Aphidius colemani Behavior Changes Depending on Volatile Organic Compounds Emitted by Plants Infected with Viruses with Different Modes of Transmission
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Growing Conditions
2.2. Insect Rearing
2.3. Virus Isolates and Inoculations
2.4. Aphid Infestation of Viral-Infected Plants
2.5. Olfactometer Bioassays
2.6. Dual-Choice Bioassay on the Parasitism Rate of Aphidius colemani on CABYV-Infected and Mock-Inoculated Plants
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Virus-Infected Melon on the Olfactory Response of Aphidius colemani
3.2. Effect of CABYV-Infected Melon on the Parasitism Rate of Aphidius colemani
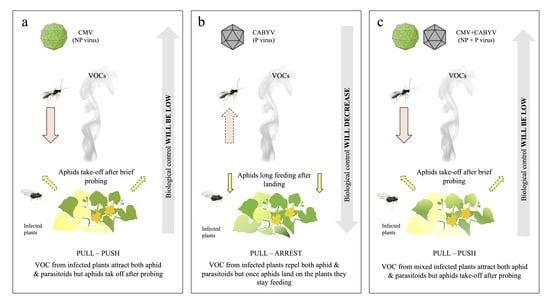
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Volatiles Emitted by Infected-Melon on Male Parasitoids
4.2. Effects of Volatiles Emitted by Infected Melon on Female Parasitoids in Absence and Presence of Its Main Aphid Host
4.3. Impact on Biological Control
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MAPA. 2023. Available online: https://www.mapa.gob.es/es/estadistica/temas/estadisticas-agrarias/ (accessed on 3 April 2023).
- Blackman, R.L.; Eastop, V.F. Aphids on the World’s Trees: An Identification and Information Guide; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1994; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, S.; Agrom, I.C. Vector Transmission of Plant Viruses. Encycl. Virol. 2008, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenbrode, S.D.; Ding, H.; Shiel, P.; Berger, P.H. Volatiles from Potato Plants Infected with Potato Leafroll Virus Attract and Arrest the Virus Vector, Myzus Persicae (Homoptera: Aphididae). Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2002, 269, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietzgen, R.G.; Mann, K.S.; Johnson, K.N. Plant Virus-Insect Vector Interactions: Current and Potential Future Research Directions. Viruses 2016, 8, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeger, M.; Chen, Z.; Cunningham, E.; Martin, G.; Powell, G. Population Biology and Epidemiology of Plant Virus Epidemics: From Tripartite to Tritrophic Interactions. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 133, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereres, A.; Moreno, A. Behavioural Aspects Influencing Plant Virus Transmission by Homopteran Insects. Virus Res. 2009, 141, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmo-Sousa, M.; Moreno, A.; Garzo, E.; Fereres, A. A Non-Persistently Transmitted-Virus Induces a Pull-Push Strategy in Its Aphid Vector to Optimize Transmission and Spread. Virus Res. 2014, 186, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo-Sousa, M.; Moreno, A.; Plaza, M.; Garzo, E.; Fereres, A. Cucurbit Aphid-Borne Yellows Virus (CABYV) Modifies the Alighting, Settling and Probing Behaviour of Its Vector Aphis Gossypii Favouring Its Own Spread. Ann. Appl. Bio 2016, 169, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Prados, J.L.; Fraile, A.; García-Arenal, F. Impact of Cucumber Mosaic Virus and Watermelon Mosaic Virus 2 Infection on Melon Production in Central Spain. Plant Pathol. J. 1997, 79, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Juárez, M.; Kassem, M.A.; Sempere, R.N.; Truniger, V.; Moreno, I.M.; Aranda, M.A. El Virus Del Amarilleo de Las Cucurbitáceas Transmitido Por Pulgones (Cucurbit Aphid-Borne Yellows Virus, CABYV ): Un Nuevo Virus Encontrado En Los Cultivos de Cucurbitáceas Del Sureste Peninsular. Bol. Sanid Veg. Plagas. 2005, 31, 587–598. [Google Scholar]
