Presintered Titanium-Hydroxyapatite Composite Fabricated via PIM Route
Abstract
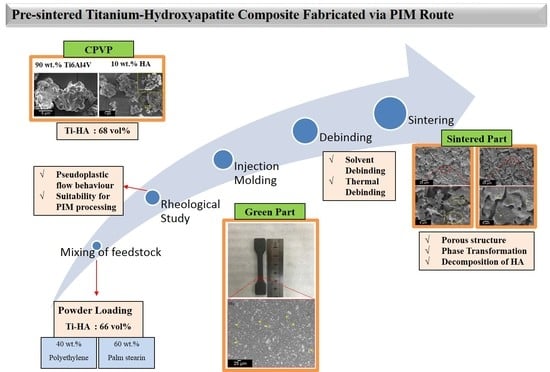
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Green Part
2.2. Debinding Process
2.3. Sintering Process
2.4. Rheological Analysis
2.5. Characterisation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology of Powders
3.2. Rheology Behaviour of Ti-HA Feedstock
3.3. SEM Analysis for Sintered Parts
3.4. Phase Analysis for Sintered Parts
3.5. Bending Strength of Sintered Parts
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Ti6Al4V-HA feedstock under a powder loading of 66 vol.% showed a pseudoplastic behaviour with a low viscosity and low activation energy and was successfully injection molded, with no crack and distortion being observed in the green parts.
- (2)
- Presintered Ti-HA showed no decomposition of HA, resulting in a higher density and higher bending strength.
- (3)
- The Ti-HA composite produced by PIM could produce porous-structured parts, which is promising for biomedical implantations that require highly inter-connected pores.
- (4)
- Ti-HA sintered parts achieved a Young modulus that was close to that of human bone.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, W.; Wang, X.X. Morphologies of Hydroxyapatite Crystal Deposited on Titanium Surface with Electrochemical Technique. Key Eng. Mater. 2007, 330–332, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Mashima, T.; Uenoyama, K. The Effect of Hydroxyapatite Coating on Bony Ingrowth into Grooved Titanium Implants. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.Q.; Zhou, Y. In Vitro Bioactivity of a Biocomposite Fabricated from HA and Ti Powders by Powder Metallurgy Method. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2909–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinand, W.R.; Gonçalves, F.F.R.; Lima, W.M. Effect of Sintering Temperature in Physical-Mechanical Behaviour and in Titanium-Hydroxyapatite Composite Sinterability. Mater. Sci. Forum 2006, 530–531, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtekin, L.; Taskin, A. Ti–6Al–4V Alloy Cortical Bone Screw Production by Powder Injection Molding Method. Mater. Express 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Agarwal, A.; Pandey, A.; Nautiyal, V. Tissue Response to Titanium Implant Using Scanning Electron Microscope. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramli, M.I.; Bakar, A.; Arifin, A.; Sriwijaya, U.; Muchtar, A. Powder Injection Molding of SS316L/HA Composite: Rheologi-cal Properties and Mechanical Properties of the Green Part. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 8, 5317–5321. [Google Scholar]
- Sridhar, T.M.; Mudali, U.K.; Subbaiyan, M. Preparation and Characterisation of Electrophoretically Deposited Hydroxyapatite Coatings on Type 316L Stainless Steel. Corros. Sci. 2003, 45, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.B.; Miao, X.; Chen, Y.; Cheang, P.; Khor, K.A. Characterization of Hydroxyapatite- and Bioglass-316L Fibre Composites Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramli, M.I.; Sulong, A.B.; Muhamad, N.; Muchtar, A.; Arifin, A.; Foudzi, F.M.; Hammadi Al-Furjan, M.S. Effect of Sintering Parameters on Physical and Mechanical Properties of Powder Injection Moulded Stainless Steel-Hydroxyapatite Composite. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arifin, A.; Sulong, A.B.; Muhamad, N.; Syarif, J.; Ramli, M.I. Material Processing of Hydroxyapatite and Titanium Alloy (HA/Ti) Composite as Implant Materials Using Powder Metallurgy: A Review. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deram, V.; Minichiello, C.; Vannier, R.N.; Le Maguer, A.; Pawlowski, L.; Murano, D. Microstructural Characterizations of Plasma Sprayed Hydroxyapatite Coatings. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2003, 166, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niespodziana, K. Synthesis and Properties of Porous Ti-20 Wt.% HA Nanocomposites. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 2245–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhao, H.; Qu, S.; Li, X.; Li, Y. New Developments of Ti-Based Alloys for Biomedical Applications. Materials 2014, 7, 1709–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geetha, M.; Singh, A.K.; Asokamani, R.; Gogia, A.K. Ti Based Biomaterials, the Ultimate Choice for Orthopaedic Implants—A Review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchanek, W.; Yoshimura, M. Processing and Properties of Hydroxyapatite-Based Biomaterials for Use as Hard Tissue Replacement Implants. J. Mater. Res. 1998, 13, 94–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, R.M.; Bose, A. Injection Molding of Metals and Ceramics; Metal Powder Industry: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- German, R.M. Progress in Titanium Metal Powder Injection Molding. Materials 2013, 6, 3641–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, A.; Bakar, A.; Muhamad, N.; Syarif, J.; Ikram, M. Powder Injection Molding of HA / Ti6Al4V Composite Using Palm Stearin as Based Binder for Implant Material. J. Mater. 