Reaction Mechanism and Process Control of Hydrogen Reduction of Ammonium Perrhenate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Chemical Reaction Considerations
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrument
2.2. Materials
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Reduction Mechanism Analysis
3.2. Influence of Particle Size on Reduction
3.3. Analysis of the Products of the Rhenium Ingots
3.4. Proposed Flow Sheet
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Li, L.P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, L.J.; Zhang, W.Z. Recent Development of Rhenium Technology. China Molybdenum Ind. 2016, 40, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Noar, A.; Eliaz, N.; Gileadi, E.; Taylor, S.R. Properties and applications of rhenium and its alloys. AMMTIAC Q. 2010, 5, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.M.; He, X.T.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, J.M.; Han, S.L.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Tan, M.L. Resources, Application and Extraction Status of Rhenium. Precious Met. 2014, 35, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Jurewicz, J.W.; Guo, J.Y. Process for Plasma Synthesis of Rhenium Nano and Micro Powders, and for Coating and New Net Shape Deposits Thereof and Apparatus Therefor. U.S. Patent 2005/0211018A1, 29 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Leonhardt, T.; Trybus, C.; Hickman, R. Consolidation Methods for Spherical Rhenium and Rhenium Alloys. Powder Metall. 2003, 46, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrebler, R.; Cury, P.; Orellana, M.; Gómez, H.; Córdova, R.; Dalchiele, E.A. Electrochemical and Nanoelectrogravimetric Studies of the Nucleation and Growth Mechanisms of Rhenium on Polycrystalline Gold Electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2001, 46, 4309–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, S.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, J. Principle and Research Development of Powder Materials Prepared by Chemical Vapor Deposition. Mater. Sci. Eng. Powder Metall. 2009, 14, 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Stefan, L.; Helumt, A. Hydrogen as a reducing agent: State-of-the-art science and technology. JOM 2007, 59, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mannheim, R.L.; Garin, J.L. Microstructural characterization of rhenium powder obtained at various temperatures. Adv. Powder Technol. 2003, 416, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trybus, C.L.; Wang, C.M.; Pandheeradi, M.; Meglio, C.A. Powder metallurgical processing of rhenium. Adv. Mater. Process. 2002, 160, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.Y.; Yi, X.M.; Liao, B.B. A Preparation Method of High Purity Rhenium Powders. CN Patent NO. 1396027, 12 February 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.B.; Peng, J.Y.; Cheng, T.Y.; Xiong, N.; Yin, J.C.; Chen, F.X. A Manufacturing Method of Pure Rhenium Flakes with Difficulty in Deformation. CN Patent NO. 101177748A, 14 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bartosz, T.; Beata, B.; Kusz, B. A study of a reduction of a micro-and nanometric bismuth oxide in hydrogen atmosphere. Ther. Acta 2018, 669, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, J.; Wu, Y.J.; Lv, Z.P.; You, Z.X.; Zhang, S.F.; Lv, X.W. A new kinetic model for hydrogen reduction of metal oxides under external gas diffusion controlling condition. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2018, 77, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.P.; Bai, Y.; Yi, S.F.; An, P.F. The Effect of Hydrogen Dew Point on the Properties of Molybdenum Dioxide and Molybdenum Powder. China Tungsten Ind. 2018, 33, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, H.O.; Ye, N.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, W.S.; Tang, J.C. Comparative study of tungsten powders prepared by carbon-hydrogen co-reduction and common hydrogen reduction. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2018, 28, 743–748. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.J.; Xie, Z.H.; Wang, R.X.; Tian, L.; Nie, H.P. Reduction Carbonization Mechanism Analysis of Tungsten Oxide Powder and Preparation of Ultrafine Tungsten Carbide Powder. Rare Met. Cem. Carbides 2018, 46, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.L.; Jiang, P.G.; Liu, W.J.; Wang, Z.B. Research progress on hydrogen reduction kinetics of tungsten oxide. Nonferrous Met. Sci. Eng. 2017, 8, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Vesel, A.; MoZetic, M.; Marianne, B.P. Sequential oxidation and reduction of tungsten/tungsten oxide. Thin Solid Film 2015, 591, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.N.; Mao, M.H.; Liang, H.Z.; Xu, J. Preparation of Ultrafine Co Powder from Basic Co(OH)2 Slurry by Hydrogen Reduction. Chin. J. Process Eng. 2001, 1, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Z.Z.; Wang, H.; Kumar, V. Coarsening, densification, and grain growth during sintering of nano-sized powders—A perspective. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2017, 62, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.H.; Sun, G.D.; Zhang, G.H. Preparation of ultrafine Mo powders via carbothermic pre-reduction of molybdenum oxide and deep reduction by hydrogen. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2018, 75, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Jeong, Y.K.; Oh, S.T. Hydrogen reduction behavior and microstructural characteristics of WO3 and WO3-NiO powders. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2019, 80, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.Y.; Qin, M.L.; Zhang, H.A.; Ma, J.D.; Qu, X.H. Preparation of Mo nanopowders through hydrogen reduction of a combustion synthesized foam-like MoO2 precursor. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2018, 76, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colton, R. Some Complex anioks containing rhenium. Aust. J. Chem. 1965, 18, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhou, L.J.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, C.F. Preparation of ultrafine rhenium powders by CVD hydrogen reduction of volatile rhenium oxides. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.J. Research on Preparation of Ultrafine Rhenium Powder by Chemical Vapor Deposition. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Hunan, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.J.; Sun, Y.; Hou, G.C.; Ding, Y.T.; He, F.; Zhou, Y.Z. Studies on Influencing Factors of Ammonium Rhenate Recovery from Waste Superalloy. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.J.; Feng, L.; Zhang, C.W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Fang, D.W.; Liu, Y. The Influences of Stirring on the Recrystallization of Ammonium Perrhenate. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okal, J.; Tylus, W.; Kepi´nski, L. XPS study of oxidation of rhenium metal on γ-Al2 O3 support. J. Catal. 2004, 225, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, V.V.; Gamburg, Y.D.; Zhulikov, V.V.; Batalov, R.S.; Filatova, E.A. Re-Ni cathodes obtained by electrodeposition as a promising electrode material for hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 317, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Shozi, M.L.; Morgan, D.J. X-ray induced reduction of rhenium salts and supported oxide catalysts. Surf. Interface Anal. 2017, 49, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, Y.Z.; Wang, W.H. Line Shapes Used in XPS and Background Subtraction. Phys. Exam. Test. 2011, 1, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hillig, W.B.; Adjerid, S.; Flaherty, J.E.; Hudson, J.B. The effect of combined diffusion and kinetic transport barriers on multi-phase solid state reactions with a vapour reactant. J. Mater. Sci. 1996, 31, 5865–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ler, K.M.K.; Götze, L.C.; Rybacki, E.; Dresen, G.; Abart, R. Enhancement of solid-state reaction rates by non-hydrostatic stress effects on polycrystalline diffusion kinetics. Am. Mineral. 2010, 95, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar]











| Ammonium Perrhenate | Specific Surface (m2/kg) | D50 (µm) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 rpm stirring strength recrystallized | 21.72 | 81.05 |
| 200 rpm stirring strength recrystallized | 26.93 | 71.17 |
| Raw material particles | 14.79 | 123.90 |
| Fitting Parameters | Re | Re4+ | Re6+ | Re7+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B.E (4f7/2) | 40.31 | 42.7 | 45.2 | 46.1 |
| B.E (4f5/2) | 42.71 | 45.1 | 47.6 | 48.5 |
| FWHM | 1.3 | 1.7 | 1.75 | 1.8 |
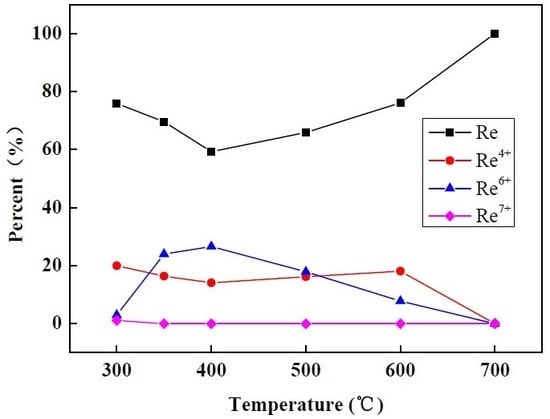
| Reduction Temperature (°C) | Re (%) | Re4+ (%) | Re6+ (%) | Re7+ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 75.9 | 20.0 | 3.0 | 1.1 |
| 350 | 69.6 | 16.4 | 24.0 | 0.0 |
| 400 | 59.3 | 14.1 | 26.6 | 0.0 |
| 500 | 65.9 | 16.2 | 17.9 | 0.0 |
| 600 | 76.1 | 18.1 | 7.8 | 0.0 |
| 700 | 100 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Reduction Temperature (°C) | Re (%) | Re4+ (%) | Re6+ (%) | Re7+ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 65.7 | 20.0 | 10.8 | 3.5 |
| 350 | 58.9 | 21.8 | 19.1 | 0.2 |
| 400 | 36.3 | 10.7 | 45.9 | 7.1 |
| 500 | 68.1 | 15.7 | 16.2 | 0.0 |
| 600 | 72.2 | 18.2 | 9.6 | 0.0 |
| 700 | 72.7 | 22.0 | 5.3 | 0.0 |
| 800 | 79.0 | 17.2 | 3.8 | 0.0 |
| 900 | 80.1 | 19.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| D50 of Ammonium Perrhenate (µm) | D50 of Re Powders (µm) | Specific Surface Area of Re (m2/kg) | Density of Rhenium Ingots (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 81.05 | 34.04 | 97.54 | 18.779 |
| 71.17 | 19.74 | 163.70 | 20.106 |
| 123.90 | 52.15 | 72.73 | 17.726 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Fang, D.; Liu, Y. Reaction Mechanism and Process Control of Hydrogen Reduction of Ammonium Perrhenate. Metals 2020, 10, 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050640
Tang J, Sun Y, Zhang C, Wang L, Zhou Y, Fang D, Liu Y. Reaction Mechanism and Process Control of Hydrogen Reduction of Ammonium Perrhenate. Metals. 2020; 10(5):640. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050640
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Junjie, Yuan Sun, Chunwei Zhang, Long Wang, Yizhou Zhou, Dawei Fang, and Yan Liu. 2020. "Reaction Mechanism and Process Control of Hydrogen Reduction of Ammonium Perrhenate" Metals 10, no. 5: 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050640
APA StyleTang, J., Sun, Y., Zhang, C., Wang, L., Zhou, Y., Fang, D., & Liu, Y. (2020). Reaction Mechanism and Process Control of Hydrogen Reduction of Ammonium Perrhenate. Metals, 10(5), 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050640