Design, Analysis and Testing of a New Compliant Compound Constant-Force Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
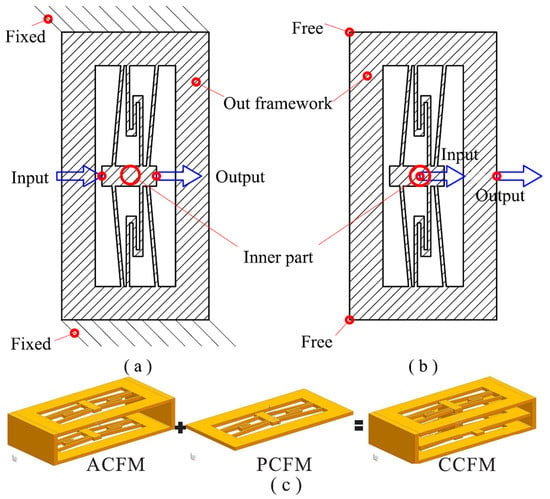
2. Mechanical Design
2.1. Schematic Design
2.2. Analytical Modeling
2.3. Parametric Study
3. Simulation Study with FEA
3.1. Static Structural Results of Constant-Force Test
3.2. Stress Analysis Results
3.3. Modal Analysis Results
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Experimental Results
4.3. Further Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howell, L.L. Compliant Mechanisms; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lobontiu, N. Compliant Mechanisms: Design of Flexure Hinges; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q. Design and Implementation of Large-Range Compliant Micropositioning Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, W. Analysis of the displacement of distributed compliant parallel-guiding mechanism considering parasitic rotation and deflection on the guiding plate. Mech. Mach. Theory 2014, 80, 151–165. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Qu, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J. A compliant dual-axis gripper with integrated position and force sensing. Mechatronics 2017, 47, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q. Micromachines for Biological Micromanipulation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Shim, J.; Lee, D.Y. A compact vertical scanner for atomic force microscopes. Sensors 2010, 10, 10673–10682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q. Robust impedance control of a compliant microgripper for high-speed position/force regulation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Han, Y.; Kim, J.; Cheong, C. Force tracking control of a flexible gripper featuring shape memory alloy actuators. Mechatronics 2001, 11, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herder, J.L.; Van Den Berg, F.P.A. Statically balanced compliant mechanisms (SBCMs), an example and prospects. In Proceedings of the Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computer in Engineering Conference DETC2000/MECH-14144, Baltimore, MD, USA, 10–13 September 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Tolman, K.A.; Merriam, E.G.; Howell, L.L. Compliant constant-force linear-motion mechanism. Mech. Mach. Theory 2016, 106, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Hao, G. Nonlinear behaviour design using the kinematic singularity of a general type of double-slider four-bar linkage. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 129, 106–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanaty, M.; Vardi, I.; Henein, S. Programmable multistable mechanisms: Synthesis and modeling. J. Mech. Des. 2018, 140, 042301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Chen, F.; Gao, F.; Yang, M.; Sun, L.; Du, Z.; Tang, J.; Zhang, D. Development and analysis of a bridge-lever-type displacement amplifier based on hybrid flexure hinges. Precis. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xu, Q. Design and testing of a flexure-based constant-force stage for biological cell micromanipulation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2018, 15, 1114–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y. A compliant constant-force mechanism for adaptive robot end-effector operations. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–8 May 2010; pp. 2131–2136. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, L.; Magleby, S. Substantially Constant-Force Exercise Machine. U.S. Patent 20040198571A1, 7 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Q. Design and Control of a Novel Compliant Constant-Force Gripper Based on Buckled Fixed-Guided Beams. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 2017, 22, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrella, A.; Brennan, M.; Kovacic, I.; Waters, T. On the force transmissibility of a vibration isolator with quasi-zero-stiffness. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 322, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacic, I.; Brennan, M.J.; Waters, T.P. A study of a nonlinear vibration isolator with a quasi-zero stiffness characteristic. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 315, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrella, A.; Brennan, M.; Waters, T.; Shin, K. On the design of a high-static–low-dynamic stiffness isolator using linear mechanical springs and magnets. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 315, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Liu, K. A tunable high-static–low-dynamic stiffness vibration isolator. J. Sound Vib. 2010, 329, 1254–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.T.; Badami, V.G.; Dale, J.S.; Xu, Y. Elliptical flexure hinges. Rev Sci Instrum. 1997, 68, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseytlin, Y.M. Notch flexure hinges: an effective theory. Rev Sci Instrum. 2002, 73, 3363–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verotti, M. Effect of initial curvature in uniform flexures on position accuracy. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 119, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verotti, M. Analysis of the center of rotation in primitive flexures: Uniform cantilever beams with constant curvature. Mech. Mach. Theory 2016, 97, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.T.; Wang, D.A. A constant-force bistable mechanism for force regulation and overload protection. Mech. Mach. Theory 2011, 46, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xu, Q. Design of a flexure-based constant-force XY precision positioning stage. Mech. Mach. Theory 2017, 108, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.A.; Chen, J.H.; Pham, H.T. A constant-force bistable micromechanism. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 189, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chang, H.; Li, G. Design of Constant-Force Compliant Sarrus Mechanism Considering Stiffness Nonlinearity of Compliant Joints. In Advances in Reconfigurable Mechanisms and Robots II; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Xu, Q. Design and modeling of constant-force mechanisms: A survey. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 119, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q. Design of a Large-Stroke Bistable Mechanism for the Application in Constant-Force Micropositioning Stage. J. Mech. Robot. 2017, 9, 011006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lan, C. A constant-force compliant gripper for handling objects of various sizes. J. Mech. Des. 2014, 136, 071008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Q. Design and analysis of a constant-force parallel micro-gripper. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Macau, China, 5–8 December 2017; pp. 1112–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Q. Design and Analysis of a Compound Constant-Force Mechanism for Compliant Gripper. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Manipulation, Automation and Robotics at Small Scales (MARSS), Nagoya, Japan, 4–8 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Jia, J.; He, X.; Wang, H. Post-buckling and snap-through behavior of inclined slender beams. J. Appl. Mech. 2008, 75, 041020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABSplus. Available online: http://www.stratasys.com/materials/search/absplus (accessed on 19 September 2018).
- Linß, S.; Gräser, P.; Räder, T.; Henning, S.; Theska, R.; Zentner, L. Influence of geometric scaling on the elasto-kinematic properties of flexure hinges and compliant mechanisms. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 125, 220–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, U.; Lovasz, E.C.; Zichner, M.; Modler, N.; Comsa, A.; Modler, K.H. Synthesis of PR/RP-chain based compliant mechanisms: Design of applications exploiting fibre reinforced material characteristics. Mach. Sci. 2015, 6, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 1040 kg/m3 |
| Poisson ratio | 0.394 |
| Young’s modulus | 2.2 GPa |
| Yield strength | 25 MPa |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| 19 mm | |
| 8 mm | |
| 19 mm | |
| L | 30 mm |
| 1 mm | |
| 2 mm | |
| 5° |
| Mode | Value (Hz) |
|---|---|
| First mode | 46.7 |
| Second mode | 85.0 |
| Third mode | 85.7 |
| Fourth mode | 115.4 |
| Fifth mode | 150.0 |
| Sixth mode | 201.3 |
| Method | Value (N) | Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical model | 9.0 | 12.5% |
| FEA simulation | 8.9 | 11.3% |
| Experimental study | 8.0 | - |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Xu, Q. Design, Analysis and Testing of a New Compliant Compound Constant-Force Mechanism. Actuators 2018, 7, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/act7040065
Zhang X, Wang G, Xu Q. Design, Analysis and Testing of a New Compliant Compound Constant-Force Mechanism. Actuators. 2018; 7(4):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/act7040065
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaozhi, Guangwei Wang, and Qingsong Xu. 2018. "Design, Analysis and Testing of a New Compliant Compound Constant-Force Mechanism" Actuators 7, no. 4: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/act7040065
APA StyleZhang, X., Wang, G., & Xu, Q. (2018). Design, Analysis and Testing of a New Compliant Compound Constant-Force Mechanism. Actuators, 7(4), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/act7040065