Relationship between Latent Toxoplasmosis and Depression in Clients of a Center for Assisted Reproduction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of Sample
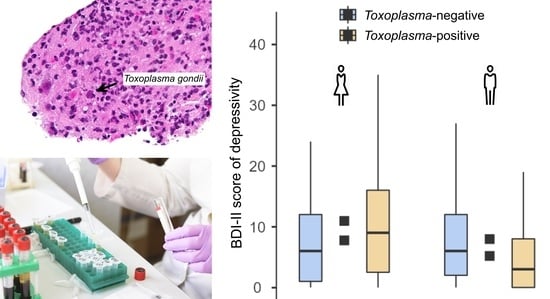
2.2. A Study of Depression in Women
2.3. A Study of Depression in Men
3. Discussion
Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Participants
4.2. Questionnaire BDI-II
4.3. Serological Testing for Toxoplasmosis
4.4. Fertility Assessment
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tenter, A.M.; Heckeroth, A.R.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasma Gondii: From Animals to Humans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1217–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, J.P.; Lindsay, D.S.; Speer, C.A. Structures of Toxoplasma Gondii Tachyzoites, Bradyzoites, and Sporozoites and Biology and Development of Tissue Cysts. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 267–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, J.P. Long-Term Persistence of Toxoplasma Gondii in Tissues of Pigs Inoculated with T. Gondii Oocysts and Effect of Freezing on Viability of Tissue Cysts in Pork. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1988, 49, 910–913. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Garcia, F.; Regadera, J.; Mayer, R.; Sanchez, S.; Nistal, M. Protozoan Infections in the Male Genital Tract. J. Urol. 1996, 156, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegr, J.; Havlíček, J. Changes in the Personality Profile of Young Women with Latent Toxoplasmosis. Folia Parasitol. 1999, 46, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Flegr, J.; Kodym, P.; Tolarová, V. Correlation of Duration of Latent Toxoplasma Gondii Infection with Personality Changes in Women. Biol. Psychol. 2000, 53, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegr, J.; Zitková, Š.; Kodym, P.; Frynta, D. Induction of Changes in Human Behaviour by the Parasitic Protozoan Toxoplasma Gondii. Parasitology 1996, 113 Pt 1, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindová, J.; Novotná, M.; Havlíček, J.; Jozífková, E.; Skallová, A.; Kolbeková, P.; Hodný, Z.; Kodym, P.; Flegr, J. Gender Differences in Behavioural Changes Induced by Latent Toxoplasmosis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindová, J.; Kuběna, A.A.; Šturcová, H.; Křivohlavá, R.; Novotná, M.; Rubesová, A.; Havlícek, J.; Kodym, P.; Flegr, J. Pattern of Money Allocation in Experimental Games Supports the Stress Hypothesis of Gender Differences in Toxoplasma Gondii-Induced Behavioural Changes. Folia Parasitol. 2010, 57, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flegr, J. Effects of Toxoplasma on Human Behavior. Schizophr. Bull. 2007, 33, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamal, A.M.; Kamal, A.M.; Abd El-Fatah, A.S.; Rizk, M.M.; Hassan, E.E. Latent Toxoplasmosis Is Associated with Depression and Suicidal Behavior. Arch. Suicide Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Esquivel, C.; Sánchez-Anguiano, L.F.; Hernández-Tinoco, J.; Berumen-Segovia, L.O.; Torres-Prieto, Y.E.; Estrada-Martínez, S.; Pérez-Álamos, A.R.; Ortiz-Jurado, M.N.; Molotla-de-León, G.; Beristain-García, I.; et al. Toxoplasma Gondii Infection and Depression: A Case-Control Seroprevalence Study. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 6, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Hussainy, N.H.; Al-Saedi, A.M.; Al-Lehaibi, J.H.; Al-Lehaibi, Y.A.; Al-Sehli, Y.M.; Afifi, M.A. Serological Evidences Link Toxoplasmosis with Schizophrenia and Major Depression Disorder. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2015, 3, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duffy, A.R.; Beckie, T.M.; Brenner, L.A.; Beckstead, J.W.; Seyfang, A.; Postolache, T.T.; Groer, M.W. Relationship between Toxoplasma Gondii and Mood Disturbance in Women Veterans. Mil. Med. 2015, 180, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Groër, M.W.; Yolken, R.H.; Xiao, J.; Beckstead, J.W.; Fuchs, D.; Mohapatra, S.S.; Seyfang, A.; Postolache, T.T. Prenatal Depression and Anxiety in Toxoplasma Gondii Positive Women. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 204, 433.e1–433.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suvisaari, J.; Torniainen-Holm, M.; Lindgren, M.; Härkänen, T.; Yolken, R.H. Toxoplasma Gondii Infection and Common Mental Disorders in the Finnish General Population. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 223, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flegr, J. Neurological and Neuropsychiatric Consequences of Chronic Toxoplasma Infection. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2015, 2, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, B.D.; Kruszon-Moran, D.; Jones, J.L. The Relationship between Toxoplasma Gondii Infection and Mood Disorders in the Third National Health and Nutrition Survey. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 72, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nayeri Chegeni, T.; Sharif, M.; Sarvi, S.; Moosazadeh, M.; Montazeri, M.; Aghayan, S.A.; Balalami, N.J.; Gholami, S.; Hosseininejad, Z.; Saberi, R.; et al. Is There Any Association between Toxoplasma Gondii Infection and Depression? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutterland, A.L.; Fond, G.; Kuin, A.; Koeter, M.W.J.; Lutter, R.; van Gool, T.; Yolken, R.; Szoke, A.; Leboyer, M.; de Haan, L. Beyond the Association. Toxoplasma Gondii in Schizophrenia, Bipolar Disorder, and Addiction: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2015, 132, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegr, J.; Prandota, J.; Sovičková, M.; Israili, Z.H. Toxoplasmosis--a Global Threat. Correlation of Latent Toxoplasmosis with Specific Disease Burden in a Set of 88 Countries. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rooney, K.L.; Domar, A.D. The Relationship between Stress and Infertility. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 20, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Diseases; 11th Revision (ICD-11); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, B.D.; Gold, L.; Feingold, T. The Experience and Influence of Infertility: Considerations for Couple Counselors. Fam. J. 2007, 15, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahzadeh, H.; Zareei Mahmood Abadi, H.; Momayyezi, M.; Malaki Moghadam, H.; Keyghobadi, N. The Comparison of Depression and Anxiety between Fertile and Infertile Couples: A Meta-Analysis Study. Int. J. Reprod. Biomed. 2019, 17, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayley, T.M.; Slade, P.; Lashen, H. Relationships between Attachment, Appraisal, Coping and Adjustment in Men and Women Experiencing Infertility Concerns. Hum. Reprod. Oxf. Engl. 2009, 24, 2827–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faramarzi, M.; Pasha, H.; Esmaelzadeh, S.; Jorsarai, G.; Mir, M.R.A.; Abedi, S. Is Coping Strategies Predictor of Anxiety and Depression in Couple Infertile? Health 2013, 5, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaňková, Š.; Flegr, J.; Calda, P. The Influence of Latent Toxoplasmosis on Women’s Reproductive Function: Four Cross-Sectional Studies. Folia Parasitol. 2015, 62, 041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Cui, L.; Zhao, J.; Dai, P.; Zong, S.; Zuo, W.; Chen, C.; Jin, H.; Gao, H.; Liu, Q. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma Gondii Infection in Female Sterility Patients in China. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 529–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tantawy, N.; Taman, A.; Shalaby, H. Toxoplasmosis and Female Infertility: Is There a Co-Relation? Am. J. Epidemiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 2, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-H.; Lu, Y.-J.; Wang, R.-B.; Song, L.-M.; Shi, F.; Gao, Q.-F.; Luo, Y.-F.; Gu, X.-F.; Wang, P. Survey of Infection of Toxoplasma Gondii in Infertile Couples in Suzhou Countryside. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue Natl. J. Androl. 2002, 8, 350–352. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, R.; Su, X.; Gao, X.; Liang, X. Toxoplasma Infection in Males with Sterility in Shenyang, China. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue Natl. J. Androl. 2005, 11, 503–504. [Google Scholar]
- Hlaváčová, J.; Flegr, J.; Řežábek, K.; Calda, P.; Kaňková, Š. Association between Latent Toxoplasmosis and Fertility Parameters of Men. Andrology 2021, 9, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegr, J. Predictors of Toxoplasma Gondii Infection in Czech and Slovak Populations: The Possible Role of Cat-Related Injuries and Risky Sexual Behavior in the Parasite Transmission. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kodym, P.; Malý, M.; Švandová, E.; Lekatková, H.; Badoutová, M.; Vlková, J.; Beneš, C.; Zástra, M. Toxoplasma in the Czech Republic 1923-1999: First Case to Widespread Outbreak. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Gaddi, P.J.; Yap, G.S. Cytokine Regulation of Immunopathology in Toxoplasmosis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2007, 85, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matowicka-Karna, J.; Dymicka-Piekarska, V.; Kemona, H. Does Toxoplasma Gondii Infection Affect the Levels of IgE and Cytokines (IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, and TNF-Alpha)? Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2009, 2009, 374696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaňková, Š.; Holáň, V.; Zajícová, A.; Kodym, P.; Flegr, J. Modulation of Immunity in Mice with Latent Toxoplasmosis--the Experimental Support for the Immunosuppression Hypothesis of Toxoplasma-Induced Changes in Reproduction of Mice and Humans. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deckert-Schlüter, M.; Buck, C.; Weiner, D.; Kaefer, N.; Rang, A.; Hof, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Schlüter, D. Interleukin-10 Downregulates the Intracerebral Immune Response in Chronic Toxoplasma Encephalitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 1997, 76, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.H.; Wille-Reece, U.; Dzierszinski, F.; Hunter, C.A. A Critical Role for IL-10 in Limiting Inflammation during Toxoplasmic Encephalitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2005, 165, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegr, J.; Preiss, M.; Balátová, P. Depressiveness and Neuroticism in Bartonella Seropositive and Seronegative Subjects-Preregistered Case-Controls Study. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flegr, J.; Hrdý, I. Influence of Chronic Toxoplasmosis on Some Human Personality Factors. Folia Parasitol. 1994, 41, 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, A.A.; Neale, J.M. New Measure of Daily Coping: Development and Preliminary Results. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1984, 46, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, M.; Shinn, M.; Mørch, H.; Huckabee, C.B. Gender Differences in Coping and Social Supports: Testing Socialization and Role Constraint Theories. J. Community Psychol. 1988, 16, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, C.S.; Scheier, M.F.; Weintraub, J.K. Assessing Coping Strategies: A Theoretically Based Approach. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1989, 56, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobfoll, S.E.; Dunahoo, C.L.; Ben-Porath, Y.; Monnier, J. Gender and Coping: The Dual-Axis Model of Coping. Am. J. Community Psychol. 1994, 22, 49–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.E.; Klein, L.C.; Lewis, B.P.; Gruenewald, T.L.; Gurung, R.A.; Updegraff, J.A. Biobehavioral Responses to Stress in Females: Tend-and-Befriend, Not Fight-or-Flight. Psychol. Rev. 2000, 107, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudielka, B.M.; Kirschbaum, C. Sex Differences in HPA Axis Responses to Stress: A Review. Biol. Psychol. 2005, 69, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preiss, M.; Vacíř, K. Beckova Sebeposuzovací Škála pro Dospělé; BDI-II Brno Psychodiagnostika: Brno, Czech Republic, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, A.T.; Steer, R.A.; Brown, G.K. Manual for the Beck Depression Inventory-II; Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Barnard, C.J.; Behnke, J.M. Parasitism and Host Behaviour; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Vyas, A.; Kim, S.-K.; Giacomini, N.; Boothroyd, J.C.; Sapolsky, R.M. Behavioral Changes Induced by Toxoplasma Infection of Rodents Are Highly Specific to Aversion of Cat Odors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6442–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skallová, A.; Kodym, P.; Frynta, D.; Flegr, J. The Role of Dopamine in Toxoplasma-Induced Behavioural Alterations in Mice: An Ethological and Ethopharmacological Study. Parasitology 2006, 133, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vyas, A.; Kim, S.-K.; Sapolsky, R.M. The Effects of Toxoplasma Infection on Rodent Behavior Are Dependent on Dose of the Stimulus. Neuroscience 2007, 148, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flegr, J.; Klapilová, K.; Kaňková, Š. Toxoplasmosis Can Be a Sexually Transmitted Infection with Serious Clinical Consequences. Not All Routes of Infection Are Created Equal. Med. Hypotheses 2014, 83, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlaváčová, J.; Flegr, J.; Řežábek, K.; Calda, P.; Kaňková, Š. Male-to-Female Presumed Transmission of Toxoplasmosis between Sexual Partners. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 190, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaňková, Š.; Hlaváčová, J.; Flegr, J. Oral Sex: A New, and Possibly the Most Dangerous, Route of Toxoplasmosis Transmission. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 141, 109725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbekova, P.; Kourbatova, E.; Novotna, M.; Kodym, P.; Flegr, J. New and Old Risk-Factors for Toxoplasma Gondii Infection: Prospective Cross-Sectional Study among Military Personnel in the Czech Republic. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. WHO Laboratory Manual for the Examination and Processing of Human Semen, 5th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; ISBN 978-92-4-154778-9. [Google Scholar]
- The Jamovi Project. Jamovi. (Version 1.6) [Computer Software]. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org (accessed on 9 June 2021).