- Juarez, M.; Legua, P.; Mengual, C.M.; Kassem, M.A.; Sempere, R.N.; Gómez, P.; Truniger, V.; Aranda, M.A. Relative Incidence, Spatial Distribution and Genetic Diversity of Cucurbit Viruses in Eastern Spain. Ann. Appl. Bio 2013, 162, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, M.A.; Sempere, R.N.; Juárez, M.; Aranda, M.A.; Truniger, V. Cucurbit Aphid-Borne Yellows Virus Is Prevalent in Field-Grown Cucurbit Crops of Southeastern Spain. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauck, K.; Bosque-Pérez, N.A.; Eigenbrode, S.D.; De Moraes, C.M.; Mescher, M.C. Transmission Mechanisms Shape Pathogen Effects on Host-Vector Interactions: Evidence from Plant Viruses. Funct. Ecol. 2012, 26, 1162–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavijo McCormick, A.; Unsicker, S.B.; Gershenzon, J. The Specificity of Herbivore-Induced Plant Volatiles in Attracting Herbivore Enemies. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeger, M.J. The epidemiology of plant virus disease: Towards a new synthesis. Plants 2020, 9, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benelli, G.; Messing, R.H.; Wright, M.G.; Giunti, G.; Kavallieratos, N.G.; Canale, A. Cues Triggering Mating and Host-Seeking Behavior in the Aphid Parasitoid Aphidius Colemani (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Aphidiinae): Implications for Biological Control. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 2005–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binyameen, M.; Ali, Q.; Roy, A.; Schlyter, F. Plant Volatiles and Their Role in Insect Olfaction. Plant-Pest Interact. Mol. Mech. Chem. Ecol. 2021, 127–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudine, S.; Le Lann, C.; Bouvaine, S.; Le Ralec, A.; van Baaren, J. Can Biological Control Be a Strategy to Control Vector-Borne Plant Viruses? J. Pest Sci. 2023, 1, 451–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belliure, B.; Amorós-Jiménez, R.; Fereres, A.; Marcos-García, M.Á. Antipredator Behaviour of Myzus Persicae Affects Transmission Efficiency of Broad Bean Wilt Virus 1. Virus Res. 2011, 159, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyrnioudis, I.N.; Harrington, R.; Clark, S.J.; Katis, N. The Effect of Natural Enemies on the Spread of Barley Yellow Dwarf Virus (BYDV) by Rhopalosiphum Padi (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2001, 91, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, C.F.; Long, E.Y.; Finke, D.L. A Negative Effect of a Pathogen on Its Vector? A Plant Pathogen Increases the Vulnerability of Its Vector to Attack by Natural Enemies. Oecologia 2014, 174, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dáder, B.; Moreno, A.; Viñuela, E.; Fereres, A. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Viruses Are Differentially Affected by Parasitoids Depending on the Mode of Transmission. Viruses 2012, 4, 3069–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauck, K.E.; De Moraes, C.M.; Mescher, M.C. Infection of Host Plants by Cucumber Mosaic Virus Increases the Susceptibility of Myzus Persicae Aphids to the Parasitoid Aphidius Colemani. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffrey, M.; Chesnais, Q.; Spicher, F.; Verrier, E.; Ameline, A.; Couty, A. Plant Virus Infection Influences Bottom-up Regulation of a Plant-Aphid-Parasitoid System. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, Y.; Xie, W.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. Infection of Tomato by Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus Alters the Foraging Behavior and Parasitism of the Parasitoid Encarsia Formosa on Bemisia Tabaci. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2018, 21, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, X.; Pelz-Stelinski, K.S.; Stelinski, L.L. Plant Pathogen-Induced Volatiles Attract Parasitoids to Increase Parasitism of an Insect Vector. Front Ecol. Evol. 2014, 2, 83020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milonas, P.G.; Anastasaki, E.; Psoma, A.; Partsinevelos, G.; Fragkopoulos, G.N.; Kektsidou, O.; Vassilakos, N.; Kapranas, A. Plant Viruses Induce Plant Volatiles That Are Detected by Aphid Parasitoids. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Guo, Y.; Xie, Y.; Ren, Y.; Bi, Y.; Wang, F.; Fang, Q.; Ye, G. Rice Volatile Compound (E)-β-Caryophyllene Induced by Rice Dwarf Virus (RDV) Attracts the Natural Enemy Cyrtorhinus Lividipennis to Prey on RDV Insect Vectors. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stary, P. Aphidius Colemani Viereck: Its Taxonomy, Distribution and Host Range (Hymenoptera, Aphidiidae). Acta Entomol. Bohemoslov. 1975, 72, 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Messing, R.H.; Rabasse, J.M. Oviposition Behaviour of the Polyphagous Aphid Parasitoid Aphidius Colemani Viereck (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1995, 52, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.I. Responses of Plants to Viruses: Proposals for the Use of Terms. Phytopathology 1983, 73, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, M.A.; Gosalvez, B.; Garzo, E.; Fereres, A.; Gómez-Guillamon, M.L.; Aranda, M.A. Resistance to Cucurbit Aphid-Borne Yellows Virus in Melon Accession TGR-1551. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enz, M.; Dachler, C. Compendio Para La Identificación de Los Estadios Fenológicos de Especies Mono-y Dicotiledóneas Cultivadas Escala BBCH Extendida; BBA: Limburgerhof, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, M.F.; Adams, A.N. Characteristics of the Microplate Method of Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay for the Detection of Plant Viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1977, 34, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, I.L.; Silva, D.B.; Silveira, L.C.P.; Bento, J.M.S.; Peñaflor, M.F.G.V.; Marucci, R.C. A Parasitoid’s Dilemma between Food and Host Resources: The Role of Volatiles from Nectar-Providing Marigolds and Host-Infested Plants Attracting Aphidius Platensis. Sci. Nat. 2022, 109, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoza, Y.J.; Teal, P.E.A.; Tumlinson, J.H. Effect of Peanut Plant Fungal Infection on Oviposition Preference by Spodoptera Exigua and on Host-Searching Behavior by Cotesia Marginiventris. Environ. Entomol. 2003, 32, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostás, M.; Ton, J.; Mauch-Mani, B.; Turlings, T.C.J. Fungal Infection Reduces Herbivore-Induced Plant Volatiles of Maize but Does Not Affect Naïve Parasitoids. J. Chem. Ecol. 2006, 32, 1897–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Veyrat, N.; Degen, T.; Turlings, T.C.J. Exceptional Use of Sex Pheromones by Parasitoids of the Genus Cotesia: Males Are Strongly Attracted to Virgin Females, but Are No Longer Attracted to or Even Repelled by Mated Females. Insects 2014, 5, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelli, G.; Kavallieratos, N.G.; Donati, E.; Mencattelli, M.; Bonsignori, G.; Stefanini, C.; Canale, A.; Messing, R.H. May the Wild Male Loose? Male Wing Fanning Performances and Mating Success in Wild and Mass-Reared Strains of the Aphid Parasitoid Aphidius Colemani Viereck (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Aphidiinae). BioControl 2014, 59, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelli, G.; Giunti, G.; Messing, R.H.; Wright, M.G. Visual and Olfactory Female-Borne Cues Evoke Male Courtship in the Aphid Parasitoid Aphidius Colemani Viereck (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). J. Insect Behav. 2013, 26, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinson, S.B. Host Selection by Insect Parasitoids. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1976, 21, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randlkofer, B.; Obermaier, E.; Hilker, M.; Meiners, T. Vegetation Complexity-The Influence of Plant Species Diversity and Plant Structures on Plant Chemical Complexity and Arthropods. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2010, 11, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalule, T.; Wright, D.J. The Influence of Cultivar and Cultivar-Aphid Odours on the Olfactory Response of the Parasitoid Aphidius Colemani. J. Appl. Entomol. 