The Effect of Temperature and Mo Content on the Lattice Misfit of Model Ni-Based Superalloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
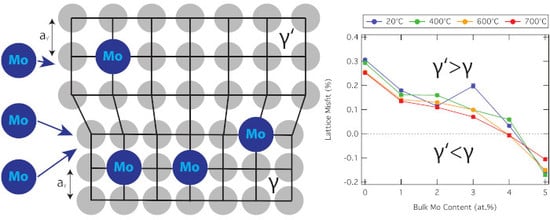
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Decker, R.F.; Mihalisin, J.R. Coherency strains in γ′ hardened nickel alloys. Trans. Am. Soc. Met. 1969, 62, 481–489. [Google Scholar]
- Raynor, D.; Silcock, J.M. Strengthening mechanisms in γ′ precipitating alloys. Met. Sci. J. 1970, 4, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerold, V.; Haberkorn, H. On the critical resolved shear stress of solid solutions containing coherent precipitates. Phys. Status Solidi B 1966, 16, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.F.; Ansell, G.S. Low temperature mechanical behavior of Ni-15Cr-Al-Ti-Mo alloys. Metall. Trans. A 1977, 8, 1979–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melander, A.; Persson, P.A. Strength of γ′ hardened nickel-base alloy. Met. Sci. 1978, 12, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, V.A. Hardening mechanisms in a precipitation hardenable nickel-12·71 at.% aluminium alloy. Philos. Mag. 1967, 16, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, L.K.; Martin, J.W. The mechanism of tensile yield in an age-hardened steel containing γ′ (ordered Ni3Ti) precipitates. Acta Metall. 1968, 16, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricks, R.A.; Porter, A.J.; Ecob, R.C. The growth of γ′ precipitates in nickel-base superalloys. Acta Metall. 1983, 31, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grose, D.A.; Ansell, G.S. The influence of coherency strain on the elevated temperature tensile behaviour of Ni-15Cr-A1-Ti-Mo alloys. Metall. Trans. A 1980, 12, 1631–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKay, R.A.; Nathal, M.V.; Pearson, D.D. Influence of Molybdenum on the creep properties of nickel-base superalloy single crystals. Metall. Trans. A 1990, 21, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniar, G.N.; Bridge, J.E., Jr. Effect of gamma-gamma prime mismatch, volume fraction gamma prime, and gamma prime morphology on elevated temperature properties of Ni, 20 Cr, 5.5 Mo, Ti, Al alloys. Metall. Trans. 1971, 2, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, P.; Fielding, S.; West, D.R.F. Phase equilibria in nickel rich Ni-Al-Mo and Ni-Al-W alloys. Met. Sci. 1983, 17, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, A.K.; Chaturvedi, M.C. The role of alloying elements in the design of nickel-base superalloys. J. Mater. Sci. 1984, 19, 3121–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, E.; Miller, M.K.; Affeldt, E.; Glatzel, U. Quantitative experimental determination of the solid solution hardening potential of rhenium, tungsten and molybdenum in single-crystal nickel-based superalloys. Acta Mater. 2015, 87, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.F.; Wang, Y.M.; Chaturvedi, M.C. Strengthening in a DS casting Ni3Al base alloy IC6. Adv. Perform. Mater. 1995, 2, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, B.; Leon, H.; Huang, X. Superalloys: Alloying and Performance; ASM International: Geauga County, OH, USA, 2010; pp. 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Jin, T.; Sun, X.; Hu, Z. Effect of Mo concentration on creep properties of a single crystal nickel-base superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3051–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessah, M.; Caron, P.; Khan, T. Effect of μ phase on the mechanical properties of a nickel-base single crystal superalloy. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Symposium on Superalloys 1992, Champion, PA, USA, 20–24 September 1992; pp. 567–576. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, A.S. Formation and effect of topologically close-packed phases in nickel-base superalloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 33, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, A.J.; Galindo-Nava, E.I.; Christofidou, K.A.; Jones, N.G.; Boyer, C.D.; Martin, T.I.; Bagot, P.A.J.; Hardy, M.C.; Stone, H.J. The effect of phase chemistry on the extent of strengthening mechanisms in model Ni-Cr-Al-Ti-Mo based superalloys. Acta Mater. 2018, 153, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santisteban, J.R.; Daymond, M.R.; James, J.A.; Edwards, L. ENGIN-X: A third-generation neutron strain scanner. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2006, 39, 812–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daymond, M.R.; Priesmeyer, H.G. Elastoplastic deformation of ferritic steel and cementite studied by neutron diffraction and self-consistent modelling. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 1613–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daymond, M.R.; Withers, P.J. A new stroboscopic neutron diffraction method for monitoring materials subjected to cyclic loads: Thermal cycling of metal matrix composites. Scr. Mater. 1996, 35, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, A.C.; Von Dreele, R.B. GSAS—General Structure Analysis System; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 1994.