| Women | Men | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| toxo-neg. | toxo-pos. | toxo-neg. | toxo-pos. | |
| N = 492 | N = 172 | N = 513 | N = 164 | |
| Mean age (SD) | 33.0 (4.9) | 34.0 (4.3) | 35.5 (5.4) | 36.1 (5.4) |
| Size of place of residence (no. of inhabitants) | ||||
| Up to 1000; N (%) | 64 (13.3) | 27 (16.1) | 79 (15.6) | 35 (21.6) |
| 1000–5000; N (%) | 69 (14.3) | 22 (13.1) | 59 (11.7) | 19 (11.7) |
| 5000–50,000; N (%) | 104 (21.6) | 36 (21.4) | 107 (21.2) | 31 (19.1) |
| 50,000–100,000; N (%) | 24 (5.0) | 7 (4.2) | 19 (3.8) | 10 (6.2) |
| 100,000–500,000; N (%) | 13 (2.7) | 1 (0.6) | 7 (1.4) | 8 (4.9) |
| Over 500,000; N (%) | 208 (43.2) | 75 (44.6) | 234 (46.3) | 59 (36.4) |
| Missing data | 10 | 4 | 8 | 2 |
| Level of education | ||||
| Highschool without graduation or lower; N (%) | 63 (13.0) | 26 (15.2) | 111 (21.8) | 43 (26.9) |
| Highschool with graduation; N (%) | 187 (38.7) | 65 (38.0) | 196 (38.4) | 67 (41.9) |
| University; N (%) | 233 (48.2) | 80 (46.8) | 203 (39.8) | 50 (31.3) |
| Missing data | 9 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| Smoking | ||||
| No; N (%) | 324 (76.8) | 121 (77.6) | 301 (70.5) | 94 (69.1) |
| Yes; N (%) | 98 (23.2) | 35 (22.4) | 126 (29.5) | 42 (30.9) |
| Missing data | 70 | 16 | 86 | 28 |
| Fertility disorder | ||||
| No; N (%) | 108 (32.0) | 38 (31.7) | 276 (58.1) | 80 (51.3) |
| Yes; N (%) | 229 (68.0) | 82 (68.3) | 199 (41.9) | 76 (48.7) |
| Missing data | 155 | 52 | 38 | 8 |
| Women | Men | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean | SD | Tau | Cohen’s d | p | N | Mean | SD | Tau | Cohen’s d | p | |
| Toxo-pos. | 172 | 9.4 | 9.2 | 0.018 | 0.06 | 0.494 | 164 | 5.9 | 6.4 | −0.075 | 0.25 | 0.003 |
| Toxo-neg. | 492 | 8.8 | 8.3 | 513 | 7.4 | 7.4 | ||||||
| Fertile | 146 | 8.6 | 8.5 | 0.053 | 0.16 | 0.089 | 356 | 6.7 | 6.7 | 0.028 | 0.09 | 0.295 |
| Infertile | 311 | 9.7 | 9.1 | 275 | 7.2 | 7.3 | ||||||
| Fertile, toxo-pos. | 38 | 10.9 | 9.4 | 0.145 | 0.48 | 0.010 | 80 | 5.9 | 6.1 | −0.48 | 0.16 | 0.173 |
| Fertile, toxo-neg. | 108 | 7.8 | 8.1 | 276 | 6.9 | 6.8 | ||||||
| Infertile, toxo-pos. | 82 | 10.0 | 9.5 | 0.014 | 0.03 | 0.717 | 76 | 5.2 | 5.9 | −0.152 | 0.48 | <0.001 |
| Infertile, toxo-neg. | 229 | 9.6 | 9.0 | 199 | 8.0 | 7.7 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hlaváčová, J.; Flegr, J.; Fiurašková, K.; Kaňková, Š. Relationship between Latent Toxoplasmosis and Depression in Clients of a Center for Assisted Reproduction. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081052
Hlaváčová J, Flegr J, Fiurašková K, Kaňková Š. Relationship between Latent Toxoplasmosis and Depression in Clients of a Center for Assisted Reproduction. Pathogens. 2021; 10(8):1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081052
Chicago/Turabian StyleHlaváčová, Jana, Jaroslav Flegr, Kateřina Fiurašková, and Šárka Kaňková. 2021. "Relationship between Latent Toxoplasmosis and Depression in Clients of a Center for Assisted Reproduction" Pathogens 10, no. 8: 1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081052
APA StyleHlaváčová, J., Flegr, J., Fiurašková, K., & Kaňková, Š. (2021). Relationship between Latent Toxoplasmosis and Depression in Clients of a Center for Assisted Reproduction. Pathogens, 10(8), 1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10081052