A Novel Methods for Fracture Toughness Evaluation of Tool Steels with Post-Tempering Cryogenic Treatment
Abstract
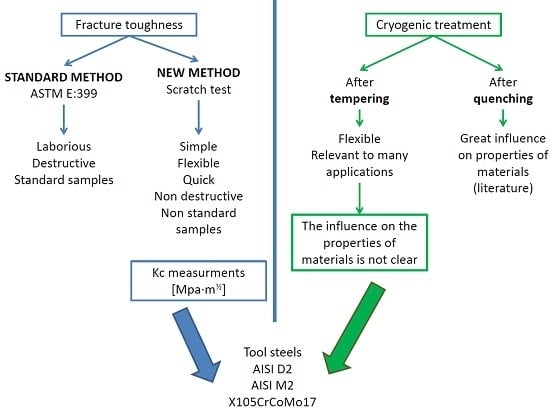
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Podgornik, B.; Paulin, I.; Zajec, B.; Jacobson, S.; Leskovsek, V. Deep Cryogenic treatment of tool steels. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 229, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldissera, P.; Delprete, D. Deep Cryogenic treatment: A bibliografic review. Open Mech. Eng. J. 2008, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskovsek, V.; Podgornik, B. Vacuum heat treatment, deep cryogenic treatment and simultaneous pulse plasma nitriding and tempering of P/M S390MC steel. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 531, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Sarkar, R.; Dutta, A.K.; Ray, K.K. Influence of sub-zero treatments on fracture toughness of AISI D2 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 528, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, A.; Pellizzari, M.; Gialanella, S.; Straffelini, G.; Stiasny, K.H. Effect of deep cryogenic treatment on the properties of tool steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 118, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellizzari, M.; Molinari, A.; Giardini, L.; Maldarelli, L. Deep Cryogenic treatment of AISI M2 high speed steel. Int. J. Microstruct. Mater. 2008, 3, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.; Kakkeri, S.; Sangamesh. Effect of cryogenic treated and untreated tool on its tool life—Review. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, M.; Belzunce, F.J. The effect of deep cryogenic treatments on the mechanical proprieties of an AISI H13 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 624, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, R.; Poli, G.; Giovanardi, R.; Veronesi, P.; Parigi, G. Effect of deep cryogenic treatment on the properties of AISI M2 steel. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Heat Treatment 2015 and 22nd Heat Treatment and Surface Engineering from Tradition to Innovation Congress, Venice, Italy, 20–22 May 2015.
- Gavrilijuk, V.; Theisen, W.; Sirosh, V.V.; Polshin, E.V.; Kortmann, A.; Mogilny, G.S.; Petrov, Y.N.; Tarusin, Y.V. Low-temperature martensitic transformation in tool steels in relation to their deep cryogenic treatment. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.; Rodriguez, C.; Belzunce, F.J. The use of cryogenic treatment to increase fracture toughness of a hot work tool steel used to make forging dies. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 3, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, M.; Pantleon, K.; Somers, M.A.J. Evolution of compressive strains in retained austenite during sub-zero Celsius martensite formation and tempering. Acta Mater. 2014, 65, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, M.; Grumsen, F.B.; Pantleon, K.; Somers, M.J. Martensitic transformation and stress partitioning in a high-carbon steel. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.; Zhu, Y.T.; Liao, X.Z.; Beyerlein, I.J.; Bourke, M.A.; Mitchell, T.E. Microstructure of cryogenic treated M2 tool steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 339, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Singh, H. Influence of deep-cryogenic treatment on the wear behavior and mechanical properties of mild steel. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2014, 4, 169–173. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. ASTM E399-12e3: Standard Test Method for Linear-Elastic Plane-Strain Fracture Toughness KIc of Metallic Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, G.D.; Bradt, R.C. On Vickers fracture Toughness Test. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 90, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, D.S.; Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. Cracking during nanoindentation and its use in the measurement of fracture toughness. In Proceedings of the Fall meeting of the Materials Research Society (MRS), Boston, MA, USA, 28 November–9 December 1994; pp. 663–668.
- Widjaja, S.; Yip, T.H.; Limarga, A.M. Measurement of creep-induced localized residual stress in soda-lime glass using nano-indentation technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 318, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akono, A.T.; Ulm, F.J. Scratch test model for the determination of fracture toughness. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2011, 78, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akono, A.T.; Randall, N.X.; Ulm, F.J. Experimental determination of the fracture toughness via microscratch tests: Application to polymers, ceramics, and metals. J. Mater. Res. 2012, 27, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouché, G.A.; Akono, A.T. Micromechanics-based estimates on the macroscopic fracture toughness of micro-particulate composites. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2015, 148, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akono, A.T.; Alm, F.J. An improved technique for characterizing the fracture toughness via scratch test experiments. Wear 2014, 313, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. ASTM Standard C1624: Standard Test Method for Adhesion Strenght and Mechanical Failure Modes of Ceramics Coatings by Quantitative Single Point Scratch Testing; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bull, S.J.; Berasetegui, E.G. An overview of the potential of quantitative coating adhesion measurement by scratch testing. Tribol. Int. 2006, 39, 91–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohava, J.; Bonferroni, B.; Bolelli, G.; Lusvarghi, L. Interesting aspects of indentation and scratch methods for characterization of thermally-sprayed coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taurino, R.; Barbieri, L.; Bondioli, F. Surface properties of new green building material after TiO2–SiO2 coatings deposition. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 4866–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, R.; Poli, G.; Veronesi, P.; Giovanardi, R. Effects of surface morphology on the wear and corrosion resistance of post-treated Nitrided and nitrocarburized 42CrMo4 steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 2827–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, R. Post-treatment surface morphology effect on the wear and corrosion resistance of nitrided and nitrocarburized 41CrAlMo7 steel. Metall. Ital. 2010, 102, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Taurino, R.; Fabbri, E.; Pospiech, D.; Synytska, A.; Messori, M. Preparation of scratch resistant superhydrophobic hybrid coatings by sol-gel process. Prog. Org. Coat. 2014, 77, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchini, G.F.; Poli, G.; Sola, R.; Veronesi, P. Comparison—By nanoindentation—Among PM steels obtained from diffusion-bonded powders (nominally equivalent). In Proceedings of the World Powder Metallurgy Congress and Exhibition, Florence, Italy, 10–14 October 2010; Volume 3.
