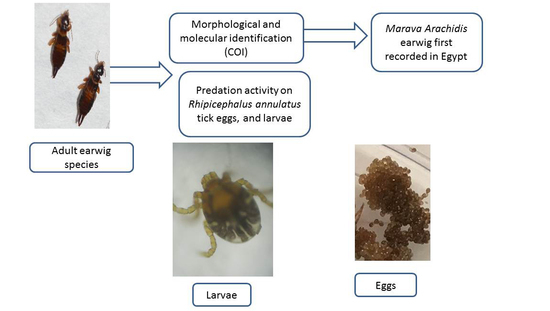
Potential of Marava arachidis, a Newly Recorded Earwig Species in Egypt as a Biological Control Agent of Rhipicephalus annulatus Tick in Laboratory
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Source of Study Earwigs
2.2. Morphological Identification
2.3. Molecular Identification
2.4. Potential Predation of Earwig on R. annulatus Tick Stages
2.4.1. R. annulatus Eggs and Larvae Preparation
2.4.2. Predation Test
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Identification of the Present Earwig
3.2. Predation Activity of Earwigs against Ticks Eggs and Larvae
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Popham, E.J. The geographical distribution of the Dermaptera (Insecta) with reference to continental drift. J. Nat. Hist. 2000, 34, 2007–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, D.; Engel, M.S. Evolution of the Insects; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, NY, USA, 2005; p. 772. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, F.; Hwen, J.T.C.; Tang, H.B. New evidence on the mechanics of wing unfolding in Dermaptera. Arthropod Syst. Phylogeny 2012, 70, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, H.; Maehr, F.; Deem, L.S. Dermaptera Species File; Version 5.0/5.0; SpeciesFile. Org.: Ithaca College, NY, USA, 2020; Available online: http://Dermaptera.SpeciesFile.org (accessed on 6 March 2022).
- Haas, F. Biodiversity of Dermaptera. In Insect Biodivers: Science and Society. Volume II; Foottit, R.G., Adler, P.H., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 315–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigm, F.H.; Hussain, A.E. Taxonomical studies on five Dermapterous species in Egypt. Ann. Agric. Sci. Moshtohor. 1996, 34, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Steinmann, H. Dermaptera. Eudermaptera I. In Das Tierreich; Werrnuth, H., Möhn, E., Fischer, M., Eds.; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1990; Volume 106, pp. 1–558. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, P.N.; Habib, M.E.M. Biological and behavorial studies of an ovoviviparous earwig, Marava Arachidis (Yersin 1860) (Dermaptera; Forficulidae. Riv. Biol. Trop. 1978, 26, 385–389. [Google Scholar]
- Dowell, R.V.; Gill, D.R.; Jeske, D.R.; Hoddle, M.S. Exotic terrestrial macro-invertebrate invaders in California from 1700 to 2015: An analysis of records. Proc. Calif. Acad. Sci. 2016, 63, 269–278. [Google Scholar]
- Herter, K. Vergleichende Beobachtungen und Betrachtungen uber die Fortpflanzungsbiologie der Ohrwurmer. Z. Naturforsch. C 1965, 20, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, Y.; Nishikawa, M.; Lee, C.Y. The earwig fauna (Insecta: Dermaptera) of Penang Island, Malaysia, with descriptions of two new species. Zootaxa 2016, 4084, 233–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samish, M.; Rehacek, J. Pathogens and predators of ticks and their potential in biological control. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1999, 44, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samish, M.; Alekseev, E. Arthropods as predators of ticks (Ixodoidea). J. Med. Entomol. 2001, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samish, M.; Ginsberg, H.; Glazer, I. Biological control of ticks. Parasitol 2004, 129, S389–S403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulart, S.; Christoforo, M.T.; Amexeiro, A.R.; Lamounier, J.L.; Ferreira, J.R.; Ferrari, O.; Rocha, U.R. Ecology of ticks XVII Forficulidae preying on Boophilus microplus eggs. Ars. Vet. 1986, 2, 233–236. [Google Scholar]
- Verissimo, C.J. Natural enemies of the cattle tick. Agropecu. Catarin. 1995, 8, 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lamb, R.J. Parental behavior in the Dermaptera with special reference to Forficula auricularia (Dermaptera: Forficulidae). Can. Entomol. 1976, 108, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, C.I.; Wanderley, P.A.; Miná, A.J.S.; Wanderley, M.J.A. Capacity of earwig Marava arachidis (Yersin) to access fennel plants Foeniculum vulgare Mill in laboratory and field. Ciênc. Rural. 2007, 37, 1524–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hadley, A. Combine ZM Imaging Software. 2008. Available online: https://combinezm.en.lo4d.com/details (accessed on 10 February 2018).
