Electroslag Hollow Ingots for Nuclear and Petrochemical Pressure Vessels and Pipes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Requirements for Pressure Vessel Steel Quality and Content of Impurities
3. Hollow Ingots: State-of-the-Art and Challenges
- -
- favorable solidification conditions allow suppressing segregation (metal free of segregation at the inner surface and subsurface area, and with minimized development of A-type segregation), micro-porosity, anisotropy in the mechanical properties, and reduction of the irradiation embrittlement effect;
- -
- clean internal surface and good inner quality ensure a more significant yield of forgings providing economic efficiency and a high safety factor relative to the risk of reactor failure [25].
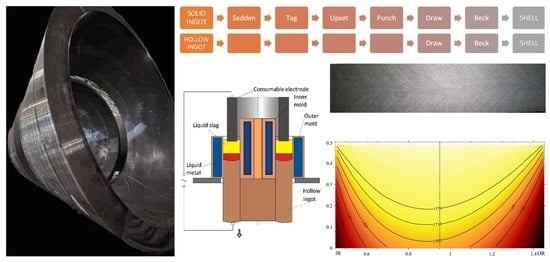
4. ESR for Heavy Wall Pipes Manufacturing Used As-Cast
5. Concept of ESR of Heavy Wall Big Hollow Ingots for RPV
6. Simulation of the Hollow ESR Ingot Solidification
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nisbett, E.G. Steel Forgings: Design, Production, Selection, Testing, and Application; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Nuclear Organisation. Available online: https://www.world-nuclear.org/information-library/nuclear-fuel-cycle/nuclear-power-reactors/heavy-manufacturing-of-power-plants.aspx (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Sandusky, D.; Lunceford, W.; Bruemmer, S.M.; Catalan, M.A. Assessment of Materials Issues for Light-Water Small Modular Reactors; PNNL: Richland, WA, USA, 2013; PNNL-22290. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, K. Reactor Pressure Vessel Materials (IWG-LMNPP--98/3); International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Vienna, Austria, 1998; pp. 70–164. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/etdeweb/servlets/purl/322673 (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Shinozaki, T.; Komura, T.; Fujitsuna, N.; Nakashima, H.; Yamada, M.; Nakanishi, T.; Business, S. Fabrication and Properties of Forged Rings made of Modified 9Cr-1Mo-V Steel for High-Temperature and High-Pressure Reactor. KOBELCO Technol. Rev. 2015, 33, 39–43. Available online: https://www.kobelco.co.jp/english/ktr/pdf/ktr_33/039-043.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Khattak, M.A.; Mukhtar, A.; Rafique, A.; Zareen, N. Reactor Pressure Vessel (RPV) Design and Fabrication: A Literature Review. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Mech. 2016, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Agency Cast++. Available online: https://on-v.com.ua/novosti/biznes/energomashspecstal-izgotovila-obechajku-korpusa-reaktora-vver-toi (accessed on 12 July 2023). (In Russian).
- Dillinger/Heavy Plate for Petrochemical Reactors, Sophistication in Chromium-Molybdenum Steel, Dillinger Hütte GTS 2006. Available online: https://www.dillinger.de/imperia/md/content/dillinger/publikationen/kesselapparatebau/produktfolder/crmo_folder_e_rev_03_2007.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Gillemot, F. Review on Steel Enhancement for Nuclear RPVs. Metals 2021, 11, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FSUE TsNII KM Prometheus. Materials for Vessels of Water-Cooled Nuclear Reactors. Available online: www.crism-prometey.ru/about/activities/VVER.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2023). (In Russian).
