G.; Menn, J.J. Biopesticides: A review of their action, applications and efficacy. Pest Manag. Sci. 2000, 56, 651–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaverde, J.J.; Sevilla-Morán, B.; Sandín-España, P.; López-Goti, C.; Alonso-Prados, J.L. Biopesticides in the framework of the European Pesticide Regulation (EC) No. 1107/2009. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glare, T.; Caradus, J.; Gelernter, W.; Jackson, T.; Keyhani, N.; Köhl, J.; Marrone, P.; Morin, L.; Stewart, A. Have biopesticides come of age? Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, G.; Quero, C.; Coll, J.; Guerrero, A. Biorational insecticides in pest management. J. Pestic. Sci. 2008, 33, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seiber, J.N.; Coats, J.; Duke, S.O.; Gross, A.D. Pest management with biopesticides. Front Agric. Sci Eng. 2018, 5, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Regnault-Roger, C.; Vincent, C.; Arnason, J.T. Essential oils in insect control: Low-risk products in a high-stakes world. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2012, 57, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isman, M.B.; Grieneisen, M.L. Botanical insecticide research: Many publications, limited useful data. Trends Plant. Sci. 2014, 19, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damalas, C.A.; Koutroubas, S.D. Current status and recent developments in biopesticide use. Agriculture 2018, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coats, J.R. Risks from natural versus synthetic insecticides. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1994, 39, 489–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahlai, C.A.; Xue, Y.; McCreary, C.M.; Schaafsma, A.W.; Hallett, R.H. Choosing organic pesticides over synthetic pesticides may not effectively mitigate environmental risk in soybeans. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, W.F.; Tomé, H.V.; Bernardes, R.C.; Siqueira, M.A.L.; Smagghe, G.; Guedes, R.N.C. Biopesticide-induced behavioral and morphological alterations in the stingless bee Melipona quadrifasciata. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 2149–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomé, H.V.; Barbosa, W.F.; Martins, G.F.; Guedes, R.N.C. Spinosad in the native stingless bee Melipona quadrifasciata: Regrettable non-target toxicity of a bioinsecticide. Chemosphere 2015, 124, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, E.V.R.; Proença, P.L.F.; Oliveira, J.L.; Bakshi, M.; Abhilash, P.C.; Fraceto, L.F. Use of botanical insecticides for sustainable agriculture: Future perspectives. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miresmailli, S.; Isman, M.B. Botanical insecticides inspired by plant-herbivore chemical interactions. Trends Plant. Sci. 2014, 19, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasques, J.; Cardoso, M.H.; Abrantes, G.; Frihling, B.E.; Franco, O.L.; Migliolo, L. The rescue of botanical insecticides: A bioinspiration for new niches and needs. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 143, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, T.P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing 2020. Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Schwarzer, G.; Carpenterm, J.R.; Rücker, G. Meta-Analysis with R, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; p. XII-252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavela, R. History, presence and perspective of using plant extracts as commercial botanical insecticides and farm products for protection against insects—A review. Plant. Prot. Sci. 2016, 52, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isman, M.B. Botanical insecticides in the twenty-first century—Fulfilling their promise? Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2020, 65, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, C. Impacts of sublethal insecticide exposure on insects—Facts and knowledge gaps. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2018, 30, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, A.; Mommaerts, V.; Smagghe, G.; Viñuela, E.; Zappalà, L.; Desneux, N. The non-target impact of spinosyns on beneficial arthropods. Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 1523–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, E.M.G.; Corrêa, A.S.; Venzon, M.; Guedes, R.N.C. Insecticide survival and behavioral avoidance in the lacewings Chrysoperla externa and Ceraeochrysa cubana. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 1352–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, W.F.; Smagghe, G.; Guedes, R.N.C. Perspective Pesticides and reduced-risk insecticides, native bees and pantropical stingless bees: Pitfalls and perspectives. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, L.H.; Greenamvre, J.T. Oxidative damage to macromolecules in human Parkinson disease and the rotenone model. Free Radic. Bio. Med. 2013, 62, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patocka, J. Strychnine. In Handbook of Toxicology of Chemical Warfare Agents; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turchen, L.M.; Cosme-Júnior, L.; Guedes, R.N.C. Plant-Derived Insecticides Under Meta-Analyses: Status, Biases, and Knowledge Gaps. Insects 2020, 11, 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11080532
Turchen LM, Cosme-Júnior L, Guedes RNC. Plant-Derived Insecticides Under Meta-Analyses: Status, Biases, and Knowledge Gaps. Insects. 2020; 11(8):532. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11080532
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurchen, Leonardo M., Lírio Cosme-Júnior, and Raul Narciso C. Guedes. 2020. "Plant-Derived Insecticides Under Meta-Analyses: Status, Biases, and Knowledge Gaps" Insects 11, no. 8: 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11080532
APA StyleTurchen, L. M., Cosme-Júnior, L., & Guedes, R. N. C. (2020). Plant-Derived Insecticides Under Meta-Analyses: Status, Biases, and Knowledge Gaps. Insects, 11(8), 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11080532