- Hajibabaei, M.; deWaard, J.R.; Ivanova, N.V.; Ratnasingham, S.; Dooh, R.T.; Kirk, S.L.; Mackie, P.M.; Hebert, P.D. Critical factors for assembling a high volume of DNA barcodes. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- deWaard, J.R.; Ivanova, N.V.; Hajibabaei, M.; Hebert, P.D.N. Assembling DNA barcodes. Analytical protocols. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 410, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, Y.; Tee, H.S.; Lee, C.Y. Ovoviviparity and genital evolution: A lesson from an earwig species with coercive traumatic mating and accidental breakage of elongated intromittent organs. Biol. J. Linn. Soci. 2016, 118, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D. RASCAL: Rapid scanning and correction of multiple sequence alignments. Bioinform 2003, 19, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Peña, A. Ticks of Domestic Animals in the Mediterranean Region: A Guide to Identification of Species; University of Zaragoza: Zaragoza, Spain, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dib, H.; Jamont, M.; Sauphanor, B.; Capowiez, Y. Predation potency and intraguild interactions between generalist (Forficula auricularia) and specialist (Episyrphus balteatus) predators of the rosy apple aphid (Dysaphis plantaginea). Biol. Control 2011, 59, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyuli, T.M.B.; Luther, G.C.; Kyamanywa, S. Effects of groundnut genotypes, cropping systems and insecticides on the abundance of native arthropod predators from Uganda and Democratic Republic of Congo. Bull. Insectology 2008, 61, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa, M. A checklist of the Dermaptera recorded from Thailand. THNHMJ 2005, 1, 149–164. [Google Scholar]
- Aboelhadid, S.M.; Arafa, W.M.; Mahrous, L.N.; Fahmy, M.M.; Kamel, A.A. Molecular detection of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) annulatus resistance against deltamethrin in middle Egypt. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2018, 13, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxton, J.H.; Madge, D.S. The evaluation of the European earwig (Forficula auricularia) as a predator of the damson-hop aphid (Phorodon humuli). I. Feeding experiments. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1976, 19, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debras, J.F.; Dussaud, A.; Rieux, R.; Dutoit, T. Recherche prospective sur le rôle «source» des haies en production fruitière intégrée. Le cas des perce-oreilles: Forficula auricularia L. et Forficula pubescens Gené. CR Biol. 2007, 330, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeu-Dalmau, C.; Gu, P.; Scott, S.; Grafton-Cardwell, B. Earwigs: Pests or beneficials in california citrus orchards? Citrograph 2012, 3, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Nava, S.; Gamietea, I.J.; Morel, N.; Guglielmone, A.A.; Estrada-Peña, A. Assessment of habitat suitability for the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus in temperate areas. Res. Vet. Sci. 2022, 150, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, D.P.; Hoyt, S.C. Augmentation of European earwigs (Dermaptera: Forficulidae) for biological control of apple aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) in an apple orchard. J. Econ. Entomol. 1984, 77, 738–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, D.P.; Walker, J.T.S.; Hoyt, S.C. European earwigs (Dermaptera: Forficulidae) fail to control apple aphids on bearing apple trees and woolly apple aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) in apple rootstock stool beds. J. Econ. Entomol. 1985, 78, 972–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante, S.K. Functional responses of the European earwig and two species of Coccinellids to densities of Eriosoma lanigerum (Hausmann) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J. Aust. Entomol. 1995, 34, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenoglio, M.S.; Trumper, E.V. Influence of Weather Conditions and Density of Doru luteipes (Dermaptera: Forficulidae) on Diatraea saccharalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) egg Mortality. Environ. Entomol. 2007, 36, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagnoux, L.; Marliac, G.; Simon, S.; Rault, M.; Capowiez, Y. Management strategies in apple orchards influence earwig community. Chemosphere 2015, 124, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.-R.; Kajimura, H. Earwig preying on ambrosia beetle: Evaluating predatory process and prey preference. J. Appl. Entomol. 2020, 144, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, M.L. The Ecology of the Common Earwig Forficula auricularia in Apple Orchard. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK, 1981; p. 244. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.; Gislstrap, F.; Andrews, K. Biology and life table for the predaceous earwig, Doru taeniatum (Derm.: Forficulidae). Entomophaga 1988, 33, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuessly, G.S.; Hentz, M.G.; Biriger, R.; Scully, B.T. Insects associated with Faba bean, Vicia faba (Fabales: Fabaceae), in Southern Florida. Fla. Entomol. 2004, 87, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crumb, S.E.; Bonn, A.E. The European earwig. Bull. U.S. Dep. Agric. 1995, 166, 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Logan, D.P.; Maher, B.J.; Rowe, C.A. Predation of diaspidid scale insects on kiwifruit vines by European earwigs, Forficula auricularia, and steel-blue ladybirds, Halmus chalybeus. Bio. Control 2017, 62, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharboutli, M.S.; Mack, T.P. Effect of temperature, humidity and prey density on feedings rate of the striped earwig (Dermaptera: Labiduridae). Environ. Entomol. 1993, 22, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.J.; McDonald, G. European earwig, Forficula auricularia L. (Dermaptera: Forficularidae), as a predator of the red legged earth mite, Halotydeus destructor (Tucker) (Acarina: Penthaleidae). Aust. J. Entomol. 1998, 37, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.Z.; Wang, Q.; Xu, J. European earwig as a potential biological control agent of apple leaf-curling midge. N. Z. Plant Prot. 2008, 61, 343–349. [Google Scholar]
- Travis, J.; Keen, W.H.; Juilianna, J. The role of relative body size in a predator-prey relationship between dragonfly naiads and larval anurans. Oikos 1985, 45, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, M.; Vogelweith, F.; Foitzik, S.; Meunier, J. Conditiondependent trade-off between weapon size and immunity in males of the European earwig. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tworzydlo, W.; Kisiel, E.; Bilinski, S.M. Embryos of the viviparous 628 dermapteran, Arixenia esau develop sequentially in two compartments: 629 terminal ovarian follicles and the uterus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, M.P.; Binns, M.; Umina, P.A.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Macfadyen, S. Climate, human influence, and the distribution limits of the invasive European earwig, Forficula auricularia, in Australia. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 75, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanderley, P.A.; Wanderley, M.J.A.; Alves, E.U. O Surpreendente Cuidado Maternal Dos Dermápteros. Ciência Hoje. Revista Eletrônica. 2006. Available online: http://www.cienciahoje.pt/9080 (accessed on 2 June 2007).





