Cloning, Expression, Sequence Analysis and Homology Modeling of the Prolyl Endoprotease from Eurygaster integriceps Puton
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Harvesting Sunn Pest of Various Life Stages
2.2. Synthesis of cDNA
2.2.1. Total RNA Isolation
2.2.2. mRNA Enrichment
2.2.3. First Strand cDNA Synthesis
2.3. Amplification of spPEP Transcript
2.3.1. Design of Degenerate Primers
| Primer Name | Sequence 5ꞌ→3ꞌ |
|---|---|
| P1gen | CCCCTACAGGTGGCTGgargayccnga |
| P24gen | TGAACTTGTGGAACCTCAGCatrtccatnac |
| P1 | CCCCTACAGGTGGCTGGA |
| 265 | TGGTCGTCATCGATTTTGAA |
| 415 | TTCACAGTTTGGTGGATGGA |
| 707 | CCTGGAACAAAACGGAAAAA |
| PEP Start | ATGAAAAAGTTCCAATACCCTGAAGCTCGG |
| 1747 | CGCTTCTGCAAACATAAGGGGAGGA |
| 312 | ACGTCACCCAATTTTCTTCG |
| 434 | TCCATCCACCAAACTGTGAA |
| 980 | TCGCCAGACAACTCTTATTG |
| Lic PEP Start | TATTTTCAATCCTACGTAATGAAAAAGTTCCAATACCCTG |
| Lic PEP Stop | CCCTCAATATTATACGGGTCA AATGATCTGACAAAC |
2.3.2. Amplification from Degenerate Primers
2.3.3. Amplification of the 5ꞌ and 3ꞌ Ends

2.3.4. Confirmation of cDNA Clones
2.3.5. Final Assembly of the PEP cDNA Sequence
2.4. Cloning of the Sunn Pest PEP Construct into the Expression Vector
2.5. Sequence Analysis
2.6. Expression and Purification of Recombinant PEP
2.6.1. Expression
2.6.2. Affinity Purification of PEP
2.7. Measurement of PEP Activity
2.7.1. zGly-Pro-pNA Assay for PEP Activity
2.7.2. Glutenase Activity
2.7.3. Kinetic Assay
2.7.4. Gluten Isolation and Digestion
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Total RNA Isolation and mRNA Enrichment
3.2. SMARTer RACE cDNA Synthesis
3.3. Amplification Using Degenerate Primers
3.4. Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (RACE)
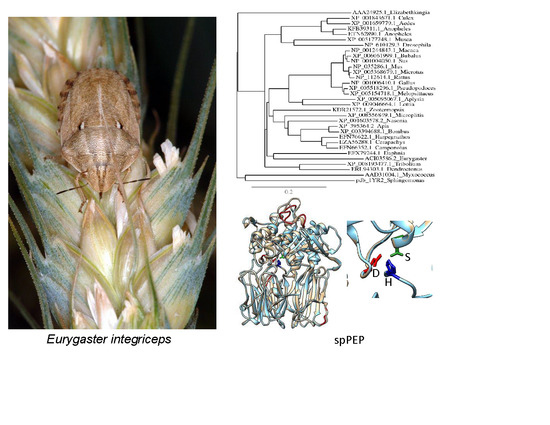
3.5. Sequence Analysis
3.6. Structure Analysis of spPEP Based on Amino Acid Sequence


