Core Genome Multilocus Sequence Typing for Food Animal Source Attribution of Human Campylobacter jejuni Infections
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MLST and cgMLST Diversity Indices
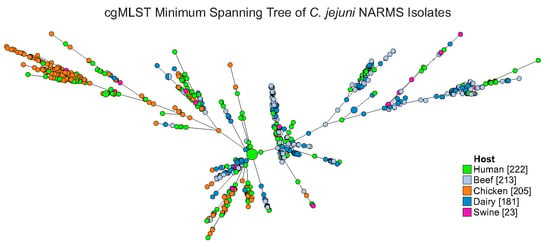
2.2. Typing Schema and Source Attribution
2.3. Validation of Typing Schema
2.4. Antimicrobial Resistance Genotypes and cgMLST
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Sequencing
4.2. Traditional Multilocus Sequence Typing
4.3. Core Genome MLST
4.4. Hierarchical Clustering of cgMLST Data
4.5. Analysis of Population Composition
4.6. Identification of Antimicrobial Resistance Genotypes
4.7. PorA Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tack, D.M.; Marder, E.P.; Griffin, P.M.; Cieslak, P.R.; Dunn, J.; Hurd, S.; Scallan, E.; Lathrop, S.; Muse, A.; Ryan, P. Preliminary incidence and trends of infections with pathogens transmitted commonly through food—Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network, 10 US sites, 2015–2018. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Ed.; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Campylobacter. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/campylobacter (accessed on 3 January 2020).
- Fischer, G.H.; Paterek, E. Campylobacter. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gallo, M.T.; Di Domenico, E.G.; Toma, L.; Marchesi, F.; Pelagalli, L.; Manghisi, N.; Ascenzioni, F.; Prignano, G.; Mengarelli, A.; Ensoli, F. Campylobacter jejuni fatal sepsis in a patient with Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Case report and literature review of a difficult diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusulja, M.; Santini, M.; Margetić, K.; Guzvinec, M.; Šoprek, S.; Butić, I.; Tambić Andrašević, A. Meningitis caused by Campylobacter jejuni: A case presentation and literature review. Acta Clin. Belg. 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, T.; Kon, T.; Kurihara, A.-I.; Tomiyama, M. Unilateral oculomotor nerve palsy following Campylobacter infection: A mild form of Miller Fisher syndrome without ataxia. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 2929–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- St Charles, J.; Bell, J.; Gadsden, B.; Malik, A.; Cooke, H.; Van de Grift, L.; Kim, H.; Smith, E.; Mansfield, L. Guillain Barré Syndrome is induced in Non-Obese Diabetic (NOD) mice following Campylobacter jejuni infection and is exacerbated by antibiotics. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 77, 11–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouhani, S.; Griffin, N.W.; Yori, P.P.; Olortegui, M.P.; Siguas Salas, M.; Rengifo Trigoso, D.; Moulton, L.H.; Houpt, E.R.; Barratt, M.J.; Kosek, M.N.; et al. Gut microbiota features associated with Campylobacter burden and postnatal linear growth deficits in a Peruvian birth cohort. Eur. PMC 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thépault, A.; Méric, G.; Rivoal, K.; Pascoe, B.; Mageiros, L.; Touzain, F.; Rose, V.; Béven, V.; Chemaly, M.; Sheppard, S.K. Genome-wide identification of host-segregating epidemiological markers for source attribution in Campylobacter jejuni. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e03085–e030816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thépault, A.; Rose, V.; Queguiner, M.; Chemaly, M.; Rivoal, K. Dogs and Cats: Reservoirs for Highly Diverse Campylobacter jejuni and a Potential Source of Human Exposure. Animals 2020, 10, 838. [Google Scholar]
- Mourkas, E.; Florez-Cuadrado, D.; Pascoe, B.; Calland, J.K.; Bayliss, S.C.; Mageiros, L.; Méric, G.; Hitchings, M.D.; Quesada, A.; Porrero, C. Gene pool transmission of multidrug resistance among Campylobacter from livestock, sewage and human disease. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 4597–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beauchamp, J.M.; Leveque, R.M.; Dawid, S.; DiRita, V.J. Methylation-dependent DNA discrimination in natural transformation of Campylobacter jejuni. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8053–E8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Sánchez, L.; Melero, B.; Jaime, I.; Hänninen, M.-L.; Rossi, M.; Rovira, J. Campylobacter jejuni survival in a poultry processing plant environment. Food Microbiol. 2017, 65, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Zhu, W. Characterising the bacterial microbiota across the gastrointestinal tracts of dairy cattle: Membership and potential function. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- FDA. National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System-Enteric Bacteria (NARMS): 2007 Executive Report; Department of Health and Human Services, US FDA: Rockville, MD, USA, 2010.
- Hänninen, M.-L.; Pajarre, S.; Klossner, M.-L.; Rautelin, H. Typing of Human Campylobacter jejuniIsolates in Finland by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 1787–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tyson, G.H.; Tate, H.P.; Abbott, J.; Tran, T.-T.; Kabera, C.; Crarey, E.; Young, S.; McDERMOTT, P.F.; Sprague, G.; Campbell, M. Molecular subtyping and source attribution of Campylobacter isolated from food animals. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 1891–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyhs, U.; Katzav, M.; Isohanni, P.; Heiska, H.; Maijala, R. The temporal, PFGE and resistance pattern associations suggest that poultry products are only a minor source of human infections in western Finland. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughini Gras, L.; Smid, J.H.; Wagenaar, J.A.; de Boer, A.G.; Havelaar, A.H.; Friesema, I.H.; French, N.P.; Busani, L.; van Pelt, W. Risk factors for campylobacteriosis of chicken, ruminant, and environmental origin: A combined case-control and source attribution analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Giannatale, E.; Garofolo, G.; Alessiani, A.; Di Donato, G.; Candeloro, L.; Vencia, W.; Decastelli, L.; Marotta, F. Tracing back clinical Campylobacter jejuni in the Northwest of Italy and assessing their potential source. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.V.; Kimball, T.J.; Bennett, P.; Johnson, Y.; Wakely, D.; Nolan, C.M. Campylobacter jejuni enteritis associated with raw goat’s milk. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1987, 126, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System: Enteric Bacteria; NARMS Integrated Report: 2012–2013; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2013.
- Korczak, B.M.; Zurfluh, M.; Emler, S.; Kuhn-Oertli, J.; Kuhnert, P. Multiplex strategy for multilocus sequence typing, fla typing, and genetic determination of antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolates collected in Switzerland. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 1996–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ragimbeau, C.; Colin, S.; Devaux, A.; Decruyenaere, F.; Cauchie, H.-M.; Losch, S.; Penny, C.; Mossong, J. Investigating the host specificity of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli by sequencing gyrase subunit A. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovanen, S.; Rossi, M.; Pohja-Mykrä, M.; Nieminen, T.; Raunio-Saarnisto, M.; Sauvala, M.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Hänninen, M.-L.; Kivistö, R. Population genetics and characterization of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from western jackdaws and game birds in Finland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02365–e023618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosner, B.M.; Schielke, A.; Didelot, X.; Kops, F.; Breidenbach, J.; Willrich, N.; Gölz, G.; Alter, T.; Stingl, K.; Josenhans, C. A combined case-control and molecular source attribution study of human Campylobacter infections in Germany, 2011–2014. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gripp, E.; Hlahla, D.; Didelot, X.; Kops, F.; Maurischat, S.; Tedin, K.; Alter, T.; Ellerbroek, L.; Schreiber, K.; Schomburg, D. Closely related Campylobacter jejuni strains from different sources reveal a generalist rather than a specialist lifestyle. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ravel, A.; Hurst, M.; Petrica, N.; David, J.; Mutschall, S.K.; Pintar, K.; Taboada, E.N.; Pollari, F. Source attribution of human campylobacteriosis at the point of exposure by combining comparative exposure assessment and subtype comparison based on comparative genomic fingerprinting. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frazão, M.R.; de Souza, R.A.; Medeiros, M.I.C.; da Silva Duque, S.; Cao, G.; Allard, M.W.; Falcão, J.P. Molecular typing of Campylobacter jejuni strains: Comparison among four different techniques. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2020, 51, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietzka, A. Expert Opinion on the Introduction of Next-Generation Typing Methods for Food-and Waterborne Diseases in the EU and EEA; ECDC: Solna, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nadon, C.; Van Walle, I.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Campos, J.; Chinen, I.; Concepcion-Acevedo, J.; Gilpin, B.; Smith, A.M.; Kam, K.M.; Perez, E. PulseNet International: Vision for the implementation of whole genome sequencing (WGS) for global food-borne disease surveillance. Eurosurveillance 2017, 22, 30544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cody, A.J.; Bray, J.E.; Jolley, K.A.; McCarthy, N.D.; Maiden, M.C. Core genome multilocus sequence typing scheme for stable, comparative analyses of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli human disease isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2086–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Llarena, A.-K.; Taboada, E.; Rossi, M. Whole-genome sequencing in epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahin, O.; Fitzgerald, C.; Stroika, S.; Zhao, S.; Sippy, R.J.; Kwan, P.; Plummer, P.J.; Han, J.; Yaeger, M.J.; Zhang, Q. Molecular evidence for zoonotic transmission of an emergent, highly pathogenic Campylobacter jejuni clone in the United States. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dearlove, B.L.; Cody, A.J.; Pascoe, B.; Méric, G.; Wilson, D.J.; Sheppard, S.K. Rapid host switching in generalist Campylobacter strains erodes the signal for tracing human infections. ISME J. 2016, 10, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wegener, H.C. Antibiotics in animal feed and their role in resistance development. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Yan, M.; Sahin, O.; Pereira, S.; Chang, Y.-J.; Zhang, Q. Effect of macrolide usage on emergence of erythromycin-resistant Campylobacter isolates in chickens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1678–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hao, H.; Dai, M.; Wang, Y.; Peng, D.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, Z. 23S rRNA mutation A2074C conferring high-level macrolide resistance and fitness cost in Campylobacter jejuni. Microb. Drug Resist. 2009, 15, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.; Pu, S.; Wang, F.; Meng, J.; Ge, B. Fitness cost of macrolide resistance in Campylobacter jejuni. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 34, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luangtongkum, T.; Shen, Z.; Seng, V.W.; Sahin, O.; Jeon, B.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Q. Impaired fitness and transmission of macrolide-resistant Campylobacter jejuni in its natural host. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- USADA. FSIS Cecal Sampling under the National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS) Surveillance Program; USADA: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inouye, M.; Dashnow, H.; Raven, L.-A.; Schultz, M.B.; Pope, B.J.; Tomita, T.; Zobel, J.; Holt, K.E. SRST2: Rapid genomic surveillance for public health and hospital microbiology labs. Genome Med. 2014, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Sergeant, M.J.; Luhmann, N.; Vaz, C.; Francisco, A.P.; Carriço, J.A.; Achtman, M. GrapeTree: Visualization of core genomic relationships among 100,000 bacterial pathogens. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kittl, S.; Heckel, G.; Korczak, B.M.; Kuhnert, P. Source attribution of human Campylobacter isolates by MLST and fla-typing and association of genotypes with quinolone resistance. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feldgarden, M.; Brover, V.; Haft, D.H.; Prasad, A.B.; Slotta, D.J.; Tolstoy, I.; Tyson, G.H.; Zhao, S.; Hsu, C.-H.; McDermott, P.F. Validating the AMRFinder tool and resistance gene database by using antimicrobial resistance genotype-phenotype correlations in a collection of isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00483–e004819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Periaswamy, B.; Sahin, O.; Yaeger, M.; Plummer, P.; Zhai, W.; Shen, Z.; Dai, L.; Chen, S.L.; Zhang, Q. Point mutations in the major outer membrane protein drive hypervirulence of a rapidly expanding clone of Campylobacter jejuni. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10690–10695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madeira, F.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Buso, N.; Gur, T.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Basutkar, P.; Tivey, A.R.; Potter, S.C.; Finn, R.D. The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W636–W641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Typing Scheme | Schema Diversity | Number of Groups Generated | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Groups Identified * | Simpson’s D.I. | Beef | Chicken | Dairy | Human | Swine | |
| MLST | 174 | 0.963 | 33 | 54 | 34 | 64 | 16 |
| cgMLST200 | 197 | 0.964 | 38 | 102 | 40 | 87 | 18 |
| cgMLST100 | 298 | 0.983 | 73 | 131 | 68 | 103 | 22 |
| cgMLST50 | 422 | 0.991 | 115 | 150 | 107 | 122 | 22 |
| cgMLST25 | 543 | 0.997 | 149 | 168 | 141 | 145 | 23 |
| cgMLST10 | 652 | 0.999 | 175 | 187 | 162 | 156 | 23 |
| cgMLST5 | 734 | 0.999 | 196 | 196 | 173 | 175 | 23 |
| cgMLST0 | 828 | 1 | 211 | 205 | 180 | 216 | 23 |
| Sequence a,b,c | cgMLST200-12 vs. MLST-8 d | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 170- | * * * * * * * * * * * | −209 | Conserved residues |
| NCTC11168 | FMAAEQGADLLEHSNISTTS NQAPFKVDSVGNLY | Reference sequence | |
| N48272F | FMAEEQGADLLGKST ISTTQKAAPFQADSLGNLY | 55:53 | SA clonal sequence |
| N43804F | FMAEEQGADLLGKST ISIT QKAAPFQADSLGNLY | 1:1 | Substitution not in SA loci |
| N45191FR | FMAEEQGT DLLGKST ISTTQKAAPFQADSLGNLY | 1:1 | Substitution not in SA loci |
| N46355F | FMAEEQGADLLGKSTISTT QKAAPFQTNSLGNLY | 1:1 | Substitution in SA loci |
| N49694F | FMEKEQ I S DLVG SNSSTFNVDSI GNLY | 16:16 | Deletion and substitutions in SA loci |
| N44409F | FMAAEQSS DLVG ANGSAFKVDSI ENLY | 1:1 | Deletion and substitutions in SA loci |
| N45200F | FMAKEQGSDLVG ANGSAFNVDSIGNLY | 1:1 | Deletion and substitutions in SA loci |
| Strain ID | MLST | cgMLST200 | cgMLST5 | cgMLST0 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group ID | Source * | Group ID | Source | Group ID | Source | Group ID | Source | |
| N46804F | 982 | B,D,H | 28 | B,C,D,H,S | 57 | D,H | 250 | D |
| SRR5217159 | 982 | B,D,H | 28 | B,C,D,H,S | 57 | D,H | 754 | H |
| N45809F | 982 | B,D,H | 28 | B,C,D,H,S | 209 | D,H | 209 | D |
| SRR5878335 | 982 | B,D,H | 28 | B,C,D,H,S | 209 | D,H | 826 | H |
| N48272F | 8 | B,C,D,H,S | 12 | B,C,D,H,S | 223 | D,H | 291 | D |
| SRR2970498 | 8 | B,C,D,H,S | 12 | B,C,D,H,S | 223 | D,H | 528 | H |
| N50152F | 806 | B,D,H,S | 18 | B,D,H,S | 362 | B,H | 362 | B |
| SRR5604241 | 806 | B,D,H,S | 18 | B,D,H,S | 362 | B,H | 806 | H |
| SRR5152202 | 50 | C,D,H | 100 | C,D,H | 400 | C,H | 719 | C |
| SRR1794080 | 50 | C,D,H | 100 | C,D,H | 400 | C,H | 400 | H |
| SRR2075414 | 45 | B,C,D,H,S | 407 | C,H | 407 | C,H | 407 | C |
| SRR3029056 | 45 | B,C,D,H,S | 407 | C,H | 407 | C,H | 407 | H |
| SRR2094236 | 353 | C,D,H | 412 | C,H | 412 | C,H | 412 | C |
| SRR2182579 | 353 | C,D,H | 412 | C,H | 412 | C,H | 444 | H |
| SRR3092138 | 52 | C,H,S | 510 | C,H,S | 512 | S,H | 822 | S |
| SRR5754156 | 52 | C,H,S | 510 | C,H,S | 512 | S,H | 551 | H |
| SRR5152177 | 2083 | C,H | 584 | C,H | 593 | C,H | 714 | C |
| SRR5932391 | 2083 | C,H | 584 | C,H | 593 | C,H | 833 | H |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, C.-H.; Harrison, L.; Mukherjee, S.; Strain, E.; McDermott, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, S. Core Genome Multilocus Sequence Typing for Food Animal Source Attribution of Human Campylobacter jejuni Infections. Pathogens 2020, 9, 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9070532
Hsu C-H, Harrison L, Mukherjee S, Strain E, McDermott P, Zhang Q, Zhao S. Core Genome Multilocus Sequence Typing for Food Animal Source Attribution of Human Campylobacter jejuni Infections. Pathogens. 2020; 9(7):532. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9070532
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Chih-Hao, Lucas Harrison, Sampa Mukherjee, Errol Strain, Patrick McDermott, Qijing Zhang, and Shaohua Zhao. 2020. "Core Genome Multilocus Sequence Typing for Food Animal Source Attribution of Human Campylobacter jejuni Infections" Pathogens 9, no. 7: 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9070532
APA StyleHsu, C. -H., Harrison, L., Mukherjee, S., Strain, E., McDermott, P., Zhang, Q., & Zhao, S. (2020). Core Genome Multilocus Sequence Typing for Food Animal Source Attribution of Human Campylobacter jejuni Infections. Pathogens, 9(7), 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9070532