Distribution and Excretion of Arsenic Metabolites after Oral Administration of Seafood-Related Organoarsenicals in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
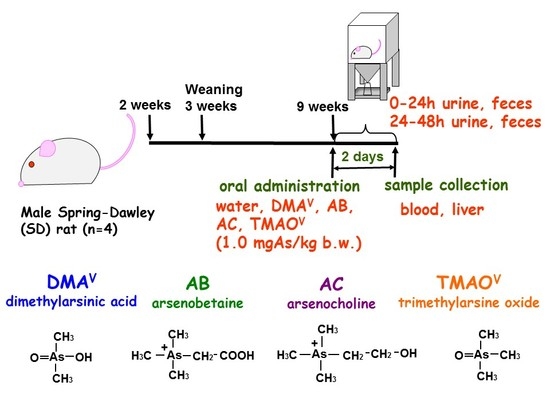
2.2. Animals
2.3. Preparation of Rodent Chows and Tap Water for Analysis
2.4. Synthesis of Dimethylthioarsenicals
2.5. Procedure for Elemental Analyses
2.6. HPLC-ICP-MS Analysis
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Changes in the Concentration of Total Arsenic in Rats Fed Standard or Arsenic-Depleted Chow
3.2. Speciation of Arsenic in Rodent Chow
3.3. Tissue Distribution and Excretion of Metabolites Following Oral Administration of Organoarsenicals in Rats
3.4. HPLC-ICP-MS Analysis of Arsenic Standards and Biological Samples
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| As | arsenic |
| AB | arsenobetaine |
| AC | arsenocholine |
| DDW | deionized-distilled water |
| DMAV | dimethylarsinic acid |
| DMAIII | dimethylarsinous acid |
| DMDTAV | dimethyldithioarsinic acid |
| DMMTAV | dimethylmonothioarsinic acid |
| HPLC | high performance liquid chromatography |
| ICP-MS | inductively-coupled argon plasma mass spectrometry |
| iAsV | inorganic arsenate |
| iAsIII | inorganic arsenite |
| MMAV | monomethylarsonic acid |
| MMAIII | monomethylarsonous acid |
| RBCs | red blood cells |
| TeMA | tetramethylarsonium |
| TMAOV | trimethylarsine oxide |
| TMASV | trimethylarsine sulfide |
References
- Crecelius, E.A. Changes in the chemical speciation of arsenic following ingestion by man. Environ. Health Perspect. 1977, 19, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.J.; Crecelius, E.A.; Reading, J.C. Airborne arsenic exposure and excretion of methylated arsenic compounds. Environ. Health Perspect. 1977, 19, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aposhian, H.V.; Zheng, B.S.; Aposhian, M.M.; Le, X.C.; Cebrian, M.E.; Cullen, W.; Zakharyan, R.A.; Ma, H.S.; Dart, R.C.; Cheng, Z.; et al. DMPS—Arsenic Challenge Test II. Modulation of arsenic species, including monomethylarsonous acid (MMA(III)), excreted in human urine. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2000, 165, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, B.K.; Ogra, Y.; Suzuki, K.T. Identification of dimethylarsinous and monomethylarsonous acids in human urine of the arsenic-affected areas in West Bengal, India. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Styblo, M.; del Razo, L.M.; Vega, L.; Germolec, D.R.; LeCluyse, E.L.; Hamilton, G.A.; Reed, W.; Wang, C.; Cullen, W.R.; Thomas, D.J. Comparative toxicity of trivalent and pentavalent inorganic and methylated arsenicals in rat and human cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2000, 74, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Cui, X.; Kanno, S.; Hayakawa, T.; Shraim, A. The accumulation and toxicity of methylated arsenicals in endothelial cells: Important roles of thiol compounds. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 198, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, S.; Kobayashi, Y. Cytotoxic effects of S-(dimethylarsino)-glutathione: A putative intermediate metabolite of inorganic arsenicals. Toxicology 2006, 227, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Kuroda, K.; Inoue, Y.; Chen, H.; Date, Y.; Wanibuchi, H.; Fukushima, S. Metabolism of dimethylarsinic acid in rats: Production of unidentified metabolites in vivo. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2001, 15, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Kuroda, K.; Zhou, X.; Inoue, Y.; Date, Y.; Wanibuchi, H.; Fukushima, S.; Endo, G. Urinary sulfur-containing metabolite produced by intestinal bacteria following oral administration of dimethylarsinic acid to rats. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2003, 16, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, H.R.; Raab, A.; Jaspars, M.; Milne, B.F.; Feldmann, J. Sulfur-containing arsenical mistaken for dimethylarsinous acid DMA(III) and identified as a natural metabolite in urine: Major implications for studies on arsenic metabolism and toxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2004, 17, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raml, R.; Rumpler, A.; Goessler, W.; Vahter, M.; Li, L.; Ochi, T.; Francesconi, K.A. Thio-dimethylarsinate is a common metabolite in urine samples from arsenic-exposed women in Bangladesh. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 222, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranmandura, H.; Ogra, Y.; Iwata, K.; Lee, J.; Suzuki, K.T.; Weinfeld, M.; Le, X.C. Evidence for toxicity differences between inorganic arsenite and thioarsenicals in human bladder cancer cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norin, H.; Ryhage, R.; Christakopoulos, A.; Sandstrom, M. New evidence for the presence of arsenocholine in shrimps (Pandalus borealis) by use of pyrolysis-gas chromatography-atomic-absorption spectrometry mass-spectrometry. Chemosphere 1983, 12, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goessler, W.; Rudorfer, A.; Mackey, E.A.; Becker, P.R.; Irgolic, K.J. Determination of arsenic compounds in marine mammals with high-performance liquid chromatography and an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer as element-specific detector. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1998, 12, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, J.S.; Francesconi, K.A.; Cannon, J.R.; Raston, C.L.; Skelton, B.W.; White, A.H. Isolation, crystal structure and synthesis of arsenobetaine, the arsenical constituent of the western rock lobster Panulirus longipes cygnus George. Tetrahedron Lett. 1977, 18, 1543–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, J.R.; Edmonds, J.S.; Francesconi, K.A.; Raston, C.L.; Saunders, J.B.; Skelton, B.W.; White, A.H. Isolation, crystal-structure and synthesis of arsenobetaine, a constituent of the western rock lobster, the dusky shark, and some samples of human-urine. Aust. J. Chem. 1981, 34, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaoka, K.; Tagawa, S. Isolation, and identification of arsenobetaine as a major water-soluble arsenic compound from muscle of blue pointer isurus-oxyrhincus and whitetip shark carcarhinus-longimanus. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish 1985, 51, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norin, H.; Christakopoulos, A.; Sandstrom, M.; Ryhage, R. Mass fragmentographic estimation of trimethylarsine oxide in aquatic organisms. Chemosphere 1985, 14, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, J.S.; Francesconi, K.A. Arseno-sugars from brown keip (Ecklonia radiata) as intermediats in cycling of arsenic in a marine ecosystem. Nature 1981, 289, 602–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaoka, K.; Goessler, W.; Yoshida, K.; Fujitaka, Y.; Kaise, T.; Irgolic, K.J. Arsenocholine- and dimethylated arsenic-containing lipids in starspotted shark Mustelus manazo. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1999, 13, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleshi, M.S.; Edmonds, J.S.; Goessler, W.; Ruiz-Chancho, M.J.; Raber, G.; Jensen, K.B.; Francesconi, K.A. Arsenic-Containing lipids Are Natural Constituents of Sashimi Tuna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francesconi, K.A.; Tanggaard, R.; McKenzie, C.J.; Goessler, W. Arsenic metabolites in human urine after ingestion of an arsenosugar. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raml, R.; Goessler, W.; Traar, P.; Ochi, T.; Francesconi, K.A. Novel thioarsenic metabolites in human urine after ingestion of an arsenosugar, 2′,3′-dihydroxypropyl 5-deoxy-5-dimethylarsinoyl-β-d-riboside. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmeisser, E.; Goessler, W.; Francesconi, K.A. Human metabolism of arsenolipids present in cod liver. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marafante, E.; Vahter, M.; Dencker, L. Metabolism of arsenocholine in mice, rats and rabbits. Sci. Total. Environ. 1984, 34, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahter, M.; Marafante, E.; Dencker, L. Metabolism of arsenobetaine in mice, rats and rabbits. Sci. Total. Environ. 1983, 30, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Kuroda, K.; Inoue, Y.; Chen, H.; Wanibuchi, H.; Fukushima, S.; Endo, G. Metabolites of arsenobetaine in rats: Does decomposition of arsenobetaine occur in mammals? Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2001, 15, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kuroda, K.; Chen, H.; Wanibuchi, H.; Fukushima, S.; Endo, G. Urinary excretion of arsenic metabolites after long-term oral administration of various arsenic compounds to rats. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 1998, 54, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lerman, S.; Clarkson, T.W. The Metabolism of Arsenite and Arsenate by the Rat. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1983, 3, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahter, M.; Marafante, E.; Dencker, L. Tissue distribution and retention of 74As-dimethylarsinic acid in mice and rats. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1984, 13, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Wang, H.; Li, X.F.; Lu, X.; Cullen, W.R.; Arnold, L.L.; Cohen, S.M.; Le, X.C. Evidence of hemoglobin binding to arsenic as a basis for the accumulation of arsenic in rat blood. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2004, 17, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.L.; Wang, H.L.; Li, X.F.; Arnold, L.L.; Cohen, S.M.; Le, X.C. Binding of dimethylarsinous acid to Cys-13α of rat hemoglobin is responsible for the retention of arsenic in rat blood. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2007, 20, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, Y.; Yoshinaga, J.; Morita, M. Detection of arsenobetaine in human blood. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1994, 8, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.K.; Ogra, Y.; Anzai, K.; Suzuki, K.T. Speciation of arsenic in biological samples. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 198, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, B.K.; Suzuki, K.T.; Anzai, K. Impact of arsenic in foodstuffs on the people living in the arsenic-affected areas of West Bengal, India. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Toxic Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2007, 42, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petursdottir, A.H.; Gunnlaugsdottir, H.; Joerundsdottir, H.; Mestrot, A.; Krupp, E.M.; Feldmann, J. HPLC-HG-ICP-MS: A sensitive and selective method for inorganic arsenic in seafood. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 2185–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.T.; Katagiri, A.; Sakuma, Y.; Ogra, Y.; Ohmichi, M. Distributions and chemical forms of arsenic after intravenous administration of dimethylarsinic and monomethylarsonic acids to rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 198, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, P.G.; Nielsen, F.H.; Fahey, G.C. AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents—Final report of the american institute of nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J. Nutr. 1993, 123, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naranmandura, H.; Suzuki, N.; Suzuki, K.T. Trivalent arsenicals are bound to proteins during reductive methylation. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2006, 19, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.B.; Blaufox, M.D. Blood-volume in the rat. J. Nucl. Med. 1985, 26, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shraim, A.; Sekaran, N.C.; Anuradha, C.D.; Hirano, S. Speciation of arsenic in tube-well water samples collected from West Bengal, India, by high-performance liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2002, 16, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council, Recommendation. Arsenic: Medical and Biologic Effects of Environmental Pollutants; National Academy of Sciences: Washinton, DC, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Buchet, J.P.; Lauwerys, R.; Roels, H. Comparison of the urinary-excretion of arsenic methabolites after a single oral dose of sodium arsenite, monomethylarsonate, or dimethylarsinate in man. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 1981, 48, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranmandura, H.; Suzuki, K.T. Identification of the major arsenic-binding protein in rat plasma as the ternary dimethylarsinous-hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Column | Mobile Phase | Temperature | Flow Rate | Injection Volume | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reversed-phase | ODS-3 (150 mm × 4.6 mm, 3-µm) | 5 mM TBAH, 3 mM malonic acid and 5% (v/v) methanol (pH approximately 5.6) | 50 °C | 1.0 mL/min | 20 µL |
| Anion-exchange | Shodex RSpak JJ50-4D (150 mm × 4.6 mm) | 20 mM oxalic acid (pH 2.3, pH was adjusted with ammonium solution) | 25 °C | 0.6 mL/min | 20 µL |
| Gel filtration | Shodex Asahipak GS-220 HQ (300 mm × 7.6 mm) | 50 mM ammonium acetate (pH approximately 6.5) | 25 °C | 0.5 mL/min | 20 µL |
| Cation-exchange | Shodex RSpak NN-614 (150 mm × 6.0 mm) | 5 mM HNO3, 8 mM NH4NO3 (pH approximately 2.4) | 25 °C | 0.8 mL/min | 20 µL |
| Treatment | Species Determined | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBC Lysate | Plasma | Urine | Feces | |||
| Gel Filtration | Gel Filtration | Gel Filtration | Cation Exchange | Gel Filtration | Cation Exchange | |
| Control | Protein-bound | Protein-bound | DMAV | |||
| DMA | Protein-bound DMAV | Protein-bound DMAV | DMAV TMAOV DMDTAV DMMTAV TMASV | DMDTAV TMASV DMMTAV DMAV TMAOV | DMAV TMAOV DMDTAV DMMTAV TMASV | DMDTAV TMASV DMMTAV DMAV TMAOV |
| AB | Protein-bound AB | Protein-bound AB | AB TMASV | TMASV AB TMAOV | AB | AB |
| AC | Protein-bound AB | Protein-bound AB | AB AC TMASV | TMASV AB AC TMAOV | AB AC unknown | AB unknown AC |
| TMAO | Protein-bound | Protein-bound | TMAOV TMASV | TMASV TMAOV | TMAOV TMASV | TMAS TMAOV |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kobayashi, Y.; Hirano, S. Distribution and Excretion of Arsenic Metabolites after Oral Administration of Seafood-Related Organoarsenicals in Rats. Metals 2016, 6, 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6100231
Kobayashi Y, Hirano S. Distribution and Excretion of Arsenic Metabolites after Oral Administration of Seafood-Related Organoarsenicals in Rats. Metals. 2016; 6(10):231. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6100231
Chicago/Turabian StyleKobayashi, Yayoi, and Seishiro Hirano. 2016. "Distribution and Excretion of Arsenic Metabolites after Oral Administration of Seafood-Related Organoarsenicals in Rats" Metals 6, no. 10: 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6100231
APA StyleKobayashi, Y., & Hirano, S. (2016). Distribution and Excretion of Arsenic Metabolites after Oral Administration of Seafood-Related Organoarsenicals in Rats. Metals, 6(10), 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6100231