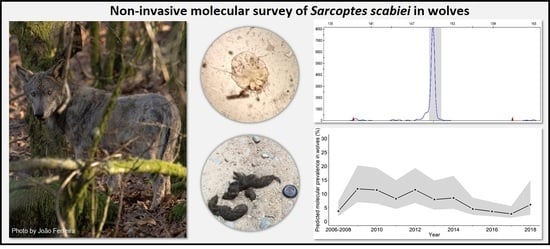
Non-Invasive Molecular Survey of Sarcoptic Mange in Wildlife: Diagnostic Performance in Wolf Faecal Samples Evaluated by Multi-Event Capture–Recapture Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Non-Invasive Molecular Method
2.2. Serology
2.3. Multi-Event Capture–Recapture Models
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Area
4.2. Molecular Screening of Faecal Samples
4.3. Collection of Invasive Samples for Serology
4.4. Serology
4.5. Statistical Analysis
4.6. Multi-Event Capture–Recapture Models
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niedringhaus, K.D.; Brown, J.D.; Sweeley, K.M.; Yabsley, M.J. A review of sarcoptic mange in North American wildlife. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 9, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kołodziej-Sobocińska, M.; Zalewski, A.; Kowalczyk, R. Sarcoptic mange vulnerability in carnivores of the Białowieża Primeval Forest, Poland: Underlying determinant factors. Ecol. Res. 2014, 29, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montecino-Latorre, D.; Cypher, B.L.; Rudd, J.L.; Clifford, D.L.; Mazet, J.A.K.; Foley, J.E. Assessing the role of dens in the spread, establishment and persistence of sarcoptic mange in an endangered canid. Epidemics 2019, 27, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleaga, A.; Casais, R.; Prieto, J.M.; Gortázar, C.; Balseiro, A. Comparative pathological and immunohistochemical features of sarcoptic mange in five sympatric wildlife species in Northern Spain. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2012, 58, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.M.; Fraser, T.A.; Lesku, J.A.; Simpson, K.; Roberts, G.L.; Garvey, J.; Polkinghorne, A.; Burridge, C.P.; Carver, S. The cascading pathogenic consequences of Sarcoptes scabiei infection that manifest in host disease. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 180018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Astorga, F.; Carver, S.; Almberg, E.S.; Sousa, G.R.; Wingfield, K.; Niedringhaus, K.D.; Van Wick, P.; Rossi, L.; Xie, Y.; Cross, P.; et al. International meeting on sarcoptic mange in wildlife, June 2018, Blacksburg, Virginia, USA. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soulsbury, C.D.; Iossa, G.; Baker, P.J.; Cole, N.C.; Funk, S.M.; Harris, S. The impact of sarcoptic mange Sarcoptes scabiei on the British fox Vulpes vulpes population. Mamm. Rev. 2007, 37, 278–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidson, R.K.; Bornstein, S.; Handeland, K. Long-term study of Sarcoptes scabiei infection in Norwegian red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) indicating host/parasite adaptation. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 156, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pence, D.B.; Windberg, L.A.; Pence, B.C.; Sprowls, R. The epizootiology and pathology of sarcoptic mange in coyotes, Canis latrans, from South Texas. J. Parasitol. 1983, 69, 1100–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pence, D.B.; Ueckermann, E. Sarcoptic mange in wildlife. OIE Rev. Sci. Tech. 2002, 21, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, J.F.; Mahoney, P.J.; Vickers, T.W.; Sikich, J.A.; Beier, P.; Riley, S.P.D.; Ernest, H.B.; Boyce, W.M. Extinction vortex dynamics of top predators isolated by urbanization. Ecol. Appl. 2019, 29, e01868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Waits, L.P.; Luikart, G. Noninvasive genetic sampling: Look before you leap. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1999, 14, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleaga, A.; Casais, R.; Balseiro, A.; Espí, A.; Llaneza, L.; Hartasánchez, A.; Gortázar, C. New techniques for an old disease: Sarcoptic mange in the Iberian wolf. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 181, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelone-Alasaad, S.; Molinar Min, A.R.; Pasquetti, M.; Alagaili, A.N.; D’Amelio, S.; Berrilli, F.; Obanda, V.; Gebely, M.A.; Soriguer, R.C.; Rossi, L. Universal conventional and real-time PCR diagnosis tools for Sarcoptes scabiei. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bornstein, S.; Frössling, J.; Näslund, K.; Zakrisson, G.; Mörner, T. Evaluation of a serological test (indirect ELISA) for the diagnosis of sarcoptic mange in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes). Vet. Dermatol. 2006, 17, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubek, E.B.; Mattsson, R.; Mörner, T.; Mattsson, J.G.; Gavier-Widén, D. Potential application of serological tests on fluids from carcasses: Detection of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii and Sarcoptes scabiei in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes). Acta Vet. Scand. 2012, 54, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haas, C.; Rossi, S.; Meier, R.; Ryser-Degiorgis, M.-P. Evaluation of a commercial ELISA for the detection of antibodies to Sarcoptes scabiei in wild boar (Sus scrofa). J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindsjö, J.; Fahlman, Å.; Törnqvist, E. Animal welfare from mouse to moose—Implementing the principles of the 3Rs in wildlife research. J. Wildl. Dis. 2016, 52, S65–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, N.; Rio-Maior, H.; Nakamura, M.; Roque, S.; Brandão, R.; Álvares, F. Characterization and minimization of the stress response to trapping in free-ranging wolves (Canis lupus): Insights from physiology and behavior. Stress 2017, 20, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, N.; Clifford, D.; Worth, S.J.; Serieys, L.E.K.; Foley, J. Development and validation of a fecal PCR assay for Notoedres cati and application to notoedric mange cases in bobcats (Lynx rufus) in Northern California, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2013, 49, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carricondo-Sanchez, D.; Odden, M.; Linnell, J.D.C.; Odden, J. The range of the mange: Spatiotemporal patterns of sarcoptic mange in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) as revealed by camera trapping. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, J.; Serieys, L.E.K.; Stephenson, N.; Riley, S.; Foley, C.; Jennings, M.; Wengert, G.; Vickers, W.; Boydston, E.; Lyren, L.; et al. A synthetic review of Notoedres species mites and mange. Parasitology 2016, 143, 1847–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltier, S.K.; Brown, J.D.; Ternent, M.A.; Fenton, H.; Niedringhaus, K.D.; Yabsley, M.J. Assays for detection and identification of the causative agent of mange in free-ranging black bears (Ursus americanus). J. Wildl. Dis. 2018, 54, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choquet, R.; Rouan, L.; Pradel, R. Program E-SURGE: A software application for fitting multievent models. In Modeling Demographic Processes in Marked Populations. Environmental and Ecological Statistics Series; Thomson, D.L., Cooch, E.G., Conroy, M.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 3, pp. 845–865. [Google Scholar]
- Pradel, R. Multievent: An extension of multistate capture-recapture models to uncertain states. Biometrics 2005, 61, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachish, S.; Knowles, S.C.L.; Alves, R.; Wood, M.J.; Sheldon, B.C. Infection dynamics of endemic malaria in a wild bird population: Parasite species-dependent drivers of spatial and temporal variation in transmission rates. J. Anim. Ecol. 2011, 80, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chambert, T.; Staszewski, V.; Lobato, E.; Choquet, R.; Carrie, C.; Mccoy, K.D.; Tveraa, T.; Boulinier, T. Exposure of black-legged kittiwakes to Lyme disease spirochetes: Dynamics of the immune status of adult hosts and effects on their survival. J. Anim. Ecol. 2012, 81, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapron, G.; Kaczensky, P.; Linnell, J.D.C.; von Arx, M.; Huber, D.; Andrén, H.; López-bao, J.V.; Adamec, M.; Álvares, F.; Anders, O.; et al. Recovery of large carnivores in Europe’s modern human-dominated landscapes. Science 2014, 346, 1517–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forchhammer, M.C.; Asferg, T. Invading parasites cause a structural shift in red fox dynamics. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2000, 267, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domínguez, G.; Espí, A.; Prieto, J.M.; De La Torre, J.A. Sarcoptic mange in Iberian wolves (Canis lupus signatus) in northern Spain. Vet. Rec. 2008, 162, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, J.; Gigliotti, F.; Darby, S.; Lapidge, S. Dying to be clean: Pen trials of novel cat and fox control devices. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2014, 60, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almberg, E.S.; Cross, P.C.; Dobson, A.P.; Smith, D.W.; Metz, M.C.; Stahler, D.R.; Hudson, P.J. Social living mitigates the costs of a chronic illness in a cooperative carnivore. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lower, K.S.; Medleau, L.M.; Hnilica, K.; Bigler, B. Evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbant assay (ELISA) for the serological diagnosis of sarcoptic mange in dogs. Vet. Dermatol. 2001, 12, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arlian, L.G.; Morgan, M.S. A review of Sarcoptes scabiei: Past, present and future. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, B.; Zimmermann, B.; Wabakken, P.; Bornstein, S.; Månsson, J.; Evans, A.L.; Liberg, O.; Sand, H.; Kindberg, J.; Ågren, E.O.; et al. Sarcoptic mange in the Scandinavian wolf Canis lupus population. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benaglia, T.; Chauveau, D.; Hunter, D.R.; Young, D.S. Mixtools: An R package for analyzing finite mixture models. J. Stat. Softw. 2009, 32, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peel, A.J.; McKinley, T.J.; Baker, K.S.; Barr, J.A.; Crameri, G.; Hayman, D.T.S.; Feng, Y.R.; Broder, C.C.; Wang, L.-F.; Cunningham, A.A.; et al. Use of cross-reactive serological assays for detecting novel pathogens in wildlife: Assessing an appropriate cutoff for henipavirus assays in African bats. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 193, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ades, A.E.; Price, M.J.; Kounali, D.; Akande, V.A.; Wills, G.S.; McClure, M.O.; Muir, P.; Horner, P.J. Proportion of tubal factor infertility due to Chlamydia: Finite mixture modeling of serum antibody titers. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 185, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Migchelsen, S.J.; Martin, D.L.; Southisombath, K.; Turyaguma, P.; Heggen, A.; Rubangakene, P.P.; Joof, H.; Makalo, P.; Cooley, G.; Gwyn, S.; et al. Defining seropositivity thresholds for use in trachoma elimination studies. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seck, M.C.; Badiane, A.S.; Thwing, J.; Moss, D.; Fall, F.B.; Gomis, J.F.; Deme, A.B.; Diongue, K.; Sy, M.; Mbaye, A.; et al. Serological data shows low levels of chikungunya exposure in Senegalese nomadic pastoralists. Pathogens 2019, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charlier, J.; Ghebretinsae, A.; Meyns, T.; Czaplicki, G.; Vercruysse, J.; Claerebout, E. Antibodies against Dictyocaulus viviparus major sperm protein in bulk tank milk: Association with clinical appearance, herd management and milk production. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 232, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Dam-Deisz, C.; Luttikholt, S.; Maas, M.; Nielen, M.; Swart, A.; Vellema, P.; van der Giessen, J.; Opsteegh, M. Risk factors related to Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence in indoor-housed Dutch dairy goats. Prev. Vet. Med. 2016, 124, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCandia, A.L.; Schrom, E.C.; Brandell, E.E.; Stahler, D.R.; vonHoldt, B.M. Sarcoptic mange severity is associated with reduced genomic variation and evidence of selection in Yellowstone National Park wolves (Canis lupus). Evol. Appl. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.L. Hormonal and immunological mechanisms mediating sex differences in parasite infection. Parasite Immunol. 2004, 26, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuk, M. The sicker sex. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, P.; Galaverni, M.; Ortega-Del Vecchyo, D.; Fan, Z.; Caniglia, R.; Fabbri, E.; Randi, E.; Wayne, R.K.; Godinho, R. Genomic evidence for the old divergence of Southern European wolf populations. Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20201206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio-Maior, H.; Nakamura, M.; Álvares, F.; Beja, P. Designing the landscape of coexistence: Integrating risk avoidance, habitat selection and functional connectivity to inform large carnivore conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 235, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.; López-Bao, J.V.; Llaneza, L.; Álvares, F.; Lopes, S.; Blanco, J.C.; Cortés, Y.; García, E.; Palacios, V.; Rio-Maior, H.; et al. Cryptic population structure reveals low dispersal in Iberian wolves. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rocha, R.G.; Magalhães, V.; López-Bao, J.V.; Van Der Loo, W.; Llaneza, L.; Alvares, F.; Esteves, P.J.; Godinho, R. Alternated selection mechanisms maintain adaptive diversity in different demographic scenarios of a large carnivore. BMC Evol. Biol. 2019, 19, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwensow, N.; Fietz, J.; Dausmann, K.H.; Sommer, S. Neutral versus adaptive genetic variation in parasite resistance: Importance of major histocompatibility complex supertypes in a free-ranging primate. Heredity 2007, 99, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pimenta, V.; Barroso, I.; Álvares, F.; Correia, J.; Ferrão da Costa, G.; Moreira, L.; Nascimento, J.; Petrucci-Fonseca, F.; Roque, S.; Santos, E. Situação populacional do Lobo em Portugal: Resultados do Censo Nacional 2002/2003; Techincal report; Instituto de Conservação da Natureza/Grupo Lobo: Lisboa, Portugal, 2005; 158p, Available online: http://www2.icnf.pt/portal/pn/biodiversidade/patrinatur/resource/docs/Mam/rel-lobo (accessed on 15 July 2020). (In Portuguese)
- Boitani, L.; Ciucci, P. Wolf management across Europe: Species conservation without boundaries. In A new Era for Wolves and People: Wolf Recovery, Human Attitudes and Policy; Musiani, M., Boitani, L., Paquet, P., Eds.; University of Calgary Press: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2009; pp. 15–39. [Google Scholar]
- IPMA Normas Climatológicas 1981–2010. Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera. Available online: http://www.ipma.pt/pt/oclima/normais.clima/ (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- INE Instituto Nacional de Estatística-Statistics Portugal. Available online: http://www.ine.pt (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Pimenta, V.; Barroso, I.; Boitani, L.; Beja, P. Risks a la carte: Modelling the occurrence and intensity of wolf predation on multiple livestock species. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 228, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvares, F.; Ferreira, C.C.; Barbosa, A.M.; Rosalino, L.M.; Pedroso, N.M.; Bencatel, J. Carnívoros. In Atlas de Mamíferos de Portugal, 2nd ed.; Bencatel, J., Sabino-Marques, H., Álvares, F., Moura, A.E., Barbosa, A.M., Eds.; Universidade de Évora: Évora, Portugal, 2019; pp. 66–99. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, M.; Godinho, R.; Rio-Maior, H.; Roque, S.; Kaliontzopoulou, A.; Bernardo, J.; Castro, D.; Lopes, S.; Petrucci-Fonseca, F.; Álvares, F. Evaluating the predictive power of field variables for species and individual molecular identification on wolf noninvasive samples. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2017, 63, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, A.C.; Pope, L.C.; Carpenter, P.J.; Roper, T.J.; Wilson, G.J.; Delahay, R.J.; Burke, T. Reliable microsatellite genotyping of the Eurasian badger (Meles meles) using faecal DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2003, 12, 1649–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boom, R.; Sol, C.J.A.; Salimans, M.M.M.; Jansen, C.L.; Wertheim-Van Dillen, P.M.E.; Van der Noordaa, J. Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. Cinical Microbiol. 1990, 28, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godinho, R.; López-Bao, J.V.; Castro, D.; Llaneza, L.; Lopes, S.; Silva, P.; Ferrand, N. Real-time assessment of hybridization between wolves and dogs: Combining noninvasive samples with ancestry informative markers. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blacket, M.J.; Robin, C.; Good, R.T.; Lee, S.F.; Miller, A.D. Universal primers for fluorescent labelling of PCR fragments—An efficient and cost-effective approach to genotyping by fluorescence. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikes, R.S.; Gannon, W.L. Guidelines of the American Society of Mammalogists for the use of wild mammals in research. J. Mammal. 2011, 92, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnadurai, S.K.; Strahl-Heldreth, D.; Fiorello, C.V.; Harms, C.A. Best-practice guidelines for field-based surgery and anesthesia of free-ranging wildlife. I. Anesthesia and analgesia. J. Wildl. Dis. 2016, 52, S14–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroglio, E.; Rossi, L.; Gennero, S. Lung-tissue extract as an alternative to serum for surveillance for brucellosis in chamois. Prev. Vet. Med. 2000, 43, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörner, T.; Sandström, G.; Mattsson, R. Comparison animals of serum and lung extracts for surveys of wild animals for antibodies to Francisella tularensis biovar palaearctica. J. Wildl. Dis. 1988, 24, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, J.E.; Frederick, C. merTools: Tools for Analyzing Mixed Effect Regression Models. R Package Version 0.2.1. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=merTools (accessed on 17 July 2020).
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H. lmerTest package: Tests in linear mixed effects models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2019. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 17 July 2020).
- Choquet, R.; Lebreton, J.D.; Gimenez, O.; Reboulet, A.M.; Pradel, R. U-CARE: Utilities for performing goodness of fit tests and manipulating CApture-REcapture data. Ecography 2009, 32, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovart, M.; Pradel, R. Transience effect in capture-recapture studies: The importance of its biological meaning. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model. Selection and Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]



| Variable | Samples (n) | β | Standard Error (β) | z-Score | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed effects | |||||
| Intercept | −2.710 | 0.399 | −6.801 | <0.001 | |
| Sex | |||||
| Male | 237 | 0.309 | 0.371 | 0.832 | 0.405 |
| Type of sampling | |||||
| Homesites | 286 | −0.317 | 0.440 | −0.721 | 0.471 |
| Random effect | |||||
| Variance | 0.519 | ||||
| Standard deviation | 0.721 | ||||
| Years (N) | 11 | ||||
| Samples (n) | 442 | ||||
| Variable | Samples (n) | β | Standard Error (β) | z-Score | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed effects | |||||
| Intercept | −1.199 | 0.600 | −1.999 | 0.046 | |
| Test matrix | |||||
| Lung tissue extract | 54 | −1.238 | 0.698 | −1.775 | 0.076 |
| Species | |||||
| Red fox | 20 | 0.582 | 0.749 | 0.777 | 0.437 |
| Random effect | |||||
| Variance | 1.023 | ||||
| Standard deviation | 1.012 | ||||
| Years (N) | 17 | ||||
| Samples (n) | 80 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rousseau, J.; Nakamura, M.; Rio-Maior, H.; Álvares, F.; Choquet, R.; Madeira de Carvalho, L.; Godinho, R.; Santos, N. Non-Invasive Molecular Survey of Sarcoptic Mange in Wildlife: Diagnostic Performance in Wolf Faecal Samples Evaluated by Multi-Event Capture–Recapture Models. Pathogens 2021, 10, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020243
Rousseau J, Nakamura M, Rio-Maior H, Álvares F, Choquet R, Madeira de Carvalho L, Godinho R, Santos N. Non-Invasive Molecular Survey of Sarcoptic Mange in Wildlife: Diagnostic Performance in Wolf Faecal Samples Evaluated by Multi-Event Capture–Recapture Models. Pathogens. 2021; 10(2):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020243
Chicago/Turabian StyleRousseau, Julieta, Mónia Nakamura, Helena Rio-Maior, Francisco Álvares, Rémi Choquet, Luís Madeira de Carvalho, Raquel Godinho, and Nuno Santos. 2021. "Non-Invasive Molecular Survey of Sarcoptic Mange in Wildlife: Diagnostic Performance in Wolf Faecal Samples Evaluated by Multi-Event Capture–Recapture Models" Pathogens 10, no. 2: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020243
APA StyleRousseau, J., Nakamura, M., Rio-Maior, H., Álvares, F., Choquet, R., Madeira de Carvalho, L., Godinho, R., & Santos, N. (2021). Non-Invasive Molecular Survey of Sarcoptic Mange in Wildlife: Diagnostic Performance in Wolf Faecal Samples Evaluated by Multi-Event Capture–Recapture Models. Pathogens, 10(2), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020243