- Fougere, G.E.; Riester, L.; Ferber, M.; Weetman, J.R.; Siegal, R.W. Young’s modulus of nanocrystalline Fe measured by nanoindetation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1995, 204, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.T.; Yan, M.F.; Fu, S.S. Martensite transformation induced by plasma nitrocarburizing on AISI304 austenitic stainless steel. Vacuum 2014, 105, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balijepalli, S.K.; Colantoni, I.; Donnini, R.; Kaciulis, S.; Lucci, M.; Montanari, R.; Ucciardello, N.; Varone, A. Modulo elastico della fase S in un acciaio 316 L kolsterizzato. Metall. Ital. 2013, 1, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Balijepalli, S.K.; Colantoni, I.; Donnini, R.; Kaciulis, S.; Montanari, R.; Varone, A. Young’s modulus profile in kolsterized AISI 316 L steel. Mater. Sci. Forum 2013, 762, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, D. Influence of shallow and deep cryogenic treatment on residual state of stress of 4140 steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 211, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Material | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | V | W | Co | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AISI D2 | 1.50 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 11.50 | 0.70 | 1.00 | - | - | bal. |
| AISI M2 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.25 | 4.10 | 5.00 | 1.80 | 6.40 | - | bal. |
| X105CrCoMo18 | 1.09 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 17.30 | 1.10 | 0.10 | - | 1.50 | bal. |
| Material | Sample Code | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| AISI D2 | D2-C | Vacuum quenching at 1080 °C, vacuum tempering at 480 °C, cryogenic treatment at −80 °C for 2 h in liquid nitrogen (LN2), tempering at 480 °C, cryogenic treatment at −193 °C in LN2 for 24 h |
| D2 | Vacuum quenching at 1080 °C, vacuum tempering at 480 °C, cryogenic treatment at −80 °C for 2 h in LN2, tempering at 480 °C | |
| AISI M2 | M2-C | Vacuum quenching at 1080 °C, three vacuum tempering at 550 °C for 2 h, cryogenic treatment at −193 °C in LN2 for 24 h |
| M2 | Vacuum quenching at 1080 °C, three vacuum tempering at 550 °C for 2 h | |
| X105CrCoMo18 | X105-C | Vacuum quenching at 1030 °C, vacuum tempering at 500 °C for 2 h, cryogenic treatment at −193 °C in LN2 for 24 h |
| X105 | Vacuum quenching at 1030 °C, vacuum tempering at 500 °C for 2 h |
| Sample | Particle Size (μm) | Volume Fraction (%) |
|---|---|---|
| D2-C | 0.444 ± 0.1 | 19.7 ± 1 |
| D2 | 0.555 ± 0.1 | 14.5 ± 1 |
| M2-C | 0.592 ± 0.1 | 9.1 ± 1 |
| M2 | 0.617 ± 0.1 | 7.0 ± 1 |
| X105-C | 0.394 ± 0.1 | 15.9 ± 1 |
| X105 | 0.472 ± 0.1 | 11.1 ± 1 |
| Sample | Kc (MPa∙m½) | Residual Stresses (MPa) | HV1 | E (GPa) | ηp % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2-C | 47.06 ± 1 | 105 ± 35 | 807 ± 6 | 205 ± 6 | 57.7 |
| D2 | 36.24 ± 1 | 159 ± 36 | 814 ± 23 | 208 ± 5 | 50.1 |
| M2-C | 47.91 ± 2 | −66 ± 31 | 899 ± 22 | 211 ± 1 | 61.3 |
| M2 | 36.74 ± 2 | 110 ± 39 | 902 ± 16 | 209 ± 3 | 49.4 |
| X105-C | 45.91 ± 3 | 281 ± 28 | 708 ± 11 | 212 ± 2 | 55.5 |
| X105 | 29.96 ± 1 | 324 ± 36 | 699 ± 9 | 211 ± 4 | 33.4 |
| Sample | Scratch 100× |
|---|---|
| D2-C |  |
| D2 |  |
| M2-C |  |
| M2 |  |
| X105-C |  |
| X105 |  |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sola, R.; Giovanardi, R.; Parigi, G.; Veronesi, P. A Novel Methods for Fracture Toughness Evaluation of Tool Steels with Post-Tempering Cryogenic Treatment. Metals 2017, 7, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7030075
Sola R, Giovanardi R, Parigi G, Veronesi P. A Novel Methods for Fracture Toughness Evaluation of Tool Steels with Post-Tempering Cryogenic Treatment. Metals. 2017; 7(3):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7030075
Chicago/Turabian StyleSola, Ramona, Roberto Giovanardi, Giovanni Parigi, and Paolo Veronesi. 2017. "A Novel Methods for Fracture Toughness Evaluation of Tool Steels with Post-Tempering Cryogenic Treatment" Metals 7, no. 3: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7030075
APA StyleSola, R., Giovanardi, R., Parigi, G., & Veronesi, P. (2017). A Novel Methods for Fracture Toughness Evaluation of Tool Steels with Post-Tempering Cryogenic Treatment. Metals, 7(3), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7030075