| Predator-Prey Ratios | Mean Number of Eggs Consumed by Earwigs | Mean Number of Eggs Broken by Earwigs | Mean Number of Intact Eggs |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1:100 | 5.0 ± 1.41 e | 6.4 ± 1.51 c | 88.6 ± 1.52 a |
| 1:33 | 10.8 ± 1.48 d | 10.2 ± 1.48 b | 79.00 ± 1.87 b |
| 1:20 | 16.8 ± 2.77 c | 12.4 ± 0.55 b | 70.00 ± 2.95 c |
| 1:14 | 25.4 ± 2.97 b | 14.00 ± 2.65 a | 60.00 ± 3.65 d |
| 1:10 | 35.2 ± 3.96 a | 17.2 ± 4.60 a | 47.6 ± 4.72 e |
| Mean | 18.64 ± 11.18 | 12.04 ± 4.38 | 69.32 ± 14.82 |
| Predator-Prey Ratios | Mean Number of Consumed Larvae by Earwigs | Mean Number of Dead Larvae | Mean Number of Remaining Live Larvae |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1:100 | 2.8 ± 1.48 e | 11.4 ± 1.14 c | 85.4 ± 1.52 a |
| 1:33 | 5.4 ± 1.67 d | 13.8 ± 0.84 c | 80.8 ± 2.17 b |
| 1:20 | 9.0 ± 2.00 c | 34.0 ± 1.22 b | 57.4 ± 1.22 c |
| 1:14 | 18.0 ± 1.58 b | 35.2 ± 3.11 b | 46.8 ± 1.79 d |
| 1:10 | 26.4 ± 2.70 a | 38.4 ± 2.30 a | 35.2 ± 1.09 e |
| Mean | 12.32 ± 9.07 | 26.56 ± 11.88 | 61.04 ± 19.79 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aboelhadid, S.M.; Abdel-Baki, A.-A.S.; Gadelhaq, S.M.; Hassan, W.H.; Mansour, L.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Kamimura, Y.; Lee, C.-Y.; Kamel, A.A. Potential of Marava arachidis, a Newly Recorded Earwig Species in Egypt as a Biological Control Agent of Rhipicephalus annulatus Tick in Laboratory. Insects 2022, 13, 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13100934
Aboelhadid SM, Abdel-Baki A-AS, Gadelhaq SM, Hassan WH, Mansour L, Al-Quraishy S, Kamimura Y, Lee C-Y, Kamel AA. Potential of Marava arachidis, a Newly Recorded Earwig Species in Egypt as a Biological Control Agent of Rhipicephalus annulatus Tick in Laboratory. Insects. 2022; 13(10):934. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13100934
Chicago/Turabian StyleAboelhadid, Shawky M., Abdel-Azeem S. Abdel-Baki, Sahar M. Gadelhaq, Walid H. Hassan, Lamjed Mansour, Saleh Al-Quraishy, Yoshitaka Kamimura, Chow-Yang Lee, and Asmaa A. Kamel. 2022. "Potential of Marava arachidis, a Newly Recorded Earwig Species in Egypt as a Biological Control Agent of Rhipicephalus annulatus Tick in Laboratory" Insects 13, no. 10: 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13100934
APA StyleAboelhadid, S. M., Abdel-Baki, A. -A. S., Gadelhaq, S. M., Hassan, W. H., Mansour, L., Al-Quraishy, S., Kamimura, Y., Lee, C. -Y., & Kamel, A. A. (2022). Potential of Marava arachidis, a Newly Recorded Earwig Species in Egypt as a Biological Control Agent of Rhipicephalus annulatus Tick in Laboratory. Insects, 13(10), 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13100934