2004, 128, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Emden, H.F.; Vamvatsikos, P.; Hardie, J. Cultivar-Specific Plant Odour Preferences of a Generalist Aphid Parasitoid Aphidius Colemani and a Possible Mechanism for Maternal Priming of Resistance to Toxic Plant Chemistry. Physiol. Entomol. 2019, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storeck, A.; Poppy, G.M.; Van Emden, H.F.; Powell, W. The Role of Plant Chemical Cues in Determining Host Preference in the Generalist Aphid Parasitoid Aphidius Colemani. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2000, 97, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauck, K.E.; De Moraes, C.M.; Mescher, M.C. Biochemical and Physiological Mechanisms Underlying Effects of Cucumber Mosaic Virus on Host-Plant Traits That Mediate Transmission by Aphid Vectors. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewsey, M.G.; Murphy, A.M.; MacLean, D.; Dalchau, N.; Westwood, J.H.; Macaulay, K.; Bennett, M.H.; Moulin, M.; Hanke, D.E.; Powell, G.; et al. Disruption of Two Defensive Signaling Pathways by a Viral RNA Silencing Suppressor. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2010, 23, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Qi, T.; Li, W.X.; Tian, H.; Gao, H.; Wang, J.; Ge, J.; Yao, R.; Ren, C.; Wang, X.B.; et al. Viral Effector Protein Manipulates Host Hormone Signaling to Attract Insect Vectors. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo-Calap, M.L.; Moreno, A.B.; Pendón, J.A.D.; Moreno, A.; Fereres, A.; López-Moya, J.J. Assessing the Impact on Virus Transmission and Insect Vector Behavior of a Viral Mixed Infection in Melon. Phytopathology 2020, 110, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, A.B.; López-Moya, J.J. When Viruses Play Team Sports: Mixed Infections in Plants. Phytopathology 2020, 110, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyrnioudis, I.N.; Harrington, R.; Hall, M.; Katis, N.; Clark, S.J. The Effect of Temperature on Variation in Transmission of a BYDV PAV-like Isolate by Clones of Rhopalosiphum Padi and Sitobion Avenae. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2001, 107, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauck, K.E.; De Moraes, C.M.; Mescher, M.C. Effects of Pathogens on Sensory-Mediated Interactions between Plants and Insect Vectors. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2016, 32, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peñaflor, M.F.G.V.; Mauck, K.E.; Alves, K.J.; De Moraes, C.M.; Mescher, M.C. Effects of Single and Mixed Infections of Bean Pod Mottle Virus and Soybean Mosaic Virus on Host-Plant Chemistry and Host–Vector Interactions. Funct. Ecol. 2016, 30, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Clemente-Orta, G.; Cabello, Á.; Garzo, E.; Moreno, A.; Fereres, A. Aphidius colemani Behavior Changes Depending on Volatile Organic Compounds Emitted by Plants Infected with Viruses with Different Modes of Transmission. Insects 2024, 15, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15020092
Clemente-Orta G, Cabello Á, Garzo E, Moreno A, Fereres A. Aphidius colemani Behavior Changes Depending on Volatile Organic Compounds Emitted by Plants Infected with Viruses with Different Modes of Transmission. Insects. 2024; 15(2):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15020092
Chicago/Turabian StyleClemente-Orta, Gemma, Ángel Cabello, Elisa Garzo, Aranzazu Moreno, and Alberto Fereres. 2024. "Aphidius colemani Behavior Changes Depending on Volatile Organic Compounds Emitted by Plants Infected with Viruses with Different Modes of Transmission" Insects 15, no. 2: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15020092
APA StyleClemente-Orta, G., Cabello, Á., Garzo, E., Moreno, A., & Fereres, A. (2024). Aphidius colemani Behavior Changes Depending on Volatile Organic Compounds Emitted by Plants Infected with Viruses with Different Modes of Transmission. Insects, 15(2), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15020092