3.7. Cloning and Expression of Active spPEP

3.7.1. z-Gly-Pro-pNA Assay for PEP Activity

3.7.2. Determination of Km of spPEP
3.7.3. Gluten Assay



4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peiffer, M.; Felton, G.W. Insights into the saliva of the brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). PLoS One 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darkoh, C.; El-Bouhssini, M.; Baum, M.; Clack, B. Characterization of a prolyl endoprotease from Eurygaster integriceps Puton (sunn pest) infested wheat. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 74, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adldoost, H. A new technique for monitoring sunn pest. In sunn Pest Management: A Decade of Progress (1994–2004); Arab Society for Plant Protection: Beirut, Lebanon, 2007; pp. 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Critchley, B.R. Literature review of sunn pest Eurygaster integriceps Put. (Hemiptera, Scutelleridae). Crop Prot. 1998, 17, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, G.; Williams, P.C.; El-Haramein, F.J. Influence of pentatomid insects on the physical dough properties of two-layered flat bread baking quality of syrian wheat. J. Cereal Sci. 2000, 31, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bouhssini, M.; Nachit, M.; Valkoun, J.; Moussa, M.; Ketata, H.; Abdallah, O.; Abdulhai, M.; Parker, B.L.; Rihawi, F.; Joubi, A.; et al. Evaluation of wheat and its wild varieties for resistance to sunn pest under artificial infestation. In sunn Pest Management: A Decade of Progress (1994–2004); Arab Society for Plant Protection: Beirut, Lebanon, 2007; pp. 363–368. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, G.; Bonet, A.; Rosell, C.M. Relationship between gluten degradation by aelia spp and eurygaster spp. and protein structure. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Every, D. General proteinase assay by formation of SDS-protein gels of proteolyzed substrate proteins. Anal. Biochem. 1991, 197, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, T.M.; Henikoff, J.G.; Henikoff, S. CODEHOP (Consensus-Degenerate Hybrid Oligonucleotide Primer) PCR primer design. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3763–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics (Oxf. Engl.) 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozen, S.; Skaletsky, H.J. Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In Bioinformatics Methods and Protocols: Methods in Molecular Biology; Krawetz, S., Misener, S., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 365–386. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloss, B.; Ligation Independent Cloning (N-term.) Senior Research Associate, NYConsortium on Membrane Proteins, New York Structural Biology Center, New York, NY, USA. Personal Communication. 2010.
- Heinemeyer, T.; Wingender, E.; Reuter, I.; Hermjakob, H.; Kel, A.E.; Kel, O.V.; Ignatieva, E.V.; Ananko, E.A.; Podkolodnaya, O.A.; Kolpakov, F.A.; et al. Databases on Transcriptional Regulation: TRANSFAC, TRRD, and COMPEL. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 4.0: Discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dereeper, A.; Guignon, V.; Blanc, G.; Audic, S.; Buffet, S.; Chevenet, F.; Dufayard, J.F.; Guindon, S.; Lefort, V.; Lescot, M.; et al. Phylogeny.fr: Robust Phylogenetic Analysis for the Non-Specialist. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W465–W469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnold, K.; Bordoli, L.; Kopp, J.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL workspace: A web-based environment for protein structure homology modeling. Bioinformatics 2006, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiefer, F.; Arnold, K.; Künzli, M.; Bordoli, L.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL Repository and associated resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D387–D392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, H.; McIntire, J.; Kumar, P. A scaleable manufacturing for pro-EP-B2, A cysteine protease from Barley Indicated for celiac Sprue. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Broeck, H.C.; America, A.H.P.; Smulders, M.J.M.; Bosch, D.; Harner, R.J.; Gilissen, L.J.W.J.; vander Meer, I.M. A modified extraction protocol enables detection and quantification of celiac disease-related gluten proteins from wheat. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yandamuri, R. Cloning and expression of the prolyl endoprotease from Eurygaster integriceps. M.Sc. Thesis, Stephen F. Austin State University, Nacogdoches, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds, A.S.; Bristow, C.A.; Fisher, W.W.; Weiszmann, R.; Wu, S.; Hartenstein, V.; Kellis, M.; Yu, B.; Frise, E.; Celniker, S.E. Spatial expression of transcription factors in Drosophila embryonic organ development. Gen. Biol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Lamblin, A.F.; Steller, H.; Thummel, C.S. A steroid-triggered transcriptional hierarchy controls salivary gland cell death during Drosophila metamorphosis. Mol. Cell. 2000, 5, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzolovsky, G.; Deng, W.M.; Schlitt, T.; Bownes, M. The function of the broad-complex during Drosophila melanogaster oogenesis. Genetics 1999, 153, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sandstrom, D.J.; Bayer, C.A.; Fristrom, J.W.; Restifo, L.L. Broad-complex transcription factors regulate thoracic muscle attachment in Drosophila. Dev. Biol. 1997, 181, 168–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagni, C.; Bray, S.; Gogos, J.A.; Kafatos, F.C.; Hsu, T. The Drosophila zinc finger transcription factor CF2 is a myogenic marker downstream of MEF2 during muscle development. Mech. Dev. 2002, 117, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zobeck, K.L.; Buckley, M.S.; Zipfel, W.R.; Lis, J.T. Recruitment timing and dynamics of transcription factors at the Hsp70 loci in living cells. Mol. Cell. 2010, 40, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yandamuri, R.C.; Gautam, R.; Darkoh, C.; Dareddy, V.; El-Bouhssini, M.; Clack, B.A. Cloning, Expression, Sequence Analysis and Homology Modeling of the Prolyl Endoprotease from Eurygaster integriceps Puton. Insects 2014, 5, 762-782. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects5040762
Yandamuri RC, Gautam R, Darkoh C, Dareddy V, El-Bouhssini M, Clack BA. Cloning, Expression, Sequence Analysis and Homology Modeling of the Prolyl Endoprotease from Eurygaster integriceps Puton. Insects. 2014; 5(4):762-782. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects5040762
Chicago/Turabian StyleYandamuri, Ravi Chandra, Ranjeeta Gautam, Charles Darkoh, Vanitha Dareddy, Mustapha El-Bouhssini, and Beatrice A. Clack. 2014. "Cloning, Expression, Sequence Analysis and Homology Modeling of the Prolyl Endoprotease from Eurygaster integriceps Puton" Insects 5, no. 4: 762-782. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects5040762
APA StyleYandamuri, R. C., Gautam, R., Darkoh, C., Dareddy, V., El-Bouhssini, M., & Clack, B. A. (2014). Cloning, Expression, Sequence Analysis and Homology Modeling of the Prolyl Endoprotease from Eurygaster integriceps Puton. Insects, 5(4), 762-782. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects5040762