- De Bruycker, E.; De Vroey, S.; Huysmans, S.; Stubbe, J. Phenomenology of Hydrogen Flaking in Nuclear Reactor Pressure Vessels. Mater. Test. 2014, 54, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemings, M.C. Solidification Processing; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1974; p. 423. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, R.C.; Woods, A.W.; Worster, M.G.; Huppert, H.E. Disequilibrium and macrosegregation during solidification of a binary melt. Nature 1989, 340, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, X.-Q.; Fu, P.; Ma, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Luan, Y.; Li, Y. Inclusion flotation-driven channel segregation in solidifying steels. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurovich, B.; Kuleshova, E.; Frolov, A.; Zhurko, D.; Erak, D.; Maltsev, D.A.; Komolov, V.M. Structural researches of vessel steels of new generation reactors of WWER-type. Probl. At. Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, 69. [Google Scholar]
- Karzov, G.P.; Teplukhina, I.V. Material science aspects of new principles of operational characteristic improvement for heat-resistant steels for pressure vessels of NPP and their practical realization. Probl. At. Sci. Technol. 2011, 2, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Office for Nuclear Regulations. Generic Design Assessment—New Civil Reactor Build. Step 3 Structural Integrity Assessment Of The Westinghouse AP1000, Nuclear Directorate Division 6 Assessment Report No. AR 09/013-P. HSE: UK. Available online: https://www.onr.org.uk/new-reactors/reports/step3-ap1000-structural-integrity-assessment.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- United States Nuclear Regulation Commission/AP1000 Design Control Document. Chapter 5. Reactor Coolant System and Connected Systems. Available online: https://www.nrc.gov/docs/ML1117/ML11171A453.pdf5 (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Onodera, S.; Kawaguchi, S.; Tsukada, H.; Moritani, H.; Suzuki, K.; Sato, I. Manufacturing of ultra-large diameter 20 MnMoNi 5 5 steel forgings for reactor pressure vessels and their properties. Nucl. Eng. Des. 1985, 84, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizia, R.E. Next Generation Nuclear Plant Reactor Pressure Vessel Acquisition Strategy; Technical report INL/EXT-08-13951; Idaho National Laboratory: Idaho Falls, ID, USA, 2008; p. 45. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y. Reactor pressure vessel (RPV) components: Processing and properties. In Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy, Irradiation Embrittlement of Reactor Pressure Vessels (RPVs) in Nuclear Power Plants; Soneda, N., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Sato, I. Development of high purity large forgings for nuclear power plants. J. Nucl. Mater. 2011, 417, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, N.; Enami, T.; Wanaka, H.; Aso, K. Manufacturing process and properties of nuclear RPV shell ring forged from a hollow ingot. Nucl. Eng. Des. 1984, 81, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamaura, S.; Asoh, K.; Matsuno, J.; Nishioka, T. Development of Hollow Ingot for Large Forging. Trans. IISJ 1982, 22, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bocquet, P.; Saint-Ignan, J.; Blondeau, R. Application of New Types of Ingots to the Manufacturing of Heavy Pressure Vessel Forgings. In Steel Forgings; Nisbett, E., Melilli, A., Eds.; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1986; pp. 367–384. [Google Scholar]
- Nazaratin, V.V.; Kobelev, O.A.; Efimov, M.V.; Selyutin, A.A.; Yavtushenko, P.M. Analysis of technologies used to make hollow ingots and prospects for their improvement. Metallurgist 2013, 56, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medovar, L.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, A.K.; Stovpchenko, G.; Lebed, V.; Borwankar, N. Comparison of the Various Technological Ways of Heavy Wall Forged Hollow Products. In Proceedings of the 19th International Forgemasters Meeting (IFM2014), Tokyo, Japan, 29 September–3 October 2014; pp. 345–348. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson, M.; Talamantes-Silva, J.; Davies, P. The Development of Hollow Ingot Technology at Sheffield Forgemasters International Ltd. In Proceedings of the 18th International Forgemasters Meeting (IFM2011), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 12–15 September 2011; pp. 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Girardin, G.; Jobard, D.; Perdriset, F.; Tollini, P.; Poitrault, I.; Gingell, A. Hollow Ingot: Thirty Years of Use to Control Segregation and Quality for Nuclear and Petrochemical Large Shells. In Proceedings of the 18th International Forgemasters Meeting (IFM2011), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 12–15 September 2011; pp. 170–174. [Google Scholar]
