Influences of Restaurant Waste Fats and Oils (RWFO) from Grease Trap as Binder on Rheological and Solvent Extraction Behavior in SS316L Metal Injection Molding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section

| Composition wt. % | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ni | Cr | Mo | Cu |
| Balance | 0.027 | 0.84 | 0.19 | 0.016 | 0.012 | 12.2 | 16.4 | 2.1 | 0.03 |
| D10 (μm) | D50 (μm) | D90 (μm) | Pycnometric Density (g/cm3) | Tap Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.72 | 6.70 | 15.74 | 8.0471 | 4.06 |



| Material | Density (g/cm3) | Tm (°C) | Td (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PP | 0.9 | 165 | 440.5 |
| RWFO | 0.9 | 52 | 297.7 |
| Formulation | SS316L Powder (vol. %/wt. %) | Binder Composition and Contents (vol. %/wt. %) |
|---|---|---|
| F1 | 60/93 | PP (24/4.2) + RWFO (16/2.8) |
| F2 | 60/93 | PP (20/3.5) + RWFO (20/3.5) |
| F3 | 60/93 | PP (16/2.8) + RWFO (24/4.2) |
| F4 | 60/93 | PP (12/2.1) + RWFO (28/4.9) |
| Injection Temperature (°C) | Injection Pressure (MPa) | Mold Temperature (°C) | Cool Time (s) | Injection Speed (RPM) | Injection Time (s) | Packing Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 165 | 80.4 | 40 | 15 | 105 | 1 | 2 |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR and Thermal Analysis of Binder

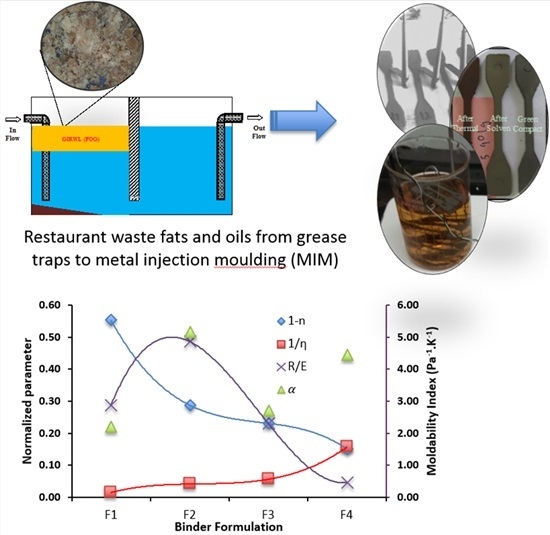
3.2. Rheological Behavior





3.3. Solvents Debinding Behavior





4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- German, R.M.; Bose, A. Injection Molding of Metals and Ceramics; Metal Powder Industries Federation: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Abolhasani, H.; Muhamad, N. A new starch-based binder for metal injection molding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2010, 210, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afian, M.; Subuki, I.; Abdullah, N. The influence of palm stearin content on the rheological behavior of 316L stainless steel mim compact. J. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, S.; Jin, S.; Lee, S.; Atre, S.V.; German, R.M. Effect of powders and binders on material properties and molding parameters in iron and stainless steel powder injection molding process. Powder Technol. 2009, 193, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.H.I.; Muhamad, N.; Sulong, A.B.; Jamaludin, K.R. Optimization of Micro Metal Injection Molding with Multiple Performance Characteristics using Grey Relational Grade. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2011, 38, 231–241. [Google Scholar]
- Karatas, C.; Kocer, A.; Ünal, H.I.I.; Saritas, S. Rheological properties of feedstocks prepared with steatite powder and polyethylene-based thermoplastic binders. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 152, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Liang, S.; Qu, X. The rheology of metal injection molding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 137, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandtland, G.H. United Nation Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: Our Common Future. Available online: http://www.un-documents.net/wced-ocf.htm (accessed on 21 December 2015).
- Gulsoy, H.O.; German, R.M. Production of micro-porous austenitic stainless steel by powder injection molding. Mater. Sci. 2008, 58, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.H.; Ahn, S.Y. Slip characterization of powder/binder mixtures and its significance in the filling process analysis of powder injection molding. Powder Technol. 1995, 85, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakbiz, M.; Simchi, A.; Bagheri, R. Investigation of rheological behavior of 316L stainless steel—3 wt. % TiC powder injection molding feedstock. Powder Metall. 2005, 48, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supriadi, S.; Baek, E.R.; Choi, C.J.; Lee, B.T. Binder system for STS 316 nanopowder feedstocks in micro-metal injection molding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 188, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, M.A.; Subuki, I.; Abdullah, N.S.; Zainon, N.M.; Roslani, N. Processing of Water-Atomised 316L Stainless Steel Powder Using Metal-Injection Processes. J. Eng. Sci. 2012, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Salmah, H.; Lim, B.Y.; Teh, P.L. Rheological and thermal properties of palm kernel shell-filled low-density polyethylene composites with acrylic acid. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, N.; Ibrahim, M.H.I.; Asmawi, R; Amin, A.M.; Masrol, S.R. Green Strength Optimization in Metal Injection Molding Applicable with a Taguchi Method. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 773–774, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canakci, M. The potential of restaurant waste lipids as biodiesel feedstocks. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaky, M.T. Effect of solvent debinding variables on the shape maintenance of green molded bodies. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 3397–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, M.T.T.; Soliman, F.S.S.; Farag, A.S.S. Influence of paraffin wax characteristics on the formulation of wax-based binders and their debinding from green molded parts using two comparative techniques. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 5981–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yang, K.; Wang, M.; Hon, M. Solvent debinding mechanism for alumina injection molded compacts with water-soluble binders. Ceram. Int. 2003, 29, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragauskas, A.M.E.; Pu, Y.; Ragauskas, A.J. Biodiesel from grease interceptor to gas tank. Energy Sci. Eng. 2013, 1, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.B.; Clarkson, C.; Mant, C.; Drinkwater, A.; May, E. Fat, oil and grease deposits in sewers: Characterisation of deposits and formation mechanisms. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6319–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bart, J.C.J.; Gucciardi, E.; Cavallaro, S. Renewable feedstocks for lubricant production. In Biolubricants Science and Technology; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Abington, UK, 2013; pp. 1–128. [Google Scholar]
- Keener, K.M.; Ducoste, J.J.; Holt, L.M. Properties Influencing Fat, Oil, and Grease Deposit Formation. Water Environ. Res. 2008, 80, 2241–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Francis, L.; Leming, M.L.; Dean, L.O.; Lappi, S.E.; Ducoste, J.J. Mechanisms of Fat, Oil and Grease (FOG) deposit formation in sewer lines. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4451–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popkin, B.M. Urbanization, Lifestyle Changes and the Nutrition Transition. World Dev. 1999, 27, 1905–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baines, T.; Brown, S.; Benedettini, O.; Ball, P. Examining green production and its role within the competitive strategy of manufacturers. J. Ind. Eng. Manag. 2013, 5, 53–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, H. Removal and recycling of pollutants from Hong Kong restaurant wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6859–6867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.M.; Ibrahim, M.H.I.; Asmawi, R.; Mustafa, N. The Influence of Sewage fat Composition on Rheological Bahavior of Metal Injection Molding. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 660, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotomayor, M.E.E.; Várez, A.; Levenfeld, B. Influence of powder particle size distribution on rheological properties of 316L powder injection molding feedstocks. Powder Technol. 2010, 200, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.H. Optimization of MicroMetal Injection Molding Parameter by Design of Experiment Method; Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia: Selangor, Malaysia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sotomayor, M.E.; Levenfeld, B.; Várez, A. Powder injection molding of premixed ferritic and austenitic stainless steel powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 3480–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaggi, H.S.; Kumar, Y.; Satapathy, B.K.; Ray, A.R.; Patnaik, A. Analytical interpretations of structural and mechanical response of high density polyethylene/hydroxyapatite bio-composites. Mater. Des. 2012, 36, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazavi, M.A.; Fallahipanah, M.; Jeshvaghani, H.S. A feasibility study on beef tallow conversion to some esters for biodiesel production. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2013, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adames, J.M. Characterization of Polymeric Binders for Metal Injection Molding (MIM) Process. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Akron, Akron, OH, USA, December 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.Q.; Luo, F.H.; Yue, J.L. Effects of surfactant on properties of MIM feedstock. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2007, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.H.I.; Muhamad, N.; Sulong, A.B. Rheological Investigation of Water Atomised Stainless Steel Powder for Micro Metal Injection Molding. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 2009, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, G.; Park, S.J.; Smid, I. Development of niobium powder injection molding: Part I. Feedstock and injection molding. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2006, 24, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, J.; Jiménez-Morales, A.; Torralba, J.M. Torque rheology of zircon feedstocks for powder injection molding. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 4063–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Mou, J.; Cheng, Y. Impact of pore structure on gas adsorption and diffusion dynamics for long-flame coal. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 22, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, M.H.I.; Mohd Amin, A.; Asmawi, R.; Mustafa, N. Influences of Restaurant Waste Fats and Oils (RWFO) from Grease Trap as Binder on Rheological and Solvent Extraction Behavior in SS316L Metal Injection Molding. Metals 2016, 6, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6020019
Ibrahim MHI, Mohd Amin A, Asmawi R, Mustafa N. Influences of Restaurant Waste Fats and Oils (RWFO) from Grease Trap as Binder on Rheological and Solvent Extraction Behavior in SS316L Metal Injection Molding. Metals. 2016; 6(2):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Mohd Halim Irwan, Azriszul Mohd Amin, Rosli Asmawi, and Najwa Mustafa. 2016. "Influences of Restaurant Waste Fats and Oils (RWFO) from Grease Trap as Binder on Rheological and Solvent Extraction Behavior in SS316L Metal Injection Molding" Metals 6, no. 2: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6020019
APA StyleIbrahim, M. H. I., Mohd Amin, A., Asmawi, R., & Mustafa, N. (2016). Influences of Restaurant Waste Fats and Oils (RWFO) from Grease Trap as Binder on Rheological and Solvent Extraction Behavior in SS316L Metal Injection Molding. Metals, 6(2), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6020019