- Le Bail, A. Whole powder pattern decomposition methods and applications: A retrospection. Powder Diffr. 2005, 20, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, M.P.; Reed, R.C. Heat treatment of UDIMET 720Li: The effect of microstructure on properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 259, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.M.; Stone, H.J. A modelling approach to yield strength optimisation in a nickel-base superalloy. Int. J. Plast. 2014, 54, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, W.W.; Orth, E.L.; Schirra, J.J.; Savage, M.F. Effects of microstructure on the high temperature constitutive behavior of IN100. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Symposium on Superalloys 2004, Champion, PA, USA, 19–23 September 2004; pp. 331–339. [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan, G.B.; Sarosi, P.M.; Henry, M.F.; Whitis, D.D.; Milligan, W.W.; Mills, M.J. Investigation of creep deformation mechanisms at intermediate temperatures in René 88 DT. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 3041–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, A.J.; Knowles, D.; Small, C.J. A Nickel Base Superalloy. European Patent EP1193321B1, 22 October 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Monajati, H.; Jahazi, M.; Bahrami, R.; Yue, S. The influence of heat treatment conditions on γ′ characteristics in Udimet 720. Acta Mater. 2004, 373, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkalla, H.J.; Wosik, J.; Czyrska-Filemonowicz, A. Quantitative microstructural characterisation of Ni-base superalloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 81, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Slater, T.J.A.; Lewis, E.A.; Francis, E.M.; Burke, M.G.; Preuss, M.; Haigh, S.J. Measurement of size-dependent composition variations for gamma prime (γ′) precipitates in an advanced nickel-based superalloy. Ultramicroscopy 2014, 144, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, A.J.; Galindo-Nava, E.I.; Christofidou, K.A.; Jones, N.G.; Martin, T.; Bagot, P.A.J.; Boyer, C.D.; Hardy, M.C.; Stone, H.J. Gamma prime precipitate evolution during aging of a model nickel-based superalloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyczak, F.; Devrient, B.; Mughrabi, H. The effects of different alloying elements on the thermal expansion coefficients, lattice constants and misfit of nickel-based superalloys investigated by X-ray diffraction. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Symposium on Superalloys 2004, Champion, PA, USA, 19–23 September 2004; pp. 827–836. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, R.J.; Preuss, M.; Hardy, M.C.; Tin, S. Influence of composition and cooling rate on constrained and unconstrained lattice parameters in advanced polycrystalline nickel-base superalloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 423, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.J.; Preuss, M.; Tin, S.; Hardy, M.C. The influence of cooling rate from temperatures above the γ′ solvus on morphology, mismatch and hardness in advanced polycrystalline nickel-base superalloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 473, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.J.; Preuss, M. Inter-relationships between composition, γ′ morphology, hardness, and γ-γ′ mismatch in advanced polycrystalline nickel-base superalloys during aging at 800 °C. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2007, 38, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Alloy (Nominal at.% Mo) | Al | Ti | Cr | Mo | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5.42 ± 0.1 | 5.12 ± 0.06 | 14.18 ± 0.07 | 0 | 75.29 ± 0.1 |
| 1 | 5.19 ± 0.1 | 4.97 ± 0.08 | 13.66 ± 0.06 | 0.73 ± 0.02 | 75.45 ± 0.07 |
| 2 | 5.54 ± 0.09 | 5.27 ± 0.04 | 14.52 ± 0.1 | 1.72 ± 0.02 | 72.94 ± 0.1 |
| 3 | 4.99 ± 0.2 | 5.06 ± 0.05 | 14.05 ± 0.1 | 2.58 ± 0.04 | 73.33 ± 0.1 |
| 4 | 4.85 ± 0.1 | 4.52 ± 0.1 | 12.82 ± 0.09 | 3.13 ± 0.07 | 74.68 ± 0.2 |
| 5 | 5.24 ± 0.06 | 5.02 ± 0.05 | 14.26 ± 0.1 | 4.48 ± 0.04 | 71.00 ± 0.1 |
| Alloy (Nominal at.% Mo) | Diameter of Secondary γ′ (nm) | Diameter of Tertiary γ′ (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 76 ± 14 | 20 ± 5 |
| 1 | 41 ± 8 | - |
| 2 | 92 ± 18 | 12 ± 3 |
| 3 | 89 ± 16 | - |
| 4 | 85 ± 11 | - |
| 5 | 105 ± 18 | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goodfellow, A.J.; Owen, L.R.; Christofidou, K.A.; Kelleher, J.; Hardy, M.C.; Stone, H.J. The Effect of Temperature and Mo Content on the Lattice Misfit of Model Ni-Based Superalloys. Metals 2019, 9, 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9060700
Goodfellow AJ, Owen LR, Christofidou KA, Kelleher J, Hardy MC, Stone HJ. The Effect of Temperature and Mo Content on the Lattice Misfit of Model Ni-Based Superalloys. Metals. 2019; 9(6):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9060700
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoodfellow, Amy J., Lewis R. Owen, Katerina A. Christofidou, Joe Kelleher, Mark C. Hardy, and Howard J. Stone. 2019. "The Effect of Temperature and Mo Content on the Lattice Misfit of Model Ni-Based Superalloys" Metals 9, no. 6: 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9060700
APA StyleGoodfellow, A. J., Owen, L. R., Christofidou, K. A., Kelleher, J., Hardy, M. C., & Stone, H. J. (2019). The Effect of Temperature and Mo Content on the Lattice Misfit of Model Ni-Based Superalloys. Metals, 9(6), 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9060700