- Sang-Hun, O.; Jung, N.; Seog-Ou, C.; Dong-Hee, L. A Study on the Fabrication of a Large Hollow Ingot by CAE. In Proceedings of the 18th International Forgemasters Meeting (IFM2011), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 12–15 September 2011; pp. 179–182. [Google Scholar]
- Machovčák, P.; Opler, A.; Carbol, Z.; Korbash, M. The development of hollow ingot casting technology at Vítkovice Heavy Machinery A.S. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Metallurgy and Materials (Metal2013), Brno, Czech Republic, 15–17 May 2013; Available online: https://www.confer.cz/metal/2014/download/2928-the-development-of-a-new-type-of-90-ton-forging-ingot.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Paton, B.; Medovar, B.; Boiko, G. Electroslag Casting; Naukova Dumka: Kyiv, Ukraine, 1980; p. 192. [Google Scholar]
- Medovar, L.; Stovpchenko, A. ESR of the Heavy Hollow Ingots. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Casting, Rolling and Forging, Aachen, Germany, 3–7 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Medovar, L.; Stovpchenko, G.; Dudka, G.; Koztninskiy, A.; Fedorovskii, B.; Lebid, V.; Gusiev, L. Evolution of ESR Technology and Equipment for Long Hollow Ingots Manufacture. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Austin, TX, USA, 22–25 September 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medovar, L.; Stovpchenko, G.; Petrenko, V.; Jiang, Z.; Lebid, V.; Fedorovskiy, B. Most Recent Development of the ESR Hollow Ingot Technology & Equipment. In Proceedings of the 19th International Forgemasters Meeting, Makuhari Messe Tokyo Bay Area, Japan, 29 September–3 October 2014; pp. 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Medovar, L.B.; Stovpchenko, A.P.; Fedorovskii, B.B. Novelty in the ESR process of making large hollow ingots. Russ. Metall. 2013, 2013, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorobogatykh, V.N.; Levkov, L.; Shchenkova, I.A.; Bazhenov, A.M.; Prudnikov, D.A.; Zadoinyi, V.A.; Starkovskii, G.L. Method of Production and Properties of Blanks of Bodies of Chromium Steel 10Kh9MFB Pipe Fittings for Thermal Power Plants. Power Technol. Eng. 2017, 51, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmolov, V.G.; Gusev, I.N.; Kazanskiy, V.R.; Povarov, V.P.; Statsura, D.B. New generation first-of-the kind unit—VVER-1200 design features. Nucl. Energy Technol. 2017, 3, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Industeel. The Subsidiary of ArcelorMittal. Available online: https://industeel.arcelormittal.com/fichier/steel-solutions-for-pressure-vessels (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Xing, J.; Song, D.; Wu, Y. HPR1000: Advanced Pressurized Water Reactor with Active and Passive Safety. Engineering 2016, 2, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Arias, P.; Vergara, D.; Orosa, J.A. A Global Review of PWR Nuclear Power Plants. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, Z.; Medovar, L.; Liu, F.; Stovpchenko, G.; Fedorovskii, B.; Vitalii, L.; Zang, X.; Deng, X. Hot Test and Simulation of ESR Hollow Ingots Formation in Current Supplying Mold with Electrodes Change. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, Austin, TX, USA, 22–25 September 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Yu, J.; Liu, F.B.; Chen, X.; Geng, X. Application of Mathematical Models for Different Electroslag Remelting Processes. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2017, 36, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medovar, L.; Stovpchenko, G.; Sybir, A. Increase of the Forging Ingot Mass—How Far. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Casting, Rolling and Forging, Milan, Italy, 7–9 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chvorinov, N. Theory of the Solidification of Castings. Giesserei 1940, 27, 177. [Google Scholar]
