Inflammatory Response in Caco-2 Cells Stimulated with Anisakis Messengers of Pathogenicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Parasite Samples and Identification
2.2. EVs-Enriched Fraction Characterization
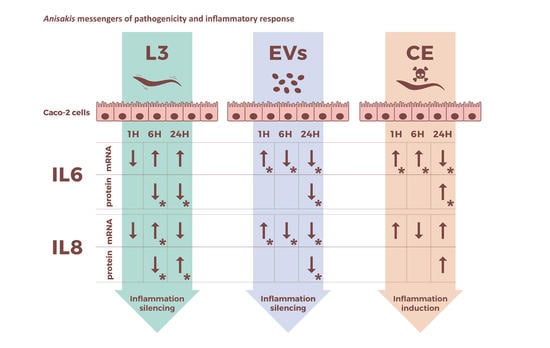
2.3. Intestinal Epithelial Cells’ Response to Live L3 Actions
2.4. Intestinal Epithelial Response to Anisakis EVs
2.5. Intestinal Epithelial Cells’ Response to Anisakis Crude Extract
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Parasites Sampling
4.2. Crude Extract
4.3. Isolation and EVs-Enriched Fraction Characterization
4.4. Cell Culture and Challenging Experiments
4.5. Cytokines’ Measurements
4.6. Relative Quantification of Gene Expression by Real-Time PCR Analyses
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klimpel, S.; Palm, H.W. Anisakid Nematode (Ascaridoidea) Life Cycles and Distribution: Increasing Zoonotic Potential in the Time of Climate Change? In Progress in Parasitology; Parasitology Research Monographs, 2; Mehlhorn, H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Panel EFSA. On biological hazards (BIOHAZ) scientific opinion on risk assessment of parasites in fishery products. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1543. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, W.; Elsheikha, H.M. Biology, Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Selected Fish-borne Parasitic Zoonoses. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2021, 30, 297–309. [Google Scholar]
- Audicana, M.T.; Ansotegui, I.J.; de Corres, L.F.; Kennedy, M.W. Anisakis simplex: Dangerous-dead and alive? Trends Parasitol. 2002, 18, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arizono, N.; Yamada, M.; Tegoshi, T.; Yoshikawa, M. Anisakis simplex sensu stricto and Anisakis pegreffii: Biological characteristics and pathogenetic potential in human anisakiasis. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrabar, J.; Trumbić, Z.; Bočina, I.; Buselić, I.; Vrbatović, A.; Mladineo, I. Interplay between proinflammatory cytokines, miRNA, and tissue lesions in Anisakis-infected Sprague-Dawley rats. PLoS Negl. Trop Dis. 2019, 13, e0007397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audicana, M.T.; Kennedy, M.W. Anisakis simplex: From obscure infectious worm to inducer of immune hypersensitivity. Clin. Microb. Rev. 2008, 21, 360–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuizen, N.E.; Lopata, A.L. Anisakis—A food-borne parasite that triggers allergic host defences. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amelio, S.; Lombardo, F.; Pizzarelli, A.; Bellini, I.; Cavallero, S. Advances in Omic Studies Drive Discoveries in the Biology of Anisakid Nematodes. Genes 2020, 11, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, J.; Murata, R.; Kodo, Y. Current Status of Anisakiasis and Anisakis Larvae in Tokyo, Japan. Food Saf. 2021, 9, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiucci, S.; Palomba, M.; Cavallero, S.; D’Amelio, S. Anisakiasis. In Helminth Infections and Their Impact on Global Public Health, 2nd ed; Bruschi, F., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 451–495. [Google Scholar]
- Jerončić, A.; Nonković, D.; Vrbatović, A.; Hrabar, J.; Bušelić, I.; Martínez-Sernández, V.; Rocamonde, S.A.L.; Ubeira, F.M.; Jaman, S.; Jeličić, E.Č.; et al. Anisakis Sensitization in the Croatian fish processing workers: Behavioral instead of occupational risk factors? PLoS Negl. Trop Dis. 2020, 14, e0008038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yera, H.; Fréalle, É.; Dutoit, E.; Dupouy-Camet, J. A national retrospective survey of anisakidosis in France (2010–2014): Decreasing incidence, female predominance, and emerging allergic potential. Parasite 2018, 25, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrador, Z.; Daschner, Á.; Perteguer, M.J.; Benito, A. Epidemiological Scenario of Anisakidosis in Spain Based on Associated Hospitalizations: The Tip of the Iceberg. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallero, S.; Martini, A.; Migliara, G.; De Vito, C.; Iavicoli, S.; D’Amelio, S. Anisakiasis in Italy: Analysis of hospital discharge records in the years 2005–2015. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, M.; Pierce, G.J.; Pascual, S.; González-Muñoz, M.; Mattiucci, S.; Mladineo, I.; Cipriani, P.; Bušelić, I.; Strachan, J.C. Assessing the risk of an emerging zoonosis of worldwide concern: Anisakiasis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surapaitoon, A.; Suttiprapa, S.; Mairiang, E.; Khuntikeo, N.; Pairojkul, C.; Bethony, J.; Brindley, P.J.; Sripa, B. Subsets of Inflammatory Cytokine Gene Polymorphisms are Associated with Risk of Carcinogenic Liver Fluke Opisthorchis viverrini-Associated Advanced Periductal Fibrosis and Cholangiocarcinoma. Korean J. Parasitol. 