2015, 65, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.E.; Chaki, T.K. Sintering Behaviour and Mechanical Properties of Hydroxyapatite and Dicalcium Phosphate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1993, 4, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Zeng, S.; De Groot, K. High Temperature Characteristics of Synthetic Hydroxyapatite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1993, 4, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralithran, G.; Ramesh, S. The Effects of Sintering Temperature on the Properties of Hydroxyapatite. Ceram. Int. 2000, 26, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D281-95. Standard Test Method for Oil Absorption of Pigments by Spatula Rub-Out; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Foudzi, F.; Muhamad, N.; Bakar Sulong, A.; Zakaria, H. Yttria Stabilized Zirconia Formed by Micro Ceramic Injection Molding: Rheological Properties and Debinding Effects on the Sintered Part. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 2665–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D1238-04. Standard Test Method for Melt Flow Rates of Thermoplastics by Extrusion; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kothapalli, C.; Wei, M.; Vasiliev, A.; Shaw, M.T. Influence of Temperature and Concentration on the Sintering Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Hydroxyapatite. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 5655–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, I.M.; Shih, W.J.; Hon, M.H.; Wang, M.C. The Properties of Sintered Calcium Phosphate with [Ca]/[P] = 1.50. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 13569–13586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.M.; Han, J.S.; Oh, J.W.; Park, S.J. Study on Rheological Behavior and Mechanical Properties of PMN–PZT Ceramic Feedstock. Met. Mater. Int. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatt, T.K.; Muhamad, N.; Hassan, C.; Haron, C.; Jamaludin, K.R. Influences of Injection Pressure and Flow Rate to the Green Properties. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2019, 8, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- de Vasconcellos, L.M.R.; de Oliveira, M.V.; de Alencastro Graça, M.L.; de Vasconcellos, L.G.O.; Carvalho, Y.R.; Cairo, C.A.A. Porous Titanium Scaffolds Produced by Powder Metallurgy for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Res. 2008, 11, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brentel, A.S.; de Vasconcellos, L.M.R.; de Vasconcellos, L.G.O.; Oliveira, M.V.; Cairo, C.A.A.; de Graca, M.L.A.; Carvalho, Y.R. Histomorphometric Analysis of Pure Titanium Implants With Porous Surface Versus Rough Surface. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2006, 14, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Lu, X.; Hayat, M.D.; Tian, J.; Huang, C.; Chen, M.; Qu, X.; Wen, C. Fabrication and Properties of Newly Developed Ti35Zr28Nb Scaffolds Fabricated by Powder Metallurgy for Bone-Tissue Engineering. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 3696–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hing, K.A.; Best, S.M.; Tanner, K.E.; Bonfield, W.; Revell, P.A. Quantification of Bone Ingrowth Within Bone-Derived Porous Hydroxyapatite Implants of Varying Density. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 10, 663–670. [Google Scholar]
- Simsek, I.; Ozyurek, D. The Effect of A2-Phase (Ti3Al) on the Wear Behavior of Titanium Alloys Added Small Amounts of Fe. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2017, 131, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Injection Temperature | 170 °C |
| Pressure | 15 MPa |
| Filling Time | 2 s |
| Mould Temperature | 70 °C |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmud, N.N.; Sulong, A.B.; Sharma, B.; Ameyama, K. Presintered Titanium-Hydroxyapatite Composite Fabricated via PIM Route. Metals 2021, 11, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11020318
Mahmud NN, Sulong AB, Sharma B, Ameyama K. Presintered Titanium-Hydroxyapatite Composite Fabricated via PIM Route. Metals. 2021; 11(2):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11020318
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmud, Nurul Nadiah, Abu Bakar Sulong, Bhupendra Sharma, and Kei Ameyama. 2021. "Presintered Titanium-Hydroxyapatite Composite Fabricated via PIM Route" Metals 11, no. 2: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11020318
APA StyleMahmud, N. N., Sulong, A. B., Sharma, B., & Ameyama, K. (2021). Presintered Titanium-Hydroxyapatite Composite Fabricated via PIM Route. Metals, 11(2), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11020318