- Marathe, S.; Quadros, C. Thermal hot spot prediction in high pressure die casting by determination of Chvorinovs rule shape constant. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 5607–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Part Name | Parameters of Pierced Forging | Solid Ingot before Piercing | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outer Diameter (OD), mm | Inner Diameter (ID), mm | Length, mm | Weight, t | Weight, t | Yield, % | |
| Shaft | 2710 | 1300 | 9410 | 173 | 290 | 60 |
| Shaft | 2180 | 800 | 9150 | 128 | 190 | 67 |
| Thrust collar | 5530 | 4390 | 1210 | 88 | 130 | 68 |
| Traverse of cylinder | 4680 | 1970 | 1190 | 136 | 190 | 72 |
| Heavy plate | 2950 | 2450 | 4650 | 2 × 35 | 124 | 56 |
| Forged pipe | 1020 | 690 | 6500 | 23 | 33 | 70 |
| Steel Grade | Tensile Strength, MPa | Yield Strength, MPa | Elongation, % | Reduction of Area, % | Impact Strength, J/cm2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KCU | KCV | |||||
| 16MnSi | 490–635 | 275 | 18 | 40 | 59 | 54 |
| 15Cr1Mo1V | 490–635 | 315 | 18 | 50 | ||
| 10Cr9MoVNb | >600 | 400 | 17 | 50 | ||
| N | Parts of RPV | Ready Shells Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height, mm | Outer Diameter (OD), mm | Wall Thickness δ, mm | Weight, t | Number of Shells for One Unit, pcs | ||
| 1 | The cylindrical part of VVER-1200 | 4000 | 4290 | 250 | 87 | 1 |
| 2 | The cylindrical part of the AP-1000 | 4000 | 4470 | 215 | 91 | 1 |
| 3 | Hydro cleaning reactor Htotal = 35.7 m | 4000 | 4600 | 250 | 107 | 9 |
| 4 | Petrochemical reactor Htotal = 30 m | 4000 | 4500 | 450 | 180 | 8 |
| RPV from Table 3 | Proposed Parameters of ESR Ingots | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingot Height, mm | Outer Diameter, mm | Inner Diameter, mm | Wall Thickness, mm | Weight, t | Deformation Ratio, Units | Melting Rate, mm/min | |
| 1 | 4300 | 1950 | 450 | 750 | 95.4 | 3 | 2 |
| 2 | 4300 | 2300 | 900 | 700 | 118.7 | 3.58 | 1.5 |
| 3 | 4300 | 2300 | 900 | 700 | 118.7 | 2.8 | 1.5 |
| 4 | 4300 | 2900 | 900 | 1000 | 201 | 2.2 | 0.9 |
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| The density of steel 15Cr1Mo1V, kg·m−3 | 7.2 |
| Liquidus temperature steel 15Cr1Mo1V, K | 1779 |
| Solidus temperature of steel 15Cr1Mo1V, K | 1710 |
| Specific heat of steel 15Cr1Mo1V, kJ·kg−1 | 243 |
| Thermal conductivity (liquid/solid) of steel 15Cr1Mo1V, W·m−1·K−1 | 34/28 |
| Heat capacity (liquid/solid) of steel 15Cr1Mo1V, J·kg−1·K−1 | 700/810 |
| Slag density, kg·m−3 | 2.8 |
| The emissivity of free slag surface | 0.6 |
| Heat transfer from the steel to copper mold, W·m−2·K | 400 |
| Water temperature, K | 303 |
| Slag temperature, K | 2053 |
| Metal overheat above liquidus temperature, K | 120 |
| Number in Table 4 | Power, kVA | Metal Pool Depth, mm | Mushy Zone Thickness, mm | The Surface of the Contact “Liquid Metal Pool—Mushy Zone”, m2 | The Volume of the Liquid Bath, m3 | Maximum Slag Temperature, K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2200 | 386 | 80 | 6.92 | 0.88 | 1892 |
| 2, 3 | 2400 | 430 | 41 | 7.11 | 1.04 | 1973 |
| 4 | 2600 | 468 | 60 | 7.38 | 1.18 | 2050 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medovar, L.; Stovpchenko, G.; Sybir, A.; Gao, J.; Ren, L.; Kolomiets, D. Electroslag Hollow Ingots for Nuclear and Petrochemical Pressure Vessels and Pipes. Metals 2023, 13, 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13071290
Medovar L, Stovpchenko G, Sybir A, Gao J, Ren L, Kolomiets D. Electroslag Hollow Ingots for Nuclear and Petrochemical Pressure Vessels and Pipes. Metals. 2023; 13(7):1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13071290
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedovar, Lev, Ganna Stovpchenko, Artem Sybir, Jianjun Gao, Liguo Ren, and Dmytro Kolomiets. 2023. "Electroslag Hollow Ingots for Nuclear and Petrochemical Pressure Vessels and Pipes" Metals 13, no. 7: 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13071290
APA StyleMedovar, L., Stovpchenko, G., Sybir, A., Gao, J., Ren, L., & Kolomiets, D. (2023). Electroslag Hollow Ingots for Nuclear and Petrochemical Pressure Vessels and Pipes. Metals, 13(7), 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13071290