2017, 55, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dematei, A.; Fernandes, R.; Soares, R.; Alves, H.; Richter, J.; Botelho, M.C. Angiogenesis in Schistosoma haematobium-associated urinary bladder cancer. APMIS 2017, 125, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.S.; Pak, J.H.; Kim, J.B.; Bahk, Y.Y. Clonorchis sinensis, an oriental liver fluke, as a human biological agent of cholangiocarcinoma: A brief review. BMB Rep. 2016, 49, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoda, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Ozeki, K.; Inoye, H.; Toda, S.; Maehara, Y. An Anisakis larva attached to early gastric cancer: Report of a case. Surg. Today 2015, 45, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, Y.; Ando, K.; Usui, M.; Sugiyama, H.; Hayashi, A.; Tanemura, A.; Kuriyama, N.; Kishiwada, M.; Mizuno, S.; Sakurai, H.; et al. A case of hepatic anisakiasis caused by Pseudoterranova decipiens mimicking metastatic liver cancer. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, R.; Hashida, H.; Uryuhara, K.; Kaihara, S. Hepatic anisakiasis mimicking metastatic liver tumour. Int. J. Surg. 2019, 60, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of colorectal cancer: Incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2019, 14, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibinu, I.E.; Smooker, P.M.; Lopata, A.L. Anisakis Nematodes in Fish and Shellfish- from infection to allergies. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 6, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petithory, J.C.; Paugam, B.; Buyet-Rousset, P.; Paugam, A. Anisakis simplex, a cofactor of gastric cancer? Lancet 1990, 336, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineta, S.; Shimanuki, K.; Sugiura, A.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Kaneko, M.; Sugiyama, Y.; Akimaru, K.; Tajiri, T. Chronic anisakiasis of the ascending colon associated with carcinoma. J. Nippon. Med. Sch. 2006, 73, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Perez, J.C.; Rodríguez-Perez, R.; Ballestero, A.; Zuloaga, J.; Fernandez-Puntero, B.; Arias-Díaz, J.; Caballero, M.L. Previous Exposure to the Fish Parasite Anisakis as a Potential Risk Factor for Gastric or Colon Adenocarcinoma. Medicine 2015, 94, e1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coakley, G.; Maizels, R.M.; Buck, A.H. Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles: The New Communicators in Parasite Infections. Trends Parasitol. 2015, 31, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.P.; Fromm, B.; Andersen, S.D.; Marcilla, A.; Andersen, K.L.; Borup, A.; Williams, A.R.; Jex, A.R.; Gasser, R.B.; Young, N.D.; et al. Exploration of extracellular vesicles from Ascaris suum provides evidence of parasite–host cross talk. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1578116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenberger, R.M.; Hasanuzzaman Talukder, M.D.; Field, M.A.; Wangchuk, P.; Giacomin, P.; Loukas, A.; Sotillo, J. Characterization of Trichuris muris secreted proteins and extracellular vesicles provides new insights into host–parasite communication. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1428004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliminejad, K.; Khorram Khorshid, H.R.; Soleymani Fard, S.; Ghaffari, S.H. An overview of microRNAs: Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 5451–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, A.; Coakley, G.; Simbari, F.; McSorley, H.J.; Quintana, J.F.; Le Bihan, T.; Kumar, S.; Abreu-Goodger, C.; Lear, M.; Harcus, Y.; et al. Exosomes secreted by nematode parasites transfer small RNAs to mammalian cells and modulate innate immunity. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, A.; Hansen, E.P.; Andersen, S.D.; Williams, A.R.; Nejsum, P. Immunomodulation by Helminths: Intracellular Pathways and Extracellular Vesicles. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, C.M.; Pizzo, F.; Santulli, A.; Bušelić, I.; Boban, M.; Orhanović, S.; Mladineo, I. Anisakis pegreffii (Nematoda: Anisakidae) products modulate oxidative stress and apoptosis-related biomarkers in human cell lines. Parasit Vectors 2016, 9, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoletano, C.; Mattiucci, S.; Colantoni, A.; Battisti, F.; Zizzari, I.G.; Rahimi, H.; Nuti, M.; Rughetti, A. Anisakis pegreffii impacts differentiation and function of human dendritic cells. Parasite Immunol. 2018, 40, e12527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speciale, A.; Trombetta, D.; Saija, A.; Panebianco, A.; Giarratana, F.; Ziino, G.; Minciullo, P.L.; Cimino, F.; Gangemi, S. Exposure to Anisakis extracts can induce inflammation on in vitro cultured human colonic cells. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 2471–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, T. Caco-2 Cell Line. In The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Models; Verhoeckx, K., Cotter, P., López-Expósito, I., Kleiveland, C., Lea, T., Mackie, A., Requena, T., Swiatecka, D., Wichers, H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bautista, D.; Rodríguez, L.S.; Franco, M.A.; Angel, J.; Barreto, A. Caco-2 cells infected with rotavirus release extracellular vesicles that express markers of apoptotic bodies and exosomes. Cell Stress Chaperones 2015, 20, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosi, C.; Pompili, M.; Scribano, D.; Limongi, D.; Petrucca, A.; Cannavacciuolo, S. The Shigella flexneri OspB effector: An early immunomodulator. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 305, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyadet, S.; Smout, M.; Johnson, M.; Whitchurch, C.; Turnbull, L.; Kaewkes, S.; Sotillo, J.; Loukas, A.; Sripa, B. Excretory/secretory products of the carcinogenic liver fluke are endocytosed by human cholangiocytes and drive cell proliferation and IL6 production. Int. J. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma’ayeh, S.Y.; Knörr, L.; Sköld, K.; Garnham, A.; Ansell, B.R.E.; Jex, A.R.; Svard, S.G. Responses of the Differentiated Intestinal Epithelial Cell Line Caco-2 to Infection with the Giardia intestinalis GS Isolate. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carballeda-Sangiao, N.; Sánchez-Alonso, I.; Navas, A.; Arcos, S.C.; de Palencia, P.F.; Careche, M.; González-Muñoz, M. Anisakis simplex products impair intestinal epithelial barrier function and occludin and zonula occludens-1 localisation in differentiated Caco-2 cells. PLoS Negl. Trop Dis. 2020, 14, e0008462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, H.; Debnath, B.; Neamati, N. Role of the CXCL8-CXCR1/2 Axis in Cancer and Inflammatory Diseases. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.A. Directing transition from innate to acquired immunity: Defining a role for IL-6. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 3463–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodero, M.; Cuéllar, C. Modulation by Anisakis simplex antigen of inflammatory response generated in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 90, 107241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora, V.; Andreu-Ballester, J.C.; Rodero, M.; Cuéllar, C. Anisakis simplex: Immunomodulatory effects of larval antigens on the activation of Toll like Receptors. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 100, 1567–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.O.; Jeon, C.H.; Nam, U.H.; Subramaniyam, S.; Yoo, S.I.; Park, J.H. Comparative transcriptome analyses of the third and fourth stage larvae of Anisakis simplex (Nematoda: Anisakidae). Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2018, 226, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochanowski, M.; Dąbrowska, J.; Różycki, M.; Sroka, J.; Karamon, J.; Bełcik, A.; Korpysa-Dzirba, W.; Cencek, T. Proteomic Profiling and In Silico Characterization of the Secretome of Anisakis simplex Sensu Stricto L3 Larvae. Pathogens 2022, 11, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrdana, F.; Buchmann, K. Excretory/secretory products of anisakid nematodes: Biological and pathological roles. Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, H.; Lambrecht, B.N. Barrier Epithelial Cells and the Control of Type 2 Immunity. Immunity 2015, 43, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, F.; Kuhring, M.; Radonić, A.; Midha, A.; Renard, B.Y.; Hartmann, S. Silent Witness: Dual-Species Transcriptomics Reveals Epithelial Immunological Quiescence to Helminth Larval Encounter and Fostered Larval Development. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo, V.; Arrieta, I.; Tuñon, T.; Cortegano, I.; Gomez, B.; Cárdaba, B. Immunopathogenesis of human gastrointestinal infection by Anisakis simplex. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 104, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drurey, C.; Lindholm, H.T.; Coakley, G.; Poveda, M.C.; Löser, S.; Doolan, R.; Gerbe, F.; Jay, P.; Harris, N.; Oudhoff, M.J.; et al. Intestinal epithelial tuft cell induction is negated by a murine helminth and its secreted products. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20211140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coakley, G.; McCaskill, J.L.; Borger, J.G.; McSorley, H.J.; Maizels, R.M.; Buck, A.H. Extracellular Vesicles from a Helminth Parasite Suppress Macrophage Activation and Constitute an Effective Vaccine for Protective Immunity. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1545–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, A.; Bennuru, S.; Tariq, S.; Kaur, S.; Wu, W.; Elkahloun, A.G.; Arakelyan, A.; Shaik, J.; Dorward, D.W.; Nutman, T.B.; et al. Extracellular vesicles released from the filarial parasite Brugia malayi downregulate the host mTOR pathway. PLoS Negl. Trop Dis. 2021, 15, e0008884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysen, A.T.; Whitehead, B.; Stensballe, A.; Carnerup, A.; Nylander, T.; Nejsum, P. Fluorescent Labeling of Helminth Extracellular Vesicles Using an In Vivo Whole Organism. Approach Biomed. 2020, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallero, S.; Bellini, I.; Pizzarelli, A.; Arcà, B.; D’Amelio, S. A miRNAs catalogue from third-stage larvae and extracellular vesicles of Anisakis pegreffii provides new clues for host-parasite interplay. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, J.A.; Bhargava, A.; Ferraz, J.G.; Yates, R.M.; Beck, P.L.; Buret, A.G. Giardia duodenalis cathepsin B proteases degrade intestinal epithelial interleukin-8 and attenuate interleukin-8-induced neutrophil chemotaxis. Infect Immun. 2014, 82, 2772–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcuera, M.T.; Rodríguez-Bobada, C.; Zuloaga, J.; Gómez-Aguado, F.; Rodríguez-Perez, R.; Mendizabal, Á.; González, P.; Arias-Díaz, J.; Caballero, M.L. Exploring tumourigenic potential of the parasite Anisakis: A pilot study. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3127–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brindley, P.J.; Loukas, A. Helminth infection–induced malignancy. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, F.H.; Rossi, A.G.; Sharkey, R.; Brown, A.P.; Pritchard, D.I.; Maizels, R.M. Ascaris suum-Derived Products Induce Human Neutrophil Activation via a G Protein-Coupled Receptor That Interacts with the Interleukin-8 Receptor Pathway. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 4007–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amelio, S.; Mathiopoulos, K.D.; Santos, C.P.; Pugachev, O.N.; Webb, S.C.; Picanço, M.; Paggi, L. Genetic markers in ribosomal DNA for the identification of members of the genus Anisakis (Nematoda: Ascaridoidea) defined by polymerase-chain-reaction-based restriction fragment length polymorphism. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiucci, S.; Colantoni, A.; Crisafi, B.; Mori-Ubaldini, F.; Caponi, L.; Fazii, P.; Nascetti, G.; Bruschi, F. IgE sensitization to Anisakis pegreffii in Italy: Comparison of two methods for the diagnosis of allergic anisakiasis. Parasite Immunol. 2017, 39, e12440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bellini, I.; Scribano, D.; Sarshar, M.; Ambrosi, C.; Pizzarelli, A.; Palamara, A.T.; D’Amelio, S.; Cavallero, S. Inflammatory Response in Caco-2 Cells Stimulated with Anisakis Messengers of Pathogenicity. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101214
Bellini I, Scribano D, Sarshar M, Ambrosi C, Pizzarelli A, Palamara AT, D’Amelio S, Cavallero S. Inflammatory Response in Caco-2 Cells Stimulated with Anisakis Messengers of Pathogenicity. Pathogens. 2022; 11(10):1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101214
Chicago/Turabian StyleBellini, Ilaria, Daniela Scribano, Meysam Sarshar, Cecilia Ambrosi, Antonella Pizzarelli, Anna Teresa Palamara, Stefano D’Amelio, and Serena Cavallero. 2022. "Inflammatory Response in Caco-2 Cells Stimulated with Anisakis Messengers of Pathogenicity" Pathogens 11, no. 10: 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101214
APA StyleBellini, I., Scribano, D., Sarshar, M., Ambrosi, C., Pizzarelli, A., Palamara, A. T., D’Amelio, S., & Cavallero, S. (2022). Inflammatory Response in Caco-2 Cells Stimulated with Anisakis Messengers of Pathogenicity. Pathogens, 11(10), 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101214