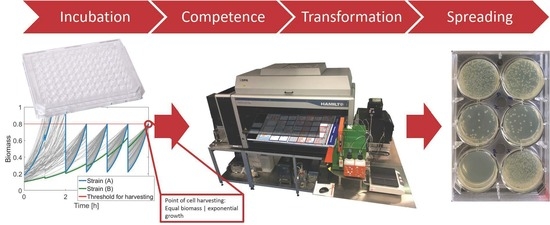
Automated Cell Treatment for Competence and Transformation of Escherichia coli in a High-Throughput Quasi-Turbidostat Using Microtiter Plates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Platform
2.2. Strains, Cell Competence and Transformation
2.3. Computational Methods
3. Results
3.1. Determination of the Optimal Harvest Conditions
3.2. Competent Cells with Batch Cultivation
3.3. Competent Cells in the Quasi-Turbidostat
3.4. Cell Treatment for Competence
3.5. Transformation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neubauer, P.; Cruz, N.; Glauche, F.; Junne, S.; Knepper, A.; Raven, M. Consistent development of bioprocesses from microliter cultures to the industrial scale. Eng. Life Sci. 2013, 13, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlec, A.; Štrukelj, B. Current state and recent advances in biopharmaceutical production in Escherichia coli, yeasts and mammalian cells. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 40, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, F.R. Optimization and scale up of industrial fermentation processes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 68, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Wen, Z.; Yang, L.; Wu, J.; Yang, S. Genome editing and transcriptional repression in Pseudomonas putida KT2440 via the type II CRISPR system. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maeda, T.; Sanchez-Torres, V.; Wood, T.K. Metabolic engineering to enhance bacterial hydrogen production. Microb. Biotechnol. 2008, 1, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagt, C.M.J. Systems metabolic engineering in an industrial setting. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 2319–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-J.; Kim, J.-W.; Lee, Y.-G.; Park, Y.-C.; Seo, J.-H. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for 2,3-butanediol production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 2241–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erb, T.J.; Jones, P.R.; Bar-Even, A. Synthetic metabolism: Metabolic engineering meets enzyme design. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 37, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanovic, E.; Fitzgerald, G.; McAuliffe, O. Advances in the genomics and metabolomics of dairy lactobacilli: A review. Food Microbiol. 2017, 61, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kruyer, N.S.; Peralta-Yahya, P. Metabolic engineering strategies to bio-adipic acid production. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.F.; Kushner, S.R. Construction of versatile low-copy-number vectors for cloning, sequencing and gene expression in Escherichia coli. Gene 1991, 100, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolivar, F.; Rodriguez, R.L.; Greene, P.J.; Betlach, M.C.; Heyneker, H.L.; Boyer, H.W.; Crosa, J.H.; Falkow, S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicle. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene 1977, 2, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanisch-Perron, C.; Vieira, J.; Messing, J. Improved Ml3 phage cloning vectors and host strains: Nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 1985, 33, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studier, F.W.; Moffatt, B.A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J. Mol. Biol. 1986, 189, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronenborn, B. Overproduction of phage lambda repressor under control of the lac promotor of Escherichia coli. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1976, 148, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, L.-M.; Belin, D.; Carson, M.J.; Beckwith, J. Tight Regulation, Modulation, and High-Level Expression by Vectors Containing the Arabinose P BAD Promoter. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 4121–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawin, A.; Valla, S.; Brautaset, T. The XylS/Pm regulator/promoter system and its use in fundamental studies of bacterial gene expression, recombinant protein production and metabolic engineering. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 702–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, T.; Ara, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Takai, Y.; Okumura, Y.; Baba, M.; Datsenko, K.A.; Tomita, M.; Wanner, B.L.; Mori, H. Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: The Keio collection. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2006, 2, 2006.0008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Nakahigashi, K.; Nakamichi, T.; Yoshino, M.; Takai, Y.; Touda, Y.; Furubayashi, A.; Kinjyo, S.; Dose, H.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. Update on the Keio collection of Escherichia coli single-gene deletion mutants. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2009, 5, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Albertini, A.; Amati, G.; Andersen, K.K.; Arnaud, M.; Asai, K.; Ashikaga, S.; Aymerich, S.; Bessieres, P.; et al. Essential Bacillus subtilis genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4678–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, M.A.; Alwood, A.; Thaipisuttikul, I.; Spencer, D.; Haugen, E.; Ernst, S.; Will, O.; Kaul, R.; Raymond, C.; Levy, R.; et al. Comprehensive transposon mutant library of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14339–14344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Berardinis, V.; Vallenet, D.; Castelli, V.; Besnard, M.; Pinet, A.; Cruaud, C.; Samair, S.; Lechaplais, C.; Gyapay, G.; Richez, C.; et al. A complete collection of single-gene deletion mutants of Acinetobacter baylyi ADP1. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008, 4, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaever, G.; Nislow, C. The yeast deletion collection: A decade of functional genomics. Genetics 2014, 197, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, R.S.; Dunlop, M.J.; Elowitz, M.B. A synthetic three-color scaffold for monitoring genetic regulation and noise. J. Biol. Eng. 2010, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, M.; Yadav, A.; Ma, X.; Amoah, E. Plasmid DNA Transformation in Escherichia Coli: Effect of Heat Shock Temperature, Duration, and Cold Incubation of CaCl 2 Treated Cells. Shock 2010, 6, 561–568. [Google Scholar]
- Mandel, M.; Higa, A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J. Mol. Biol. 1970, 53, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Jessee, J.; Bloom, F.R. bacteria. In Bacterial Genetic Systems; Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991; Volume 204, pp. 63–113. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, S.N.; Chang, A.C.Y.; Hsu, L. Nonchromosomal Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria: Genetic Transformation of Escherichia coli by R-Factor DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1972, 69, 2110–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, R.L.S.; Bevan, M.W.; Harbison, S.; Gardnerl, R.C. High efficiency transformation of E.coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taketo, A. DNA transfection of Escherichia coil by electroporation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Struct. Expr. 1988, 949, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.R.; Dowd, P.F.; Hector, R.E.; Riedmuller, S.B.; Bartolett, S.; Mertens, J.A.; Qureshi, N.; Liu, S.; Bischoff, K.M.; Li, X.-L.; et al. Cost-Effective High-Throughput Fully Automated Construction of a Multiplex Library of Mutagenized Open Reading Frames for an Insecticidal Peptide Using a Plasmid-Based Functional Proteomic Robotic Workcell with Improved Vacuum System. JALA J. Assoc. Lab. Autom. 2007, 12, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finley, J.B.; Qiu, S.H.; Luan, C.H.; Luo, M. Structural genomics for Caenorhabditis elegans: High throughput protein expression analysis. Protein Expr. Purif. 2004, 34, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohe, P.; Venkanna, D.; Kleine, B.; Freudl, R.; Oldiges, M. An automated workflow for enhancing microbial bioprocess optimization on a novel microbioreactor platform. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neubauer, P.; Cruz-Bournazou, M.N. Continuous Bioprocess Development: Methods for Control and Characterization of the Biological System. In Continuous Biomanufacturing: Innovative Technologies and Methods; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Schmideder, A.; Severin, T.S.; Cremer, J.H.; Weuster-Botz, D. A novel milliliter-scale chemostat system for parallel cultivation of microorganisms in stirred-tank bioreactors. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 210, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, S.A.; Wohltat, C.; Mu, K.M.; Arndt, K.M. A user-friendly, low-cost turbidostat with versatile growth rate estimation based on an extended Kalman filter. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, C.N.; Miller, A.W.; Ekness, F.; Dunham, M.J.; Klavins, E. A low cost, customizable turbidostat for use in synthetic circuit characterization. ACS Synth. Biol. 2015, 4, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knepper, A.; Heiser, M.; Glauche, F.; Neubauer, P. Robotic Platform for Parallelized Cultivation and Monitoring of Microbial Growth Parameters in Microwell Plates. J. Lab. Autom. 2014, 19, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmid, I.; Aschoff, J. A scalable software framework for data integration in bioprocess development. Eng. Life Sci. 2017, 17, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, R.; Bankier, A.T.; Biggin, M.D.; Deininger, P.L.; Farrell, P.J.; Gibson, T.J.; Hatfull, G.; Hudson, G.S.; Satchwell, S.C.; Seguin, C.; et al. DNA sequence and expression of the B98-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature 1984, 310, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzy-Tréboul, G.; Karmazyn-Campelli, C.; Stragier, P. Developmental regulation of transcription of the Bacillus subtilis ftsAZ operon. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 224, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datsenko, K.A.; Wanner, B.L. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enfors, S.-O.; Häggström, L. Bioprocess Technology: Fundamentals and Applications; Royal Institute of Technology: Stockholm, Sweden, 2000; ISBN 91-7170-511-2. [Google Scholar]
- Szostková, M.; Horáková, D.; Němec, M. The influence of the growth phase of enteric bacteria on electrotransformation with plasmid DNA. Folia Microbiol. 1999, 44, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anane, E.; Lopez Cárdenas, D.C.; Neubauer, P.; Cruz Bournazou, M.N. Modelling overflow metabolism in Escherichia coli by acetate cycling. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 125, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz Bournazou, M.N.; Barz, T.; Nickel, D.B.; Lopez Cárdenas, D.C.; Glauche, F.; Knepper, A.; Neubauer, P. Online optimal experimental re-design in robotic parallel fed-batch cultivation facilities. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubauer, P. Editorial: Towards faster bioprocess development. Biotechnol. J. 2011, 6, 902–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neubauer, P.; Glauche, F.; Cruz-Bournazou, M.N. Editorial: Bioprocess Development in the era of digitalization. Eng. Life Sci. 2017, 17, 1140–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleman, G.L.; Strohl, W.R. Acetate metabolism by Escherichia coli in high-cell-density fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 3952–3958. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.Y.; Mathiszik, B.; Xu, B.; Enfors, S.O.; Neubauer, P. Determination of the maximum specific uptake capacities for glucose and oxygen in glucose-limited fed-batch cultivations of Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2001, 73, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, E.; Junne, S.; Anane, E.; Nicolas, M.; Bournazou, C.; Neubauer, P. Importance of the cultivation history for the response of Escherichia coli to oscillations in scale-down experiments. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmerich, J.; Noack, S.; Wiechert, W.; Oldiges, M. Microbioreactor Systems for Accelerated Bioprocess Development. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 13, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kensy, F.; Zang, E.; Faulhammer, C.; Tan, R.; Büchs, J. Validation of a high-throughput fermentation system based on online monitoring of biomass and fluorescence in continuously shaken microtiter plates. Microb. Cell Fact. 2009, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glauche, F.; Pilarek, M.; Bournazou, M.N.C.; Grunzel, P.; Neubauer, P. Design of experiments-based high-throughput strategy for development and optimization of efficient cell disruption protocols. Eng. Life Sci. 2017, 17, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Strain | Genotype | Source |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli TG 1 | K-12 supE hsd Δ5thi Δ[lac-proAB] F′ [traD36 proAB lacIq lacZ ΔM15] | [40] |
| E. coli TG 90 | K-12 supE hsd Δ5thi Δ[lac-proAB] F′ [traD36 proAB lacIq lacZ ΔM15] pcnB80 zad::TnlO | [41] |
| E. coli BW25113 | K-12 lacI+ rrnBT14 ΔlacZWJ16 hsdR514 ΔaraBADAH33 ΔrhaBADLD78 rph-1 Δ(araB–D)567 Δ(rhaD–B)568 ΔlacZ4787(::rrnB-3) hsdR514 rph-1 | [42] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hans, S.; Gimpel, M.; Glauche, F.; Neubauer, P.; Cruz-Bournazou, M.N. Automated Cell Treatment for Competence and Transformation of Escherichia coli in a High-Throughput Quasi-Turbidostat Using Microtiter Plates. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030060
Hans S, Gimpel M, Glauche F, Neubauer P, Cruz-Bournazou MN. Automated Cell Treatment for Competence and Transformation of Escherichia coli in a High-Throughput Quasi-Turbidostat Using Microtiter Plates. Microorganisms. 2018; 6(3):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030060
Chicago/Turabian StyleHans, Sebastian, Matthias Gimpel, Florian Glauche, Peter Neubauer, and Mariano Nicolas Cruz-Bournazou. 2018. "Automated Cell Treatment for Competence and Transformation of Escherichia coli in a High-Throughput Quasi-Turbidostat Using Microtiter Plates" Microorganisms 6, no. 3: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030060
APA StyleHans, S., Gimpel, M., Glauche, F., Neubauer, P., & Cruz-Bournazou, M. N. (2018). Automated Cell Treatment for Competence and Transformation of Escherichia coli in a High-Throughput Quasi-Turbidostat Using Microtiter Plates. Microorganisms, 6(3), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms6030060