Rabies Virus Variants Detected from Cougar (Puma concolor) in Mexico 2000–2021
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Rabies Virus Diagnosis
2.2. Antigenic Characterization
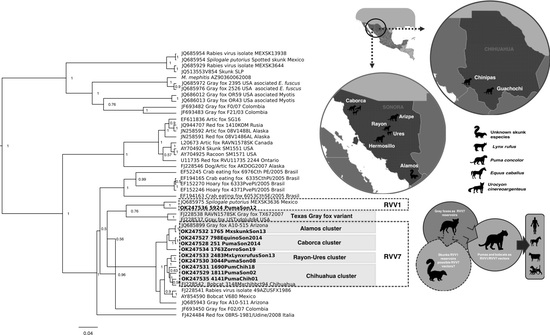
2.3. Genetic Characterization
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Samples
4.2. Caborca Case Note (2014)
4.3. Rabies Virus Diagnosis
4.4. Antigenic Characterization
4.5. RT-PCR and Partial N-Gene Sequencing
4.6. Sequencing
4.7. Phylogenetic Reconstruction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franka, R.; Smith, T.G.; Dyer, J.L.; Wu, X.; Niezgoda, M.; Rupprecht, C.E. Current and future tools for global canine rabies elimination. Antivir. Res. 2013, 100, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aréchiga-Ceballos, N.; Puebla-Rodríguez, P.; Aguilar-Setién, A. The new face of human rabies in Mexico, what’s next after eradicating rabies in dogs. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Villa, A.; Orciari, L.A.; Juárez-Islas, V.; Gómez-Sierra, M.; Padilla-Medina, I.; Flisser, A.; Souza, V.; Castillo, A.; Franka, R.; Escalante-Mañe, M.; et al. Molecular diversity of rabies viruses associated with bats in Mexico and other countries of the Americas. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1697–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Mattos, C.C.; De Mattos, C.A.; Loza-Rubio, E.; Aguilar-Setién, A.; Orciari, L.A.; Smith, J.S. Molecular characterization of rabies virus isolates from Mexico: Implications for transmission dynamics and human risk. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 61, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Procuraduría Federal de Proteccion al Ambiente (México). Mamíferos en México (Primera Parte). Available online: https://www.gob.mx/profepa/articulos/mamiferos-en-mexico-primera-parte?idiom=es (accessed on 4 December 2021).
- Velasco-Villa, A.; Mauldin, M.R.; Shi, M.; Escobar, L.E.; Gallardo-Romero, N.F.; Damon, I.; Olson, V.A.; Streicker, D.G.; Emerson, G. The history of rabies in the Western Hemisphere. Antivir. Res. 2017, 146, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aréchiga-Ceballos, N.; Velasco-Villa, A.; Shi, M.; Flores-Chávez, S.; Barrón, B.; Cuevas-Domínguez, E.; González-Origel, A.; Aguilar-Setién, A. New rabies virus variant found during an epizootic in white-nosed coatis from the Yucatan Peninsula. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 1586–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Villa, A.; Messenger, S.L.; Orciari, L.A.; Niezgoda, M.; Blanton, J.D.; Fukagawa, C.; Rupprecht, C.E. New rabies virus variant in Mexican immigrant. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1906–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés-Ayala, F.; Aréchiga-Ceballos, N.; Ortiz-Alcántara, J.M.; González-Durán, E.; Pérez-Agüeros, S.I.; Méndez-Tenorio, A.; Torres-Longoria, B.; López-Martínez, I.; Hernández-Rivas, L.; Díaz-Quiñonez, J.A.; et al. Molecular characterization of atypical antigenic variants of canine rabies virus reveals its reintroduction by wildlife vectors in southeastern Mexico. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3629–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, M.; Rosas, O.; Ríos, J.D.J.; García, N. Análisis comparativo de la alimentación del gato montés (Lynx rufus) en dos diferentes ambientes de México. Acta Zool. Mex. 2002, 87, 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Secretaría de Salud, Mexico. Guía Para La Atención Médica Y Antirrábica De La Persona Expuesta Al Virus De La Rabia. 2018. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/salud/cenaprece/documentos/guia-para-la-atencion-medica-y-antirrabica-de-la-persona-expuesta-al-virus-de-la-rabia-182293?fbclid=IwAR3z9MBOqRCLZwZ9C_HlX74e8QBh6QG98x0Wwb_Q1TGtH_lczSbtmBXZN14 (accessed on 27 January 2022).
- PAHO SIRVERA, PANAFTOSA. Regional Information System for Epidemiological Surveillance of Rabies. 2021. Available online: https://sirvera.panaftosa.org.br (accessed on 27 January 2022).
- Krebs, J.W.; Williams, S.M.; Smith, J.S.; Rupprecht, C.E.; Childs, J.E. Rabies among infrequently reported mammalian carnivores in the United States, 1960-2000. J. Wildl. Dis. 2003, 39, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crawford-Miksza, L.K.; Wadford, D.A.; Schnurr, D.P. Molecular epidemiology of enzootic rabies in California. J. Clin. Virol. 1999, 14, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, I.V.; Shi, M.; Orciari, L.A.; Yager, P.A.; Velasco-Villa, A.; Kuzmina, N.A.; Streicker, D.G.; Bergman, D.L.; Rupprecht, C.E. Molecular inferences suggest multiple host shifts of rabies viruses from bats to mesocarnivores in Arizona during 2001–2009. PLoS Pathog 2012, 8, e1002786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colorado Department of Public Health & Environment Rabid Animals by County and Species. Available online: https://cdphe.colorado.gov/rabid-animals-by-county-and-species-2020 (accessed on 9 January 2022).
- Gilbert, A.T. Rabies virus vectors and reservoir species. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2018, 37, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.; Freuling, C.M. Rabies in terrestrial animals. In Rabies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 195–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worsley-Tonks, K.E.L.; Escobar, L.E.; Biek, R.; Castaneda-Guzman, M.; Craft, M.E.; Streicker, D.G.; White, L.A.; Fountain-Jones, N.M. Using host traits to predict reservoir host species of rabies virus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, J.W.; Mandel, E.J.; Swerdlow, D.L.; Rupprecht, C.E. Rabies surveillance in the United States during 2003. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 225, 1837–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veals, A.M.; Koprowski, J.L.; Bergman, D.L.; VerCauteren, K.C.; Wester, D.B. Occurrence of mesocarnivores in montane sky islands: How spatial and temporal overlap informs rabies management in a regional hotspot. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffin, A.W. From roadkill to road ecology: A review of the ecological effects of roads. J. Transp. Geogr. 2007, 15, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plowright, R.K.; Parrish, C.R.; McCallum, H.; Hudson, P.J.; Ko, A.I.; Graham, A.L.; Lloyd-Smith, J.O. Pathways to zoonotic spillover. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, L.J.; Wesley, C.L.; Owen, R.D.; Goodin, D.G.; Koch, D.; Jonsson, C.B.; Chu, Y.K.; Shawn Hutchinson, J.M.; Paige, R.L. A habitat-based model for the spread of hantavirus between reservoir and spillover species. J. Theor. Biol. 2009, 260, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollentze, N.; Streicker, D.G.; Murcia, P.R.; Hampson, K.; Biek, R. Virulence mismatches in index hosts shape the outcomes of cross-species transmission. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 28859–28866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, C.E.; Hanlon, C.A.; Slate, D. Oral vaccination of wildlife against rabies: Opportunities and challenges in prevention and control. Dev. Biol. 2004, 119, 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- Cliquet, F.; Picard-Meyer, E.; Mojzis, M.; Dirbakova, Z.; Muizniece, Z.; Jaceviciene, I.; Mutinelli, F.; Matulova, M.; Frolichova, J.; Rychlik, I.; et al. In-Depth Characterization of Live Vaccines Used in Europe for Oral Rabies Vaccination of Wildlife. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mollentze, N.; Biek, R.; Streicker, D.G. The role of viral evolution in rabies host shifts and emergence. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 8, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- CITES. Evaluation of the Situation of the Populations of Bobcat (Lynx rufus) in Mexico. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth Meeting of the Animals Committee Geneva (Switzerland), Geneva, Switzerland, 20–24 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Velasco-Villa, A.; Gómez-Sierra, M.; Hernández-Rodríguez, G.; Juárez-Islas, V.; Meléndez-Félix, A.; Vargas-Pino, F.; Velázquez-Monroy, O.; Flisser, A. Antigenic diversity and distribution of rabies virus in Mexico. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Velasco-Villa, A.; Orciari, L.A.; Souza, V.; Juárez-Islas, V.; Gomez-Sierra, M.; Castillo, A.; Flisser, A.; Rupprecht, C.E. Molecular epizootiology of rabies associated with terrestrial carnivores in Mexico. Virus Res. 2005, 111, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.S. New aspects of rabies with emphasis on epidemiology, diagnosis, and prevention of the disease in the United States. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 9, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.S.; Orciari, L.A.; Yager, P.A.; Seidel, H.D.; Warner, C.K. Epidemiologic and historical relationships among 87 rabies virus isolates as determined by limited sequence analysis. J. Infect. Dis. 1992, 166, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohde, R.E.; Neill, S.U.; Clark, K.A.; Smith, J.S. Molecular epidemiology of rabies epizootics in Texas. Clin. Diagn. Virol. 1997, 8, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.A.; Neill, S.U.; Smith, J.S.; Wilson, P.J.; Whadford, V.W.; McKirahan, G.W. Epizootic canine rabies transmitted by coyotes in south Texas. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1994, 204, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Monroe, B.P.; Yager, P.; Blanton, J.; Birhane, M.G.; Wadhwa, A.; Orciari, L.; Petersen, B.; Wallace, R. Rabies surveillance in the United States during 2014. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2016, 248, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dean, D.J.; Abelseth, M.K.; Atanasiu, W. The fluorescent antibody test. In Laboratory Techniques in Rabies; Meslin, F.-X., Kaplan, M.M., Koprowski, H., Eds.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; pp. 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.S. Rabies virus epitopic variation: Use in ecologic studies. Adv. Virus Res. 1989, 36, 215–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, A.M.; Papo, S.; Rodriguez, A.; Smith, J.S. Antigenic analysis of rabies-virus isolates from Latin America and the Caribbean. Zent. Vet. B 1994, 41, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQuiston, J.H.; Yager, P.A.; Smith, J.S.; Rupprecht, C.E. Epidemiologic characteristics of rabies virus variants in dogs and cats in the United States, 1999. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 218, 1939–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markotter, W.; Kuzmin, I.; Rupprecht, C.E.; Randles, J.; Sabeta, C.T.; Wandeler, A.I.; Nel, L.H. Isolation of Lagos bat virus from water mongoose. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1913–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murray, P.R.; Baron, E.J.; Pfaller, M.A.; Tenover, F.C.; Yolken, R.H.; Morgan, D.R. Manual of Clinical Microbiology (6th edn). Trends Microbiol. 1995, 3, 449. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posada, D. ModelTest Server: A web-based tool for the statistical selection of models of nucleotide substitution online. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W700–W703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Case | Year | Locality | State | Species | Antigenic Rabies Virus Variant | GenBank Sequence Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4141 | 2001 | Guachochi | Chihuahua | Puma concolor | RVV7 | OK247535 |
| 1811 | 2002 | Hermosillo | Sonora | Puma concolor | RVV7 | OK247529 |
| 3044 | 2008 | Rayon | Sonora | Puma concolor | RVV7 | OK247530 |
| 5924 | 2012 | Arizpe | Sonora | Puma concolor | RVV1 | OK247536 |
| 1765 | 2013 | Alamos | Sonora | Skunk | RVV7 | OK247532 |
| 2483 | 2013 | Ures | Sonora | Lynx rufus | RVV7 | OK247533 |
| 251 | 2014 | Caborca | Sonora | Puma concolor | RVV7 | OK247528 |
| 798 | 2014 | Caborca | Sonora | Equus caballus | RVV7 | OK247527 |
| 1690 | 2018 | Chinipas | Chihuahua | Puma concolor | RVV7 | OK247531 |
| 1763 | 2019 | Caborca | Sonora | Urocyon cinereoargenteus | RVV7 | OK247534 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcés-Ayala, F.; Aguilar-Setién, Á.; Almazán-Marín, C.; Cuautle-Zavala, C.; Chávez-López, S.; Martínez-Solís, D.; Gómez-Sierra, M.; Sandoval-Borja, A.; Escamilla-Ríos, B.; López-Martínez, I.; et al. Rabies Virus Variants Detected from Cougar (Puma concolor) in Mexico 2000–2021. Pathogens 2022, 11, 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020265
Garcés-Ayala F, Aguilar-Setién Á, Almazán-Marín C, Cuautle-Zavala C, Chávez-López S, Martínez-Solís D, Gómez-Sierra M, Sandoval-Borja A, Escamilla-Ríos B, López-Martínez I, et al. Rabies Virus Variants Detected from Cougar (Puma concolor) in Mexico 2000–2021. Pathogens. 2022; 11(2):265. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020265
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcés-Ayala, Fabiola, Álvaro Aguilar-Setién, Cenia Almazán-Marín, Claudia Cuautle-Zavala, Susana Chávez-López, David Martínez-Solís, Mauricio Gómez-Sierra, Albert Sandoval-Borja, Beatriz Escamilla-Ríos, Irma López-Martínez, and et al. 2022. "Rabies Virus Variants Detected from Cougar (Puma concolor) in Mexico 2000–2021" Pathogens 11, no. 2: 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020265
APA StyleGarcés-Ayala, F., Aguilar-Setién, Á., Almazán-Marín, C., Cuautle-Zavala, C., Chávez-López, S., Martínez-Solís, D., Gómez-Sierra, M., Sandoval-Borja, A., Escamilla-Ríos, B., López-Martínez, I., & Aréchiga-Ceballos, N. (2022). Rabies Virus Variants Detected from Cougar (Puma concolor) in Mexico 2000–2021. Pathogens, 11(2), 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11020265