Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Dissimilar Al/Steel Butt Joints Produced by Autogenous Laser Keyhole Welding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Weld Appearance of Al/Steel Butt Joints
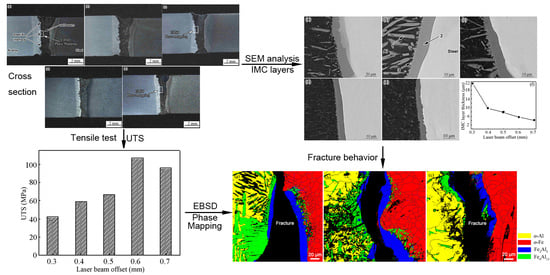
3.2. Cross Sections of Al/Steel Butt Joints
3.3. Microstructures of Al/Steel Joint
3.4. Phase Identification of Intermetallic Compound (IMC) Layers
3.5. Morphology and Thickness of IMC Layers
3.6. Microhardness Profile of Al/Steel Butt Joints
3.7. Tensile Properties of the Al/Steel Butt Joints
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of IMC Layer Thickness on Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS)
4.2. Fracture Behavior of IMC Layers
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Varying travel speeds and laser beam offsets have a more pronounced effect on the area of HAZ S than on weld width. By increasing the laser beam offsets and welding speed, the S in the Al alloy side is decreased continuously. However, travel speed has a significant effect on W1, but has less influence on W2, whereas varying laser beam offset influences W1 and W2 a little.
- (2)
- The thickness of Fe2Al5 layers decreases from 47.7 to 4.7 μm with increasing travel speeds from 0.6 to 1.2 m/min. As laser beam offset increases from 0.3 to 0.7 mm, the thickness of Fe2Al5 layers decreases from 21.0 to 4.1μm. Thus, increasing travel speeds or laser beam offsets obviously decreases the quantity of long needle-like FeAl3 phases and the thickness of the Fe2Al5 layer.
- (3)
- The UTS of Al/steel butt joints is influenced significantly by the tested travel speeds and laser beam offsets. The UTS reaches its maximum under the conditions of a travel speed of 1.0 m/min or a laser beam offset of 0.6 mm. There should be a matching relationship between the IMC layer thickness and UTS of Al/steel butt joints.
- (4)
- EBSD phase mapping proves that the IMC layers consist of Fe2Al5 phases and Fe4Al13 phases. Increasing laser beam offsets from 0.3 to 0.7 mm significantly decreases the quantity of Fe4Al13 phases and the thickness of Fe2Al5 layers at the interface of Al/steel butt joints.
- (5)
- EBSD phase mapping proves that the Fe2Al5 layer is the most brittle region having the weakest bonding strength. An intergranular fracture occurring at the Fe2Al5 layers leads to the relatively high UTS of Al/steel butt joints.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomy, C.; Vollertsen, F. Laser-MIG hybrid welding of aluminium to steel—Effect of process parameters on joint properties. Weld. World 2012, 56, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Lei, Z.; Su, Y.; Fu, B.; Meng, X.; Lin, S. Large spot laser assisted gma brazing–fusion welding of aluminum alloy to galvanized steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 2684–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, A.; Shabadi, R.; Deschamps, A.; Suery, M.; Matteï, S.; Grevey, D.; Cicala, E. Dissimilar material joining using laser (aluminum to steel using zinc-based filler wire). Opt. Laser Technol. 2007, 39, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meco, S.; Pardal, G.; Ganguly, S.; Williams, S.; Mcpherson, N. Application of laser in seam welding of dissimilar steel to aluminium joints for thick structural components. Opt. Laser Eng. 2015, 67, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tricarico, L.; Spina, R. Experimental investigation of laser beam welding of explosion-welded steel/aluminum structural transition joints. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 1981–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahdo, R.; Springer, A.; Pfeifer, R.; Stefan, K.; Ludger, O. High-power laser welding of thick steel-aluminum dissimilar joints. Phys. Procedia 2016, 83, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabaki, M.M.; Ma, J.; Liu, W.; Kovacevic, R. Hybrid laser/arc welding of advanced high strength steel to aluminum alloy by using structural transition insert. Mater. Des. 2015, 75, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.L.; Lin, S.B.; Yang, C.L.; Ma, G.C.; Liu, H. Spreading behavior and microstructure characteristics of dissimilar metals tig welding–brazing of aluminum alloy to stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 509, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreimeyer, M.; Wagner, F.; Vollertsen, F. Laser processing of aluminum–titanium-tailored blanks. Opt. Laser Eng. 2005, 43, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, L.H.; Ishak, M. Review of research progress on aluminum–steel dissimilar welding. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2014, 29, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Shi, Y.; Huang, J.K.; Wu, S.J. Effect of joining parameters on microstructure of dissimilar metal joints between aluminum and galvanized steel. Mater. Des. 2015, 66, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrisutthekul, R.; Yachi, T.; Miyashita, Y.; Mutoh, Y. Suppression of intermetallic reaction layer formation by controlling heat flow in dissimilar joining of steel and aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 467, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Huang, J.H.; Ma, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X. Influence of a Ni-foil interlayer on Fe/Al dissimilar joint by laser penetration welding. Mater. Lett. 2012, 79, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.K.; He, J.; Yu, X.Q.; Li, C.L.; Fan, D. The study of mechanical strength for fusion-brazed butt joint betweenaluminum alloy and galvanized steel by arc-assisted laser welding. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 25, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Takehiro, W.; Tang, J.G. CW/PW dual-beam YAG laser welding of steel/aluminum alloy sheets. Chin. J. Lasers 2010, 48, 732–736. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, S.W.; Gao, M.; Yan, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, G.; Zeng, X.Y. Interface properties and thermodynamic analysis of laser–arc hybrid welded Al/steel joint. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2013, 18, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Chen, C.; Mei, S.; Wang, L.; Zeng, X. Parameter optimization and mechanism of laser–arc hybrid welding of dissimilar al alloy and stainless steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 74, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmendra, C.; Rao, K.P.; Wilden, J.; Reich, S. Study on laser welding–brazing of zinc coated steel to aluminum alloy with a zinc based filler. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 1497–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukant, H.; Wallmann, C.; Korte, M.; Glatzel, U. Flux-less joining technique of aluminium with zinc-coated steel sheets by a dual-spot-laser beam. Adv. Mater. Res. 2005, 6–8, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.W.; Liu, J.S.; Lu, Y.Z.; Xu, S.H. Effect of adding powder on joint properties of laser penetration welding for dual phase steel and aluminum alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2017, 94, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wang, C.L.; Jiang, P.; Shao, X.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, Z.; Yue, C. Effect of axial magnetic field in the laser beam welding of stainless steel to aluminum alloy. Mater. Des. 2016, 109, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seffer, O.; Springer, A.; Kaierle, S. Investigations on remote laser beam welding of dissimilar joints of aluminum alloys and steel with varying sheet thicknesses for car body construction. J. Laser Appl. 2017, 29, 022414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouadri-David, A. Study of metallurgic and mechanical properties of laser welded heterogeneous joints between dp600 galvanised steel and aluminium 6082. Mater. Des. 2014, 54, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.H.; Qi, Y.; Gao, W.; Huang, J. Investigation of laser welding on butt joints of al/steel dissimilar materials. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 120–128. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.J.; Chen, G.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.R. Research on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser keyhole welding–brazing of automotive galvanized steel to aluminum alloy. Mater. Des. 2013, 45, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.H.; Huang, J.; Yan, Q.; Li, Z.G. Fiber laser butt joining of aluminum to steel using welding-brazing method. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 85, 2639–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.T.; Wan, Z.D.; Li, Y.X.; Chen, H. Intermediate layer, microstructure and mechanical properties of aluminum alloy/stainless steel butt joint using laser-MIG hybrid welding-brazing method. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2017, 31, 1744035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A. The filler wire—Laser beam interaction during laser welding with low alloyed steel filler wire. Mechanika 2010, 37, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Tomashchuk, I.; Sallamand, P.; Cicala, E.; Peyre, P.; Grevey, D. Direct keyhole laser welding of aluminum alloy AA5754 to titanium alloy Ti6Al4V. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 217, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casalino, G.; Mortello, M.; Peyre, P. Yb–yag laser offset welding of aa5754 and t40 butt joint. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 223, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, Z.Y.; Song, X.G.; Tan, C.W.; He, Z.Z.; Huang, Y.X.; Feng, J.C. Influence of laser offset on laser welding-brazing of al/brass dissimilar alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 717, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, B.; Galun, R.; Weisheit, A.; Mordike, B.L. Formation of a crack-free joint between ti alloyand al alloy by using a high-power CO2 laser. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 6191–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; He, D.Y.; Fu, G.; Li, X.Y.; Jiang, J.M. Effect of fiber laser–mig hybrid process parameters on weld bead shape and tensile properties of commercially pure titanium. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2010, 25, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Amaya, J.M.; Delgado, T.; De Damborenea, J.J.; Lopez, V.; Botana, F.J. Laser welding of AA 5083 samples by high power diode laser. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2013, 14, 78–86. [Google Scholar]
- Bouche, K.; Barbier, F.; Coulet, A. Intermetallic compound layer growth between solid iron and molten aluminium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 249, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardo, A.; Dominique, E.; Christian, H.S.; Arenholz, E.; Jank, N.; Bruckner, J.; Pyzalla, A.R. Intermetallic FexAly-phases in a steel/Al-alloy fusion weld. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 4205–4214. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.X.; Qiao, S.; Qiu, R.F.; Zhang, X.J.; Yu, H. Effect of welding time on the joining phenomena of diffusion welded joint between aluminum alloy and stainless steel. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2012, 27, 1366–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybkov, V.I. Interaction of 18Cr-10Ni stainless steel with liquid aluminium. J. Mater. Sci. 1990, 25, 3615–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.G.; Han, D.F.; Yao, J.Z.; Li, F. Microstructure and interface characteristics of laser penetration brazed magnesium alloy and steel. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2013, 15, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, G.; Peyre, P.; Deschaux-Beaume, F.; Stuart, D.; Fras, G. Steel to aluminium key-hole laser welding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 447, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouayad, A.; Gerometta, C.; Belkebir, A.; Ambari, A. Kinetic interactions between solid iron and molten aluminium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 363, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, R.M.D.; Martinelli, A.E.; Buschinelli, A.J.A. Review article: Recent advances in metal-ceramic brazing artigo revisão: Avanços recentes em brasagem metal-cerâmica. Cerâmica 2003, 49, 178–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, J.; Amirkhiz, B.S.; Liang, J.; Zhang, R. Formation of nanometer scale intermetallic phase at interface of aluminum-to-steel spot joint by welding–brazing process. Mater. Lett. 2014, 137, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, H.; Kostka, A.; Santos, J.F.D.; Raabe, D. Influence of intermetallic phases and kirkendall-porosity on the mechanical properties of joints between steel and aluminium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 4630–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















| Materials | Si | Mn | S | P | Cr | Ni | Cu | C | Fe | Mg | Zn | Ti | Other | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q235 | ≤0.35 | 0.3~0.7 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.2 | Base | - | - | - | - | - |
| 5083 | ≤0.40 | 0.4~1.0 | 0.05~0.25 | ≤0.10 | 0.4 | 4.0~4.9 | 0.25 | ≤0.15 | 0.15 | Bal. |
| Symbol | Phase | a | b | c | Alpha | Beta | Gamma | Space Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θ | Fe4Al13 | 15.49 Å | 8.08 Å | 12.48 Å | 90.00° | 107.72° | 90.00° | 12 |
| η | Fe2Al5 | 7.66 Å | 6.42 Å | 4.22 Å | 90.00° | 90.00° | 90.00° | 63 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, L.; Chen, B.; Qian, W.; He, D.; Chen, L. Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Dissimilar Al/Steel Butt Joints Produced by Autogenous Laser Keyhole Welding. Metals 2017, 7, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7110492
Cui L, Chen B, Qian W, He D, Chen L. Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Dissimilar Al/Steel Butt Joints Produced by Autogenous Laser Keyhole Welding. Metals. 2017; 7(11):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7110492
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Li, Boxu Chen, Wei Qian, Dingyong He, and Li Chen. 2017. "Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Dissimilar Al/Steel Butt Joints Produced by Autogenous Laser Keyhole Welding" Metals 7, no. 11: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7110492
APA StyleCui, L., Chen, B., Qian, W., He, D., & Chen, L. (2017). Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Dissimilar Al/Steel Butt Joints Produced by Autogenous Laser Keyhole Welding. Metals, 7(11), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7110492