mRNA Sequencing Reveals Upregulation of Glutathione S-Transferase Genes during Acanthamoeba Encystation
Abstract
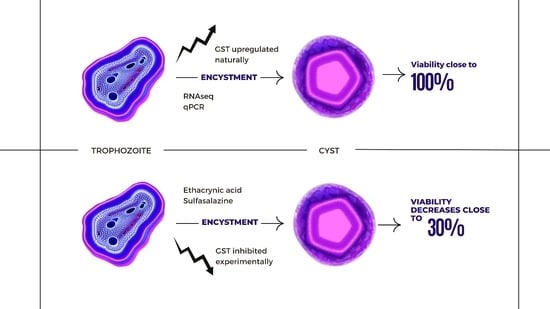
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acanthamoeba Cell Culture
2.2. Encystation and RNA Extraction
2.3. mRNA Sequencing
2.4. Differential Expression Analysis
2.5. qPCR Expression Analysis
2.6. Glutathione S-Transferase (GST) Inhibitors
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinez, A.J. Is Acanthamoeba encephalitis an opportunistic infection? Neurology 1980, 30, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visvesvara, G.S. Amebic meningoencephalitides and keratitis: Challenges in diagnosis and treatment. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 23, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Khan, N.A.; Walochnik, J. An update on Acanthamoeba keratitis: Diagnosis, pathogenesis and treatment. Parasite 2015, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Martín-Navarro, C.M.; López-Arencibia, A.; Arnalich-Montiel, F.; Piñero, J.E.; Valladares, B. Acanthamoeba keratitis: An emerging disease gathering importance worldwide? Trends Parasitol. 2013, 29, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitsch, D.; Köhsler, M.; Marchetti-Deschmann, M.; Deutsch, A.; Allmaier, G.; Duchêne, M.; Walochnik, J. Major role for cysteine proteases during the early phase of Acanthamoeba castellanii encystment. Eukaryot. Cell 2010, 9, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, E.K.; Chung, D.I.; Hong, Y.C.; Ahn, T.I.; Kong, H.H. Acanthamoeba castellanii: Gene profile of encystation by ESTs analysis and KOG assignment. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 119, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, E.K.; Chung, D.I.; Hong, Y.C.; Kong, H.H. Autophagy protein 8 mediating autophagosome in encysting Acanthamoeba. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2009, 168, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.M.; Han, B.I.; Moon, E.K.; Lee, Y.R.; Yu, H.S.; Jha, B.K.; Danne, D.B.S.; Kong, H.H.; Chung, D.I.; Hong, Y. Autophagy protein 16-mediated autophagy is required for the encystation of Acanthamoeba castellanii. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2012, 183, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, J.L.; Weisman, R.A. Correlation of cellulose synthesis in vivo and in vitro during the encystment of Acanthamoeba. Dev. Biol. 1972, 28, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirukawa, Y.; Nakato, H.; Izumi, S.; Tsuruhara, T.; Tomino, S. Structure and expression of a cyst specific protein of Acanthamoeba castellanii. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1398, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, R.W.; Hill, M.C.; Hepworth, P.; Boehmer, J. Isolation and electrophoretic analysis of nucleoli, phenol-soluble nuclear proteins and outer cyst walls from Acanthamoeba castellanii during encystation initiation. J. Cell Biol. 1976, 68, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, E.-K.; Xuan, Y.-H.; Chung, D.-I.; Hong, Y.; Kong, H.-H. Microarray analysis of differentially expressed genes between cysts and trophozoites of Acanthamoeba castellanii. Korean J. Parasitol. 2011, 49, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cádiz, A.E.; Jeelani, G.; Nakada-Tsukui, K.; Caler, E.; Nozaki, T. Transcriptome analysis of encystation in Entamoeba invadens. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrenkaufer, G.M.; Haque, R.; Hackney, J.A.; Eichinger, D.J.; Singh, U. Identification of developmentally regulated genes in Entamoeba histolytica: Insights into mechanisms of stage conversion in a protozoan parasite. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1426–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, E.K.; Chung, D.I.; Hong, Y.C.; Kong, H.H. Differentially expressed genes of Acanthamoeba castellanii during encystation. Korean J. Parasitol. 2007, 45, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Makioka, A.; Kumagai, M.; Ohtomo, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Takeuchi, T. Entamoeba invadens: Protein kinase C inhibitors block the growth and encystation. Exp. Parasitol. 2000, 95, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makioka, A.; Kumagai, M.; Ohtomo, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Takeuchi, T. Effect of calcium antagonists, calcium channel blockers and calmodulin inhibitors on the growth and encystation of Entamoeba histolytica and E. invadens. Parasitol. Res. 2001, 87, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makioka, A.; Kumagai, M.; Ohtomo, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Takeuchi, T. Effect of proteasome inhibitors on the growth, encystation, and excystation of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba invadens. Parasitol. Res. 2002, 88, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierickx, P.J.; Almar, M.M.; De Jonckheere, J.F. Glutathione transferase activity in some flagellates and amoebae, and purification of the soluble glutathione transferases from Acanthamoeba. Biochem. Int. 1990, 22, 593–600. [Google Scholar]
- Aon, M.A.; Roussel, M.R.; Cortassa, S.; O’Rourke, B.; Murray, D.B.; Beckmann, M.; Lloyd, D. The scale-free dynamics of eukaryotic cells. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Odstrcil, E.A.; Tu, B.P.; McKnight, S.L. Restriction of DNA replication to the cycle protects genome integrity. Science 2007, 316, 1916–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondarza, R. Drug targets from human pathogenic amoebas: Entamoeba histolytica, Acanthamoeba polyphaga and Naegleria fowleri. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2007, 7, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, F.Q.; Buettner, G.R. Redox environment of the cell as viewed through the redox state of the glutathione disulfide/glutathione couple. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 30, 1191–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.B.; Johnson, K.S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene 1988, 67, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.F.; Alberts, D.W.; Rush, G.F. Role of glutathione reductase during menadione-induced nadph oxidation in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1987, 36, 3879–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.D.; Akgül, B. Drosophila glutathione S-transferases. In Gluthione Transferases and Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidases; Sies, H., Packer, L.B.T.-M.E., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005; Volume 401, pp. 204–226. ISBN 00766879. [Google Scholar]
- Harwaldt, P.; Rahlfs, S.; Becker, K. Glutathione S-transferase of the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum: Characterization of a potential drug target. Biol. Chem. 2002, 383, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, R.J.; Ray, S.A.; Benton, W.F.; Wilborn, M. Chapter 4 Induction of synchronous encystment (differentiation) in Acanthamoeba sp. In Methods in Cell Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1964; pp. 55–83. [Google Scholar]
- Kersey, P.J.; Allen, J.E.; Allot, A.; Barba, M.; Boddu, S.; Bolt, B.J.; Carvalho-Silva, D.; Christensen, M.; Davis, P.; Grabmueller, C.; et al. Ensembl Genomes 2018: An integrated omics infrastructure for non-vertebrate species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 46, D802–D808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2009, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, M.D.; Oshlack, A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhsler, M.; Leitsch, D.; Müller, N.; Walochnik, J. Validation of reference genes for the normalization of RT-qPCR gene expression in Acanthamoeba spp. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3--new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strober, W. Trypan blue exclusion test of cell viability. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 1997, 21, A.3B.1–A.3B.2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, J.U.; Smythe, M.L. Sigma-class glutathione transferases. Drug Metab. Rev. 2011, 43, 194–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcerá, A.; Barreto, L.; Piedrafita, L.; Tamarit, J.; Herrero, E. Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells have three Omega class glutathione S-transferases acting as 1-Cys thiol transferases. Biochem. J. 2006, 398, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oakley, A.J. Glutathione transferases: New functions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2005, 15, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, A.J.; Lo Bello, M.; Nuccetelli, M.; Mazzetti, A.P.; Parker, M.W. The ligandin (non-substrate) binding site of human pi class glutathione transferase is located in the electrophile binding site (H-site). J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 291, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veal, E.A.; Toone, W.M.; Jones, N.; Morgan, B.A. Distinct roles for glutathione S-transferases in the oxidative stress response in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 35523–35531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, G.A.; Lin, T.H.; Sheehan, A.E.; Van der Goes van Naters, W.; Neukomm, L.J.; Graves, H.K.; Bis-Brewer, D.M.; Züchner, S.; Freeman, M.R. Glutathione S-transferase regulates mitochondrial populations in axons through increased glutathione oxidation. Neuron 2019, 103, 52–65.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, M.; Lu, K.; Reichert, A.S. Mitophagy and mitochondrial dynamics in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2015, 1853, 2766–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Klionsky, D.J. Mitochondria removal by autophagy. Autophagy 2011, 7, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamashita, S.; Kanki, T. How autophagy eats large mitochondria: Autophagosome formation coupled with mitochondrial fragmentation. Autophagy 2017, 13, 980–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.-H.; Moon, E.-K.; Hong, Y.; Chung, D.-I.; Kong, H.-H. Autophagy protein 12 plays an essential role in Acanthamoeba encystation. Exp. Parasitol. 2015, 159, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, D. Encystment in Acanthamoeba castellanii: A review. Exp. Parasitol. 2014, 145, S20–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, E.K.; Hong, Y.; Chung, D.I.; Kong, H.H. Cysteine protease involving in autophagosomal degradation of mitochondria during encystation of Acanthamoeba. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2012, 185, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsich, S.W.; Shaw, J.M. Importance of mitochondrial dynamics during meiosis and sporulation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 4369–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheckhuber, C.Q.; Erjavec, N.; Tinazli, A.; Hamann, A.; Nyström, T.; Osiewacz, H.D. Reducing mitochondrial fission results in increased life span and fitness of two fungal ageing models. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebert, D.W.; Vasiliou, V. Analysis of the glutathione S-transferase (GST) gene family. Hum. Genom. 2004, 1, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joachim, A.; Lautscham, E.; Christoffers, J.; Ruttkowski, B. Oesophagostomum dentatum: Effect of glutathione S-transferase (GST) inhibitors on GST activity and larval development. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 127, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, P.; Ouellette, M. New mechanisms of drug resistance in parasitic protozoa. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 49, 427–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.-L.; Epstein, D.L.; de Kater, A.W.; Shahsafaei, A.; Erickson-Lamy, K.A. Ethacrynic Acid Increases Facility of Outflow in the Human Eye In Vitro. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1992, 110, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melamed, S.; Kotas-Neumann, R.; Barak, A.; Epstein, D.L. The Effect of Intracamerally Injected Ethacrynic Acid on Intraocular Pressure in Patients with Glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1992, 113, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-W.; Gonzalez, P.; Yuan, F. Cellular pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analyses of ethacrynic acid: Implications in topical drug delivery in the eye. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 2507–2515. [Google Scholar]
- Cynkowska, G.; Cynkowski, T.; Al-Ghananeem, A.A.; Guo, H.; Ashton, P.; Crooks, P.A. Novel antiglaucoma prodrugs and codrugs of ethacrynic acid. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 3524–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher Kent Glaucoma Drugs: The Search for New Options. Available online: https://www.reviewofophthalmology.com/article/glaucoma-drugs-the-search-for-new-options (accessed on 3 April 2023).
- Benitez-Del-Castillo, J.M.; Garcia-Sanchez, J.; Iradier, T.; Bañares, A. Sulfasalazine in the prevention of anterior uveitis associated with ankylosing spondylitis. Eye 2000, 14, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñoz-Fernández, S.; Hidalgo, V.; Fernández-Melón, J.; Schlincker, A.; Bonilla, G.; Ruiz-Sancho, D.; Fonseca, A.; Gijón-Baños, J.; Martín-Mola, E. Sulfasalazine reduces the number of flares of acute anterior uveitis over a one-year period. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 1277–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Doan, S.; Lerouic, J.-F.; Robin, H.; Prost, C.; Savoldelli, M.; Hoang-Xuan, T. Treatment of ocular cicatricial pemphigoid with sulfasalazine. Ophthalmology 2001, 108, 1565–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, C.-K.; Choi, J.-S. The Effect of Sulfasalazine—Hyaluronic Acid Complex on Posterior Capsule Opacification. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 2955. [Google Scholar]
- Galperin, M.Y.; Koonin, E.V. Searching for drug targets in microbial genomes. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1999, 10, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, B.M.; Assmus, H.E.; Bruggeman, F.; Haanstra, J.R.; Klipp, E.; Westerhoff, H. Network-based selectivity of antiparasitic inhibitors. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2002, 29, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassidy-Stone, A.; Chipuk, J.E.; Ingerman, E.; Song, C.; Yoo, C.; Kuwana, T.; Kurth, M.J.; Shaw, J.T.; Hinshaw, J.E.; Green, D.R.; et al. Chemical inhibition of the mitochondrial division dynamin reveals its role in Bax/Bak-dependent mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lloyd, D.; Kristensen, B.; Degn, H. Oxidative detoxification of hydrogen sulphide detected by mass spectrometry in the soil amoeba Acanthamoeba castellanii. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1981, 126, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Gene | Sequence (5′-3′) | Tm | Amplicon Lenght | Source or Accesion Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GST | F: CAAGTGCTACCCCAAGGAC | 57.75 | 162 bp | NW_004457554 |
| R: CCCTTCTCGTCCGGGTAG | 58.48 | |||
| CSP21 | F: ACTTTGGCGACAAGGTGTG | 58.6 | 80 bp | XM_004337011 |
| R: CGACACGTCGTCCCTCT | 58.31 | |||
| HPRT | F: GGAGCGGATCGTTCTCTG | 58.4 | 201 bp | [35] |
| R: ATCTTGGCGTCGACGTGC | 58.4 |
| Gene_ID | Description | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACA1_116240 | GST C-terminal domain containing protein | 4.7154 | 0.4877 | 0.4623 |
| ACA1_075240 | Cyst-specific protein 21 | 6.5435 | 3.5723 | 1.7860 |
| ACA1_022350 | Hypothetical protein | 8.4458 | 3.9417 | 1.4994 |
| ACA1_096640 | Hypothetical protein | 7.0754 | 4.2638 | 1.8371 |
| ACA1_188370 | Hypothetical protein | 10.0624 | 6.1620 | 3.4728 |
| ACA1_247090 | Hypothetical protein | 7.5066 | 2.7215 | 0.8404 |
| ACA1_374130 | Hypothetical protein | 6.8663 | 2.5504 | 0.2569 |
| Gene_ID | Predicted Protein | Predicted RNA | Genomic |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACA1_188370 | 74% | 73% | 75% |
| ACA1_022350 | NA | 75% | 75% |
| ACA1_247090 | 54% | 72% | 68% |
| ACA1_096640 | 54% | 74% | 73% |
| ACA1_374130 | 79% | 81% | 79% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Obeso Fernández del Valle, A.; Scheckhuber, C.Q.; Chavaro-Pérez, D.A.; Ortega-Barragán, E.; Maciver, S.K. mRNA Sequencing Reveals Upregulation of Glutathione S-Transferase Genes during Acanthamoeba Encystation. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 992. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11040992
de Obeso Fernández del Valle A, Scheckhuber CQ, Chavaro-Pérez DA, Ortega-Barragán E, Maciver SK. mRNA Sequencing Reveals Upregulation of Glutathione S-Transferase Genes during Acanthamoeba Encystation. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(4):992. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11040992
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Obeso Fernández del Valle, Alvaro, Christian Quintus Scheckhuber, David Armando Chavaro-Pérez, Erandi Ortega-Barragán, and Sutherland K. Maciver. 2023. "mRNA Sequencing Reveals Upregulation of Glutathione S-Transferase Genes during Acanthamoeba Encystation" Microorganisms 11, no. 4: 992. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11040992
APA Stylede Obeso Fernández del Valle, A., Scheckhuber, C. Q., Chavaro-Pérez, D. A., Ortega-Barragán, E., & Maciver, S. K. (2023). mRNA Sequencing Reveals Upregulation of Glutathione S-Transferase Genes during Acanthamoeba Encystation. Microorganisms, 11(4), 992. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11040992