Model and Mechanism of Anode Effect of an Electrochemical Cell for Nd or (Nd, Pr) Reduction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study on Gas Bubble Evolution
2.1.1. Residence Time Due to Bubble Growth
2.1.2. Residence Time after Detachment
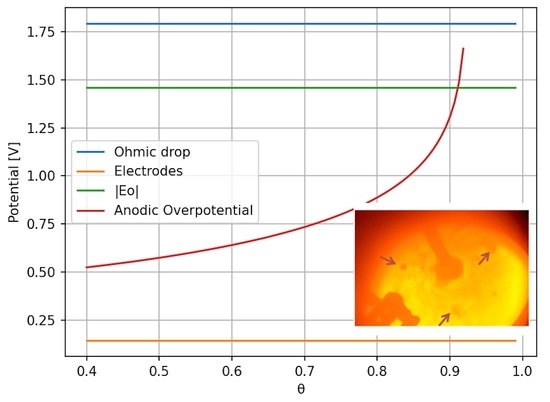
2.2. Overall Cell Voltage
2.2.1. Open-Circuit Potential
2.2.2. Ohmic Potential Drop
2.2.3. Anodic Overpotential
Charge Transfer Overpotential
Gas Diffusion Overpotential
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Summary
- For high current densities, the anode effect can occur due to mass transfer limitation. High current densities can also increase the bubble nucleation rate, leading to small bubbles and an increase in electrode surface coverage by the bubbles.
- Low neodymium or didymium oxide content can lead to low mass transfer rates to the anode, which can lead to an increase in the potential due to charge transfer limitations. Low oxide content tends to lower surface tension, increasing the nucleation rate.
- High viscosity affects the bubble dynamics, increasing the residence time at the anode and consequently the anode coverage. High viscosity also affects the mass transfer coefficient and supersaturation, which can increase the nucleation rate.
- Electrolyte composition can affect the occurrence of the anode effect by affecting viscosity and neodymium dissolution rate. Viscosity and oxide content can affect bubble nucleation, as previously mentioned.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vogel, H.; Flerus, B.; Stoffner, F.; Friedrich, B. Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emission from the Neodymium Oxide Electrolysis. Part I: Analysis of the Anodic Gas Formation. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H.; Friedrich, B. Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emission from the Neodymium Oxide Electrolysis. Part II: Basics of a Process Control Avoiding PFC Emission. Int. J. Nonferr. Metall. 2017, 6, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, A.L.N.; Neto, J.B.F.; Landgraf, F.J.G.; Ett, G.; dos Santos, C.A.L.; da Silveira, J.R.F.; Vieira, F.Y.M.; dos Santos Luz, M. Obtenção de didímio metálico a partir dos óxidos de terras raras produzidos em Araxá, Brasil. In Proceedings of the 72° Congresso Anual da ABM, Editora Edgard Blucher, Ltda., São Paulo, Brazil, 2–6 October 2017; pp. 2282–2294. [Google Scholar]
- Thonstad, J.; Nordmo, F.; Vee, K. On the anode effect in cryolite-alumina melts-I. Electrochim. Acta 1973, 18, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thonstad, J.; Fellner, P.; Haarberg, G.M.; Híves, J.; Kvande, H.; Sterten, Å. Aluminium Electrolysis/Fundamentals of the Hall-Héroult Process; Aluminium-Verl: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2001; ISBN 3-87017-270-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu-Xian, Q.; Ching-Bin, W.; Ming-Ji, C. Studies on Anode Effect in Aluminium Electrolysis. Essent. Read. Light Met. 2013, 2, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åsheim, H.; Aarhaug, T.A.; Sandnes, E.; Kjos, O.S.; Solheim, A.; Kolås, S.; Haarberg, G.M. Anode Effect Initiation During Aluminium Electrolysis in A Two Compartment Laboratory Cell. Light Metals 2016, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2007 Physical Science Basis; Working Group i Contribution Fourth Assessment Report IPCC; Climatology and Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; Available online: https://www.cambridge.org/br/academic/subjects/earth-and-environmental-science/climatology-and-climate-change/climate-change-2007-physical-science-basis-working-group-i-contribution-fourth-assessment-report-ipcc?format=PB&isbn=9780521705967 (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- Vogt, H. On the mechanism of the anode effect in aluminum electrolysis. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2000, 31, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, H. The anode effect as a fluid dynamic problem. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1999, 29, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, H. Effect of alumina concentration on the incipience of the anode effect in aluminum electrolysis. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1999, 29, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.F.; Evans, G.M.; Galvin, K.P. Bubble nucleation from gas cavities—A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 80, 27–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarsrud, K.E.; Johansen, S.T. Modelling of bubble behaviour in aluminium reduction cells. Prog. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2012, 12, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachaparambil, K.J.; Einarsrud, K.E. Explanation of Bubble Nucleation Mechanisms: A Gradient Theory Approach. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, E504–E512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubetkin, S.D. Why is it much easier to nucleate gas bubbles than theory predicts? Langmuir 2003, 19, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, T.; Hilgendorf, S.; Vogel, H.; Friedrich, B.; Pfeifer, H. A Comparison between Two Cell Designs for Electrochemical Neodymium Reduction Using Numerical Simulation. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2017, 48, 2187–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, S. Supersaturation of oxygen in acidic solution in the vicinity of an oxygen-evolving platinum anode. Electrochim. Acta 1978, 23, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, H. Mechanisms of mass transfer of dissolved gas from a gas-evolving electrode and their effect on mass transfer coefficient and concentration overpotential. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1989, 19, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, H. The Quantities Affecting the Bubble Coverage of Gas-Evolving Electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 235, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, H.; Stephan, K. Local microprocesses at gas-evolving electrodes and their influence on mass transfer. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 155, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scriven, L.E. On the dynamics of phase growth. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1959, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno Soto, A. Bubbles on Surfaces: Diffusive Growth and Electrolysis; University of Twente: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, M.; Zuber, N. Drag coefficient and relative velocity in bubbly, droplet or particulate flows. AIChE J. 1979, 25, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, H.; Thonstad, J. The voltage of alumina reduction cells prior to the anode effect. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2002, 32, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, B.; Shi, Z.; Liu, F.; Cao, X. Density and ionic structure of NdF3-LiF melts. J. Rare Earths 2010, 28, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Gao, B.; Lu, G.; Cui, J.; Cao, X.; Zhang, B. Electrical conductivity and Nd solubility of NdF3-LiF-Nd 2O3 melts. In Proceedings of the TMS Annual Meeting, Orlando, FL, USA, 25 February–1 March 2007; pp. 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.R.; Chen, J.S.; Han, Q.; Wei, X.J. Study of anodic overvoltage in neodymium electrolysis. Acta Metall. Sin. 2003, 16, 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, B.; Liu, H.; Kou, F.; Yang, Y.; Yao, B.; Chen, X.; Wong, D.S.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Kuang, G.; et al. Estimating perfluorocarbon emission factors for industrial rare earth metal electrolysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Sun, Z.; Sietsma, J.; Blanpain, B.; Guo, M.; Yang, Y. Quantitative Study on Dissolution Behavior of Nd2O3 in Fluoride Melts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feldhaus, D.; Tshcauner, M.; Friedrich, B. Influence of LiF on the synthesis of the neodymium & praseodymium molten salt electrolysis. In Proceedings of the EMC, Web Conference, 27–30 June 2021; pp. 189–200. [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, H. The actual current density of gas-evolving electrodes—Notes on the bubble coverage. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 78, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Sun, S.; Lu, S.; Huang, X.; Li, K.; Tu, G.; Huang, X.; Huang, S. Surface tension of light rare earth fluoride molten salts electrolyte system. Thermochim. Acta 2016, 636, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubetkin, S.; Blackwell, M. The nucleation of bubbles in supersaturated solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1988, 126, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverkamp, R.G. An XPS study of the fluorination of carbon anodes in molten NaF–AlF3–CaF2. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, A.; van der Linde, P.; Gardeniers, H.; Modestino, M.; Fernández Rivas, D. Influence of Bubbles on the Energy Conversion Efficiency of Electrochemical Reactors. Joule 2020, 4, 555–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berkani, M.; Gaune-Escard, M. Study of binary systems NdF3- MF (M = Li, Na, K): Experimental, modeling and thermodynamic computation. MATEC Web Conf. 2013, 3, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Cell Data | |
|---|---|
| Anode inner diameter Da [m] | 0.12 |
| Immersed anode length L [m] | 0.1 |
| Cathode diameter Dc [m] | 0.00635 |
| Current I [A] | 25–150 |
| Temperature T [K] | 1323 |
| Properties | |
| [kg m−3] [25] | 4040 |
| [Pa s] [16] | 4.95 × 10−3 |
| [m2 s−1] | 9.9 × 10−9 |
| [S m−1] [26] | |
| jo [A m−2] [2] | 1000 |
| Csat [mol m−3] [2] | 100 |
| [27] | 0.5 |
| 0.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
da Silva, A.L.N.; dos Santos, C.A.L.; de Araújo, R.d.M.R.; Feldhaus, D.; Friedrich, B.; Landgraf, F.J.G.; Guardani, R. Model and Mechanism of Anode Effect of an Electrochemical Cell for Nd or (Nd, Pr) Reduction. Metals 2022, 12, 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12030498
da Silva ALN, dos Santos CAL, de Araújo RdMR, Feldhaus D, Friedrich B, Landgraf FJG, Guardani R. Model and Mechanism of Anode Effect of an Electrochemical Cell for Nd or (Nd, Pr) Reduction. Metals. 2022; 12(3):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12030498
Chicago/Turabian Styleda Silva, Andre Luiz Nunis, Celia Aparecida Lino dos Santos, Rogério de Melo Riberio de Araújo, Dominic Feldhaus, Bernd Friedrich, Fernando José Gomes Landgraf, and Roberto Guardani. 2022. "Model and Mechanism of Anode Effect of an Electrochemical Cell for Nd or (Nd, Pr) Reduction" Metals 12, no. 3: 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12030498
APA Styleda Silva, A. L. N., dos Santos, C. A. L., de Araújo, R. d. M. R., Feldhaus, D., Friedrich, B., Landgraf, F. J. G., & Guardani, R. (2022). Model and Mechanism of Anode Effect of an Electrochemical Cell for Nd or (Nd, Pr) Reduction. Metals